Absolute Quantification of Plasma Graft-Derived Cell-Free DNA for Diagnosis of Kidney Transplant Rejection
1Austin Health, Heidelberg, Victoria, Australia
2Murdoch Childrens Research Institute, Parkville, Victoria, Australia
3St Vincent's Health, Fitzroy, Victoria, Australia.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A55
Keywords: Area-under-curve (AUC), Genomic markers, Mixed chimerism, Non-invasive diagnosis
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Biomarkers, Immune Monitoring and Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 2, 2018
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Aim: To study the performance of droplet digital PCR absolute measurement of graft-derived cell-free DNA (gdcfDNA) for the diagnosis of kidney allograft rejection.
Methods: Homozygous deletion copy number variation (CNV) was exploited to establish a “negative background” against which multiple independent informative PCR assays were used to quantify absolute levels of gdcfDNA. A panel of 31 CNV assays were run on cfDNA extracted from plasma of 61 adult kidney transplant recipients undergoing biopsy for acute graft dysfunction. GdcfDNA concentrations were measured and correlated with diagnostic histopathology.
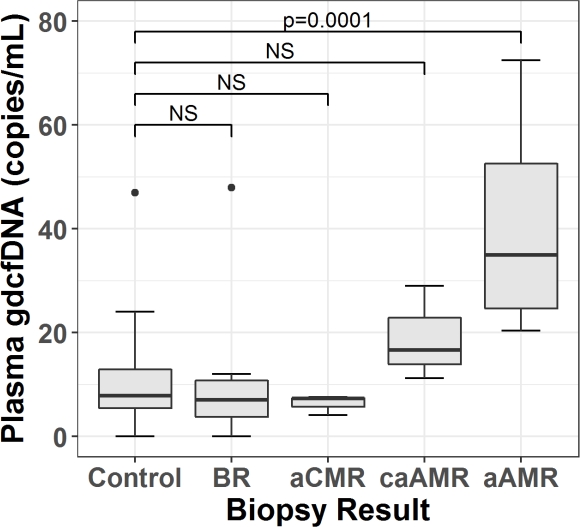
Results: There were 7 borderline rejection (BR), 3 acute cellular rejection (aCMR), 3 chronic active antibody mediated rejection (caAMR), and 9 acute antibody mediated rejection (aAMR) cases. The control group included 28 normal, 5 CNI toxicity, 3 recurrent primary disease, 1 BK nephropathy, and 2 other results.
GdcfDNA levels were significantly higher in aAMR compared to controls (median 35 vs 7.8 copies/mL, p=0.0001), and all other groups except caAMR (median 35 vs 16.6 copies/mL, p=0.89)(Figure 1). The receiver operating characteristic area under the curve (ROC AUC) for diagnosis of aAMR was 0.96 (95% CI 0.91-1). Using a diagnostic cut-off of 22 copies/mL, sensitivity for aAMR was 0.89 (95% CI 0.52-1), specificity 0.90 (95% CI 0.79-0.97) and negative predictive value (NPV) 0.98 (95% CI 0.89-1).
For the composite diagnosis of AMR (aAMR+caAMR), the ROC AUC was 0.93 (95% CI 0.86-0.99). Using a cut-off of 16.6 copies/mL, sensitivity for AMR was 0.89 (95% CI 0.52-1), specificity 0.90 (95% CI 0.79-0.97) and NPV 0.98 (95% CI 0.89-1).
Conclusions: This novel PCR-based approach permits the absolute quantification of gdcfDNA, which should be less prone to confounding than other methods that measure relative to total cfDNA levels. This new assay was useful for the diagnosis of AMR, and combined with rapid (12-24 hr) turnaround and low cost, provides support for further validation studies and clinical translation.
CITATION INFORMATION: Whitlam J., Ling L., Ierino F., Bruno D., Slater H., Power D. Absolute Quantification of Plasma Graft-Derived Cell-Free DNA for Diagnosis of Kidney Transplant Rejection Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Whitlam J, Ling L, Ierino F, Bruno D, Slater H, Power D. Absolute Quantification of Plasma Graft-Derived Cell-Free DNA for Diagnosis of Kidney Transplant Rejection [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/absolute-quantification-of-plasma-graft-derived-cell-free-dna-for-diagnosis-of-kidney-transplant-rejection/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress