Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Associated With Acute Rejection in European American Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Genome Wide Association Study (GWAS)
1Medicine, MMRF, Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN
2Psychology, University of MN, Minneapolis, MN
3Pharmacy, University of MN, Minneapolis, MN
4Biostatistics, University of MN, Minneapolis, MN
5Surgery, University of MN, Minneapolis, MN.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B258
Keywords: Genomics, Graft failure, Kidney transplantation, Polymorphism
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Translational Genetics and Proteomics in Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, May 3, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Purpose: Acute rejection (AR) is associated with increased risk of allograft loss. Therefore, we conducted a GWAS to determine SNPs associated with AR in a large, European American cohort of adult kidney or kidney pancreas transplant recipients in a 7-center consortium.
Methods: European American kidney transplant recipients (n=1,528) enrolled in the DeKAF Genomics study were genotyped using an exome-plus Affymetrix TXArray chip containing 450,130 markers after QC. The associations between SNPs and AR were evaluated using survival analysis.
Results: The median recipient age was 52.1 years (Interquartile range or IQR 42-61) yrs, 63% were males and 67% received a living donor transplant. Median time to AR was 40 days posttransplant (IQR 16-132). There were 240 AR events and 71% were cellular, 16% were antibody mediated and 10% had features of both types of AR. The AR events were treated with steroid only (57%), antibodies only (3%), steroids followed by antibodies (15%), antibodies and steroids (18%) and other (6%).
No SNP showed genome-wide significance (p<5E-8). 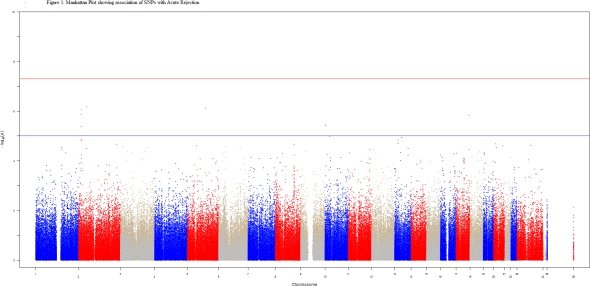 The two SNPs with smallest p-values are rs146480420 and rs59677415 (p=9E-7) in EPCAM and small nucleolar RNA genes, respectively. The top 83 SNPs with smallest p-values, were in the top canonical pathways such as NF-kappaB activation, IL-8 signaling and leukocyte extravasation signaling.
The two SNPs with smallest p-values are rs146480420 and rs59677415 (p=9E-7) in EPCAM and small nucleolar RNA genes, respectively. The top 83 SNPs with smallest p-values, were in the top canonical pathways such as NF-kappaB activation, IL-8 signaling and leukocyte extravasation signaling.
Conclusion: SNPs in novel pathways had the smallest p-values in our cohort of European Americans. Future meta-analysis with other cohorts is needed to identify less frequent SNPs associated with AR.
Supported by 5U19-AI070119 & 5U01-AI058013 from NIAID
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Israni A, Dorr C, Miller M, Schladt D, Sanghavi K, Muthusamy A, Remmel R, Guan W, Wu B, Oetting W, Jacobson P, Matas A. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Associated With Acute Rejection in European American Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Genome Wide Association Study (GWAS) [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/single-nucleotide-polymorphisms-snps-associated-with-acute-rejection-in-european-american-kidney-transplant-recipients-a-genome-wide-association-study-gwas/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
