Impact of STEEN vs Gelofusine as Perfusate During Normothermic Ex Vivo liver Perfusion on Outcome of Pig Liver Transplantation.
Multiorgan Transplant Program, Toronto General Hospital, Toronto, ON, Canada
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B116
Keywords: Graft function, Hepatocytes, Ischemia, Machine preservation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Ischemic Injury and Organ Preservation Session II
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
European and North American clinical trials have used two different perfusate solutions for normothermic ex vivo liver perfusion (NEVLP): Gelofusine (bovine derived gelatin-based solution) and STEEN (Human albumin-based solution). We aimed to determine the effects of the perfusate solution during NEVLP on outcome of pig liver transplantation.
Material and Methods:
Porcine livers were retrieved 30 minutes after circulatory death. Grafts were perfused for 5 hours and transplanted into recipient pigs. Two groups were compared based on the perfusate solution (Gelofusine vs STEEN, n=6, respectively). Hemodynamic variables, liver injury and function were evaluated. AST, alkaline phosphatase, total bilirubin and INR were measured until third postoperative day.
Results:
Hepatic artery flow during perfusion was higher in the STEEN vs Gelofusine group and within physiologic range since the beginning of perfusion (238±90 vs 97±33, p=0.015). Electrolytes and pH from the STEEN but not the Gelofusine group were within normal limits from the time when the perfusion started. Both perfusate groups achieved lactate clearance reaching normal levels by the end of perfusion (Gelofusine: 0.78±0.30 vs STEEN: 0.68±0.60, p=0.80). AST (Gelofusine: 1495±612 vs STEEN: 1160±564), alkaline phosphatase (Gelofusine: 177±128 vs STEEN: 145±47) and total bilirubin levels (Gelofusine: 11±4 vs STEEN: 5±1) were lower in the STEEN group since 1 day after transplantation. Liver function recovery was significantly improved in the STEEN vs Gelofusine perfused livers after transplantation 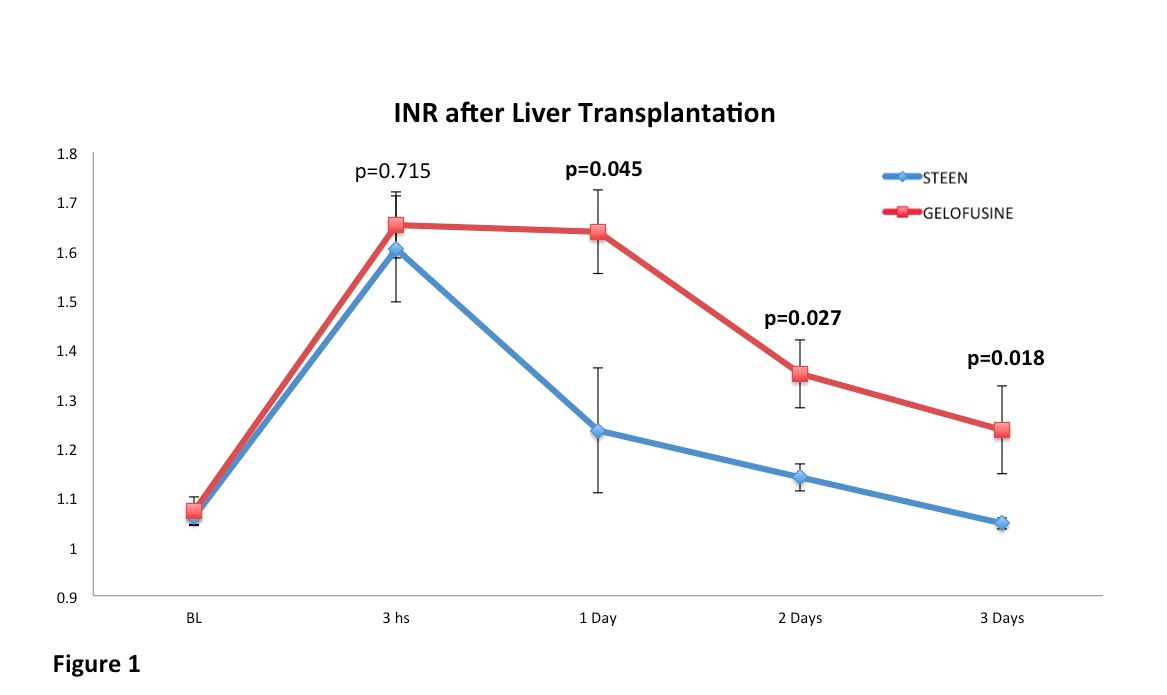 All animals in the STEEN group survived while one pig from the Gelofusine group died on the first postoperative day due to primary non-function.
All animals in the STEEN group survived while one pig from the Gelofusine group died on the first postoperative day due to primary non-function.
Conclusion
The characteristics from the STEEN based perfusate resembled more closely the physiologic conditions compared to gelatin-based perfusate. The use of STEEN based perfusate decreases hepatic injury and improves liver function recovery in pig livers retrieved after circulatory death.
CITATION INFORMATION: Linares I, Kollmann D, Echeverri J, Kaths M, Rosales R, Bruguera C, Hamar M, Urbanellis P, Ganesh S, Selzner N, Selzner M. Impact of STEEN vs Gelofusine as Perfusate During Normothermic Ex Vivo liver Perfusion on Outcome of Pig Liver Transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Linares I, Kollmann D, Echeverri J, Kaths M, Rosales R, Bruguera C, Hamar M, Urbanellis P, Ganesh S, Selzner N, Selzner M. Impact of STEEN vs Gelofusine as Perfusate During Normothermic Ex Vivo liver Perfusion on Outcome of Pig Liver Transplantation. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-steen-vs-gelofusine-as-perfusate-during-normothermic-ex-vivo-liver-perfusion-on-outcome-of-pig-liver-transplantation/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
