Suppression of Inflammation by Withaferin A in Cerulein-Induced Pancreatitis Model Results in Improved Syngeneic Islet Engraftment.
1Baylor Scott and White Research Institute, Dallas, TX
2Virginia Commonwellth University, Richmond, VA
3Baylor Simmons Transplant Institute, Dallas, TX
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A46
Keywords: Engraftment, Inflammation, Islets, Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kB)
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Cellular & Bone Marrow Transplantation Session I
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, April 29, 2017
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall D1
Introduction: Chronic pancreatitis (CP) is characterized by inflammatory damage to acinar cells followed by islets. In clinical islet autotransplantation, patients with advanced stages of CP with possible damage to islets are often treated. We analyzed the effect of Witharferin A (WA), a small molecule NFkB inhibitor, on CP progression and post-transplant islet function using a cerulein-induced CP and syngeneic islet transplant model.
Method: To induce CP, cerulein (50ug/kg) was injected intraperitoneally into C57BL/6 male mice seven times per day at hourly intervals, twice a week for one month. WA was injected once per day, 30 mins prior to cerulein injections. Pancreatitis was assessed with H&E and Sirius Red staining for fibrosis. Cytokine levels in plasma and oxidative stress markers in the pancreas were analyzed. Islets were isolated after cerulein treatment, and gene expression was evaluated using qPCR. CP islets treated with WA were transplanted intraportally into diabetic syngeneic mice and blood glucose levels were measured.
Result: WA suppressed inflammatory cytokine and chemokine secretion from cultured islets and treated animals and also suppressed cytokine mediated islet apoptosis. In vivo, WA treatment reduced pancreatic fibrosis induced by cerulein administration. The WA-treated islet transplant group showed a significantly improved glucose trend (p=0.0324) and higher achievement of normoglycemia ratio (p=0.0318) when compared to cerulein injection group.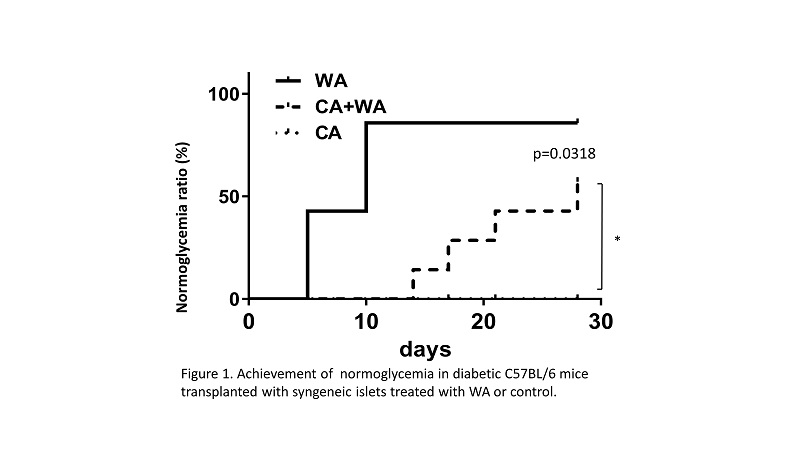 Conclusion: Witharferin A suppresses the progression of chronic pancreatitis induced by cerulein, and isolated islets from WA-treated pancreas improved glycemic control after transplantation. WA can serve as an effective agent to improve islet autotransplant outcome by minimizing inflammatory damage.
Conclusion: Witharferin A suppresses the progression of chronic pancreatitis induced by cerulein, and isolated islets from WA-treated pancreas improved glycemic control after transplantation. WA can serve as an effective agent to improve islet autotransplant outcome by minimizing inflammatory damage.
CITATION INFORMATION: Yoshimatsu G, Kanak M, Chang C, Darden C, Lawrence M, Naziruddin B. Suppression of Inflammation by Withaferin A in Cerulein-Induced Pancreatitis Model Results in Improved Syngeneic Islet Engraftment. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yoshimatsu G, Kanak M, Chang C, Darden C, Lawrence M, Naziruddin B. Suppression of Inflammation by Withaferin A in Cerulein-Induced Pancreatitis Model Results in Improved Syngeneic Islet Engraftment. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/suppression-of-inflammation-by-withaferin-a-in-cerulein-induced-pancreatitis-model-results-in-improved-syngeneic-islet-engraftment/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
