Tolerant Pediatric Liver Transplant (LT) Recipients (TOL) from WISP-R (NCT00320606) Split into Two Phenotypically Distinct Groups by PD1 Expression on CD4+ T Cells at Baseline, Prior to Immunosuppression Withdrawal (ISW).
1ITN, Bethesda
2UCSF, San Francisco
3NIAID, Bethesda
4Yale, New Haven
5Duke, Durham
6Rho, Chapel Hill
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 194
Keywords: Hyporeactivity, Liver transplantation, T cells, Tolerance
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Tolerance: Clinical Studies
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Location: E353C
Background: Combinations of cell surface markers such as PD1, CD57, and/or KLRG1 identify T cells that may fail to respond to cognate antigen challenge – a potential mechanism of organ transplant tolerance. We hypothesized that, prior ISW, TOL and non-TOL would differ in these cell surface markers. We tested 12 TOL and 7 non-TOL subjects identified by WISP-R, a multi-center ISW trial for children ≥4yrs after parental living donor LT.
Methods: Frozen, banked, pre-ISW PBMC samples were analyzed by flow cytometry (FlowJo software). Clinical characteristics of non-, HI- and LO-TOL were compared using Kruskal Wallis or Fisher's exact tests.
Results: Prior to ISW, TOL compared to non-TOL had increased CD4+PD1+cells (28 vs 16%; p=0.042; Figure). Notably, TOL separated into 2 groups based on high (HI-TOL; n=6) vs low (LO-TOL; n=6) percentage of CD4+PD1+cells. HI-TOL (38% CD4+PD1+) were distinct from LO-TOL (17%; p=0.001) and non-TOL (16%; p=0.0004); in contrast, LO-TOL were similar to non-TOL (p=0.81) (Figure; Table 1). Expanded flow panels showed similar patterns for CD4+PD1+CD57-KLRG1- and memory cells. Differences between HI- and LO-TOL did not correlate with clinical surrogates of antigen exposure: age at LT or screening, time since LT [HI-TOL tended to be younger at screening (p=0.078) and earlier after LT (p=0.11)], rejection history, EBV/CMV status, or presence of α-Class II donor specific antibody (Table 2).
Conclusions: Prior to ISW, CD4+T cell profiles separated TOL from non-TOL and divided TOL into HI- and LO-TOL based on PD1 expression. HI- compared to LO-TOL appear more antigen-experienced, suggesting hyporesponsiveness/exhaustion may contribute to tolerance in a subgroup of pediatric LT recipients. Future analyses will use additional costimulatory/coinhibitory markers to further define this potentially hyporesponsive PD1+ cell population.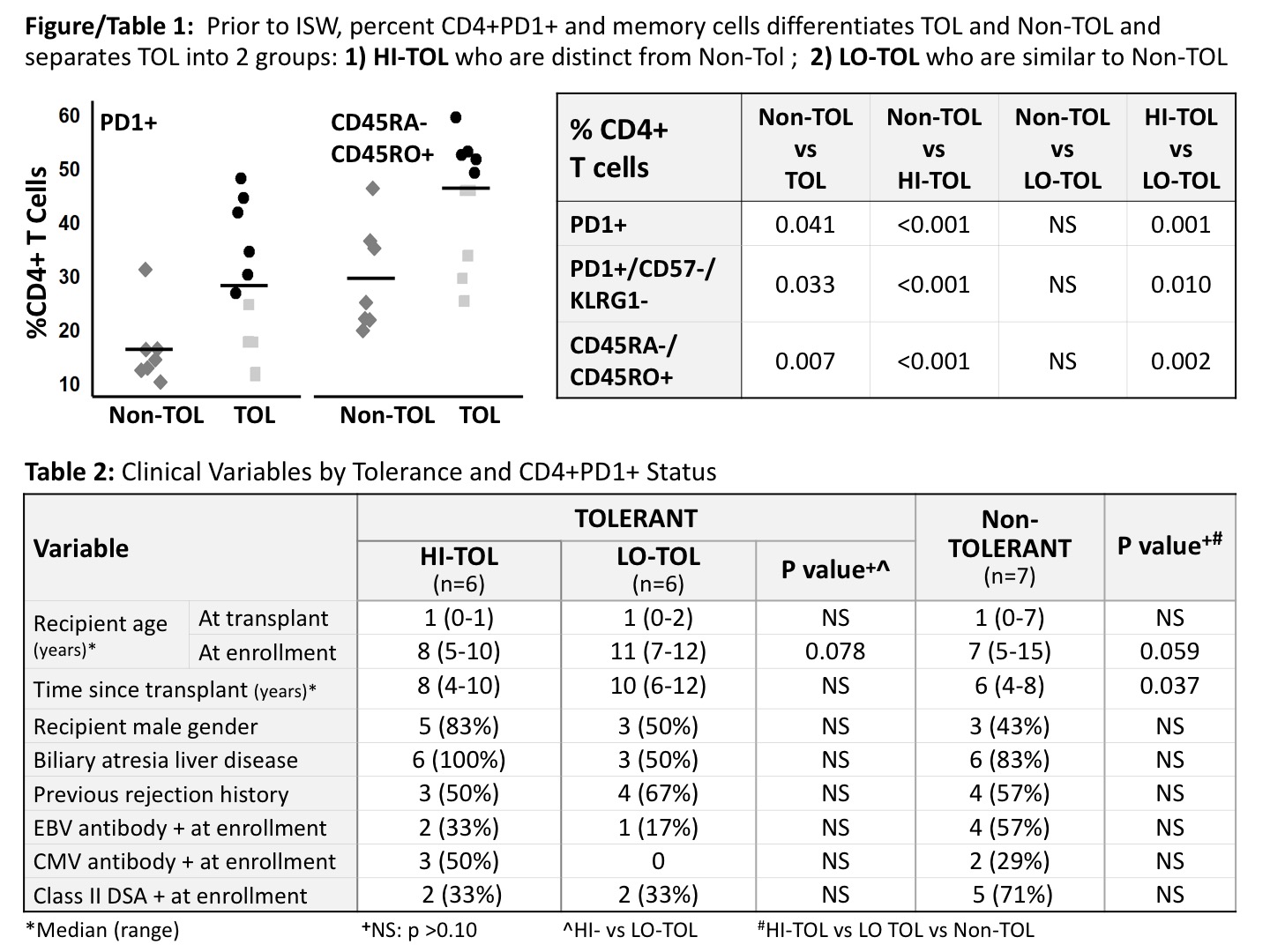
CITATION INFORMATION: Burrell B, Feng S, Bridges N, Ekong U, Kanaparthi S, Kirk A, Long A, Spain K, Stempora L, Turka L, Tchao N. Tolerant Pediatric Liver Transplant (LT) Recipients (TOL) from WISP-R (NCT00320606) Split into Two Phenotypically Distinct Groups by PD1 Expression on CD4+ T Cells at Baseline, Prior to Immunosuppression Withdrawal (ISW). Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Burrell B, Feng S, Bridges N, Ekong U, Kanaparthi S, Kirk A, Long A, Spain K, Stempora L, Turka L, Tchao N. Tolerant Pediatric Liver Transplant (LT) Recipients (TOL) from WISP-R (NCT00320606) Split into Two Phenotypically Distinct Groups by PD1 Expression on CD4+ T Cells at Baseline, Prior to Immunosuppression Withdrawal (ISW). [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/tolerant-pediatric-liver-transplant-lt-recipients-tol-from-wisp-r-nct00320606-split-into-two-phenotypically-distinct-groups-by-pd1-expression-on-cd4-t-cells-at-baseline-prior-to-immunosuppress/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
