TNX-1500, an Fc-Modified Anti-cd154 Antibody, Prolongs Nonhuman Primate Cardiac Allograft Survival
1Center for Transplantation Sciences, Department of Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, 2Tonix Pharmaceuticals, Chatham, NJ
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 582
Keywords: Co-stimulation, Graft function, Heart, T cell activation
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 12 - Immunosuppression & Tolerance: Preclinical & Translational Studies
Session Information
Session Name: Tregs and Tolerance
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:50pm-6:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:50pm-6:00pm
Location: Hynes Room 304 / 306
*Purpose: Blockade of the CD40/CD154 T cell costimulation pathway is a promising approach to replace current clinical immunosuppression. TNX-1500 (TNX) is a novel humanized anti-CD154 monoclonal antibody (mAb) that contains the hu5c8 Fab region and an Fc region engineered to modulate FcγR2 binding to reduce the risk of pro-thrombotic platelet activation and aggregation, and thus prevent the thromboembolic events seen with hu5c8 IgG1 in preclinical models and clinical trials.
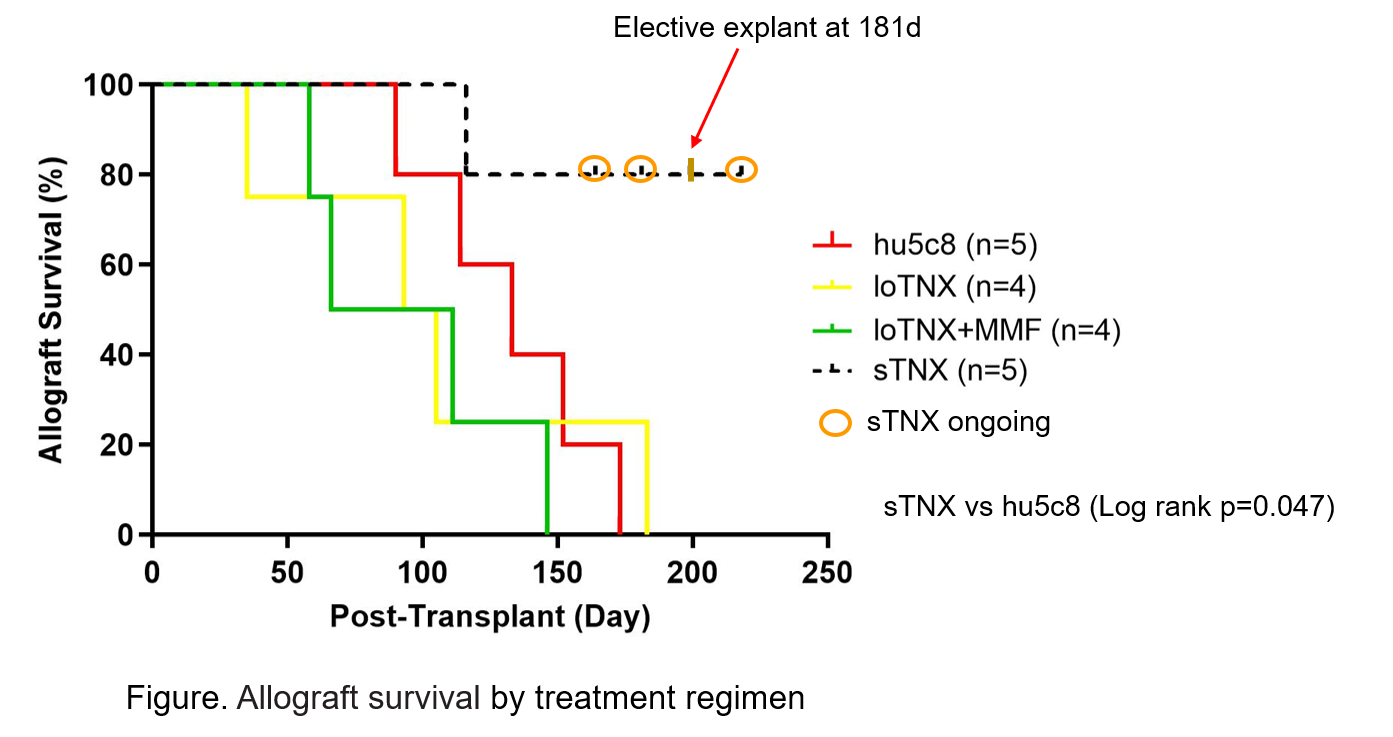
*Methods: Cynomolgus monkey heterotopic cardiac allograft recipients were treated with TNX either using a ‘standard’ regimen (sTNX; 30 mg/kg iv twice weekly x4, then 20 mg/kg weekly from d21-180, n=5), using a reduced-dose TNX maintenance regimen (loTNX; 30 mg/kg iv twice weekly x4, 10 mg/kg weekly x6, then 20 mg/kg monthly; n=4), or loTNX with mycophenolate mofetil (loTNX+MMF, 200mg/d po, n=4). Results were compared to historical data using primatized hu5c8 (n=5).
*Results: All grafts treated with loTNX, alone (MST 99d) or with MMF (MST 88d), experienced acute cellular rejection and/or antibody-mediated rejection; 7 of 8 grafts failed before scheduled study end at 180d. Four of five grafts treated with sTNX maintained good graft function (MST >190d, range 116-218, 3 of 5 ongoing); one graft was electively explanted at 181d and another rejected at 116d associated with a bacterial infection. Relative to hu5c8 alone (MST 133d), sTNX significantly prolonged cardiac allograft survival (p=0.047). Although loTNX+MMF attenuated IgG alloAb production during treatment (4/4 animals) more consistently than loTNX alone (2/4), cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV) tended to be more prominent with loTNX+MMF; alloAb and CAV in the sTNX group (in progress) will be presented. Neither sustained thrombocytopenia nor micro- or macrovascular thrombosis were observed in TNX-treated animals.
*Conclusions: Blockade of CD154 with TNX monotherapy is well tolerated and consistently prevents pathologic alloimmunity in this stringent preclinical model at least as effectively as hu5c8 monotherapy. Lower TNX maintenance dosing, with or without MMF, was less effective.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Miura S, Abady Z, Pollok F, Ma M, Kinoshita K, Fogarty S, Maguire P, Daugherty B, Lederman S, III RPierson. TNX-1500, an Fc-Modified Anti-cd154 Antibody, Prolongs Nonhuman Primate Cardiac Allograft Survival [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/tnx-1500-an-fc-modified-anti-cd154-antibody-prolongs-nonhuman-primate-cardiac-allograft-survival/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress