Recipient TIM4 Expression is Essential for Hepatocellular Function in Liver Transplantation
Dumont-UCLA Transplant Center, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C37
Keywords: Biopsy, Graft failure, Liver transplantation, Survival
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Innate Immunity; Chemokines, Cytokines, Complement
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) represents a major risk factor of early graft dysfunction and predisposes to rejection in orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT). Previous studies have reported on the pathogenic function of T-cell immunoglobulin mucin 4 (TIM4) in warm hepatic IRI. Here, we used a clinically relevant mouse model of hepatic cold storage followed by OLT to analyze the role of recipient-specific TIM4 signaling in IR-stressed OLT.
*Methods: WT liver grafts after 18h of cold storage were transplanted to groups of WT or TIM4-deficient (TIM4-KO) recipients; liver graft/blood samples were collected at 6h/24h after reperfusion. HMGB1-enriched liver flush (LF) was collected by infusing cold-stored WT livers. Bone marrow-derived neutrophil/macrophage (BMM) cultures from WT vs. TIM4-KO donors were stimulated with LPS/LF.
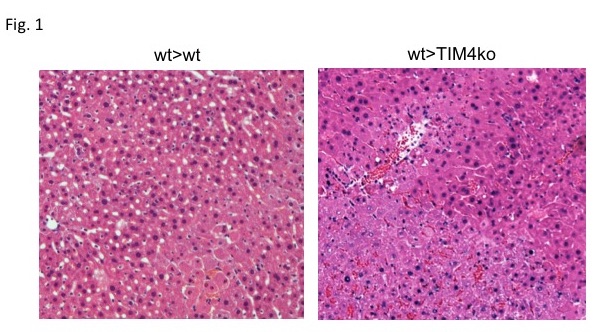
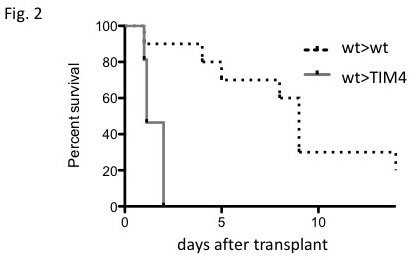
*Results: In contrast to WT>WT OLT, recipient TIM4 deficiency (WT>TIM4-KO) resulted in: 1/ increased sALT (6676±649 vs 4563±681 IU/L) levels at 6h after reperfusion (n=9/11, p<0.05); 2/ sustained elevations of sALT (4802±1086 vs 2740 ±834 IU/L) levels at 24h after OLT (n=10/4, p<0.05); 3/ augmented Suzuki's histological grading of IRI (6.7±0.5 vs 5.2±0.6, p<0.05, Fig. 1); 4/ higher frequency of TUNEL+ cells (p<0.05); 5/ enhanced macrophage/neutrophil OLT infiltration (p<0.05); 6/ increased mRNA levels coding for MCP1/CXCL1/CXCL2/CXCL10. Importantly, disruption of TIM4 signaling at the recipient site was highly pathogenic in vivo and curtailed the survival benefit in IR-stressed OLT (2-weeks: 0% vs 30%, n=16/10, p<0.001, Fig. 2). In parallel, TIM4 disruption in LPS/LF-activated BMDMs in vitro: 1/ augmented MCP1 mRNA levels, while inhibiting immunoregulatory PD1; and 2/ strongly enhanced mRNA levels coding for CXCL1/CXCL2.
*Conclusions: Cytodestructive TIM4-deficient phenotype triggered enhanced pro-inflammatory gene expression profile in bone marrow-derived macrophage/neutrophil cultures. By demonstrating unexpected requirement for TIM4 in hepatoprotection, this study highlights putative homeostatic in vivo function of recipient TIM4 signaling in controlling IR-stressed OLT.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kadono K, Kageyama S, Hirao H, Nakamura K, Dery KJ, Oncel D, Ito T, Ke B, Kaldas FM, Busuttil RW, Kupiec‐Weglinski JW. Recipient TIM4 Expression is Essential for Hepatocellular Function in Liver Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/recipient-tim4-expression-is-essential-for-hepatocellular-function-in-liver-transplantation/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress