Treg Plasticity is Induced by ENV,HERV1_I and UPR Activation in De Novo Autoimmune Hepatitis
1Yale University, New Haven, CT, 2University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 3Columbia University, New York, NY
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A38
Keywords: Autoimmunity, Inflammation, Liver transplantation, Pediatric
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: B-cell / Antibody /Autoimmunity
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
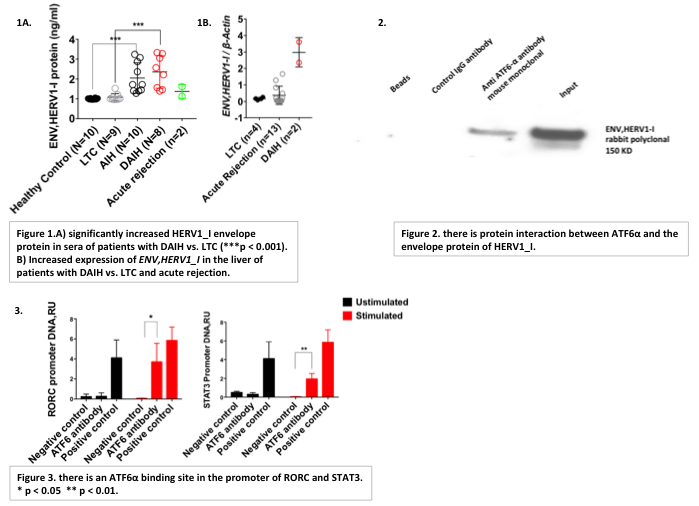
*Purpose: FOXP3+regulatory T cells (Tregs) are not a terminally differentiated population & can, under specific environmental conditions, acquire the phenotype of effector T cells. We have reported that Tregs of liver transplanted (LT) recipients with de novo autoimmune hepatitis (DAIH) display a TH17-like effector phenotype & demonstrate endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress with unfolded protein response (UPR) activation. Viruses can induce ER stress; thus given our observation of significantly increased expression of the envelope protein of HERV1_I in Tregs of LT recipients with DAIH, we sought to: (i) investigate for the presence of ENV,HERV1_I in serum & liver of LT recipients with DAIH; & (ii) determine how it induces ER stress.
*Methods: Sera was obtained from: (i) LT patients with: (a) DAIH (n=8), (b) normal graft function (LTC) (n=9), (c) acute rejection (n=2), & (ii) healthy non-transplanted children (HC) (n=10), for measurement of ENV,HERV1_I levels by ELISA. RNA was isolated from archived formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) liver tissue for determination of ENV,HERV1_I expression by qRT-PCR. FACS isolated Tregs of HC was used for: (i) Measurement of interaction between ATF6α & HERV1 using co-Immunoprecipitation Western Blot; (ii) confirmation of ATF6α binding site on RORC & STAT3 promoter using Chromatin Immunoprecipitation; (iii) transduction with ENV,HERV1_I overexpression particle. Following transduction, protein was isolated for measurement of ENV,HERV1_I, phospho-eIF-2α, CHOP, XBP-1s by WB (n = 10);RNA was harvested for measurement of ENV,HERV1_I, sXBP-1, CHOP expression by qRT-PCR (n = 10).
*Results: Significantly increased ENV,HERV1_I levels observed in sera of LT recipients with DAIH vs. sera of LT recipients with normal graft function (LTC) (p < 0.001). Moreover there is also a trend towards increased ENV,HERV1_I levels in sera of recipients with DAIH vs. LT recipients with acute rejection “$$graphicFigure 1A”. ENV,HERV1_I expression also increased in the liver of LT recipients with DAIH vs. LTC and LT recipients with acute rejection “$$graphicFigure 1B”. This confirms its presence in sera & liver of LT recipients with DAIH. In terms of how it induces ER stress, HERV1 interacts with ATF6α, one of the sentinel proteins known to elicit activation of the UPR “$$graphicFigure 2”; moreover, transduction of Tregs with ENV,HERV1_I overexpression particle results in UPR activation as evidenced by up-regulation of downstream UPR mediators, CHOP, XBP-1s & phospho-eIF-2α (p < 0.001 for CHOP & XBP-1s expression; p < 0.001 for CHOP & XBP-1s levels; p = 0.02 for phospho-eIF-2α level). Lastly, ATF6α binds to promoters in RORC & STAT3 “$$graphicFigure 3”, & drives transcription of IL-17A by Tregs (p < 0.001).
*Conclusions: ENV,HERV1_I reactivation may be the initiating event that drives Treg differentiation to TH17-effector Tregs in LT recipients with DAIH. It does this by inducing UPR activation. The subsequent binding of ATF6α to the promoter of RORC & STAT3 results in transcription of IL-17Afrom Tregs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yao J, Ling A, Arterbery A, Avitzur Y, Lobritto S, Martinez M, Ekong U. Treg Plasticity is Induced by ENV,HERV1_I and UPR Activation in De Novo Autoimmune Hepatitis [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/treg-plasticity-is-induced-by-envherv1_i-and-upr-activation-in-de-novo-autoimmune-hepatitis/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress