Precision Medicine in Renal Transplantation: T-cell Repertoire Sequencing to Define Donor-specific Clones for Post-transplant Monitoring
1University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2Vancouver General Hospital, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3Urologic Sciences, Vancouver General Hospital, Vancouver, BC, Canada
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: LB 33
Keywords: Allorecognition, Immunogenicity, T cell clones, T cell receptors (TcR)
Topic: Clinical Science » Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Measuring donor-specific clonal responses offers a precise, sensitive and specific biomarker of immune recognition and activation. Combining deep immunophenotyping (DI) and T-cell receptor (TCR) sequencing, we have developed an in vitro platform to define the cellular proliferation response and the T cell clonal repertoire during stimulation by donor antigen as a prelude for clinical post-Tx monitoring.
*Methods: A matrix design with repeated measures over time was employed using one-to-many and many-to-one stimulator/responder combinations in mixed lymphocyte culture (MLC). Donor and responder PBMC (stained respectively with Cell Trace CFSE and Violet) were cultured for 7 days in MLC. DI was performed daily with α-CD3, α-CD4, α-CD8, α-CD197, α-CD45RA, α-HLA-DR, α-CD127, α-CD25 and α-CD152. For TCR sequencing genomic DNA was isolated, library preparation performed using ImmunoSeq, sequenced on an Illumina MiSeq System and analyzed on the ImmunoSEQ 3.0 portal.
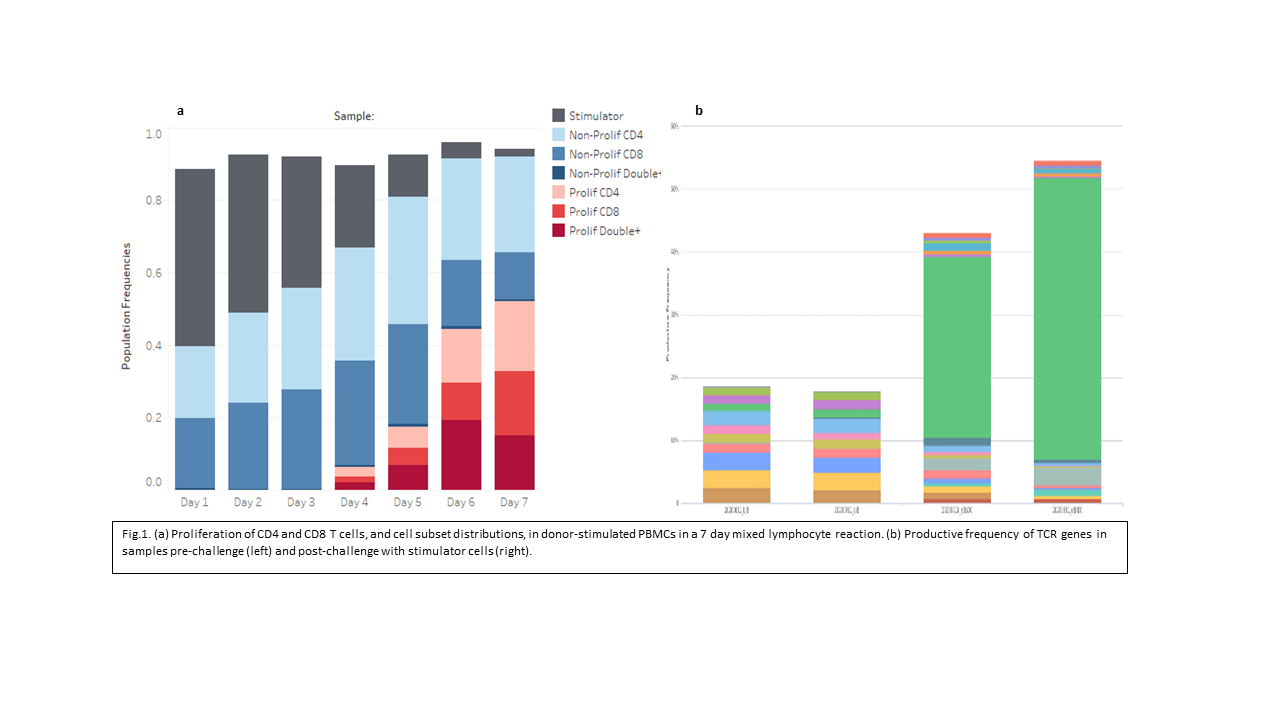
*Results: Expansion of T cell subsets are clearly observed from day 4 onwards (Fig.1a). In the proliferating T cells, a significant number were CD4 and CD8 positive (double+) and by day 7 most had become effector memory T cells (not shown). Sequence results of post-challenge samples reveals both an increase in relative diversity and maximum productive frequencies of CDR3 rearrangements. Expansion of few specific clones at high frequency post-challenge were frequently observed and were easily identified from a background of low frequency clones (Fig. 1b). Proliferation may also occur through a mechanism of polyclonal expansion (not shown). Repeated measures over time for control samples showed considerably more overlap than other pairwise comparisons. Clones that emerge in MLC response were also consistently detected at multiple time-points (not shown).
*Conclusions: This robust in vitro assay provides deep insight into the proliferating T-cell populations and TCR gene utilization following allogeneic stimulation. Baseline and stimulated TCR gene utilization varies within individual over repeated measures indicating heterogeneous clonal proliferation, but high frequency clones are identified which provide the focus for monitoring of the allogeneic response in the transplant recipient.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sherwood KR, Wong P, Fenninger F, Wu V, Beckrud J, Cina DP, Allan L, Lan J, Keown PA. Precision Medicine in Renal Transplantation: T-cell Repertoire Sequencing to Define Donor-specific Clones for Post-transplant Monitoring [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/precision-medicine-in-renal-transplantation-t-cell-repertoire-sequencing-to-define-donor-specific-clones-for-post-transplant-monitoring/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress