RBBP7 as a Novel Biomarker for the Molecular Diagnosis of BK Virus-Associated Nephropathy
Department of Urology, Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Beijing, China
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1538
Keywords: Genomic markers, Kidney transplantation, Nephropathy, Polyma virus
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Clinical Science » 17 - Biomarkers: Clinical Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers: Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
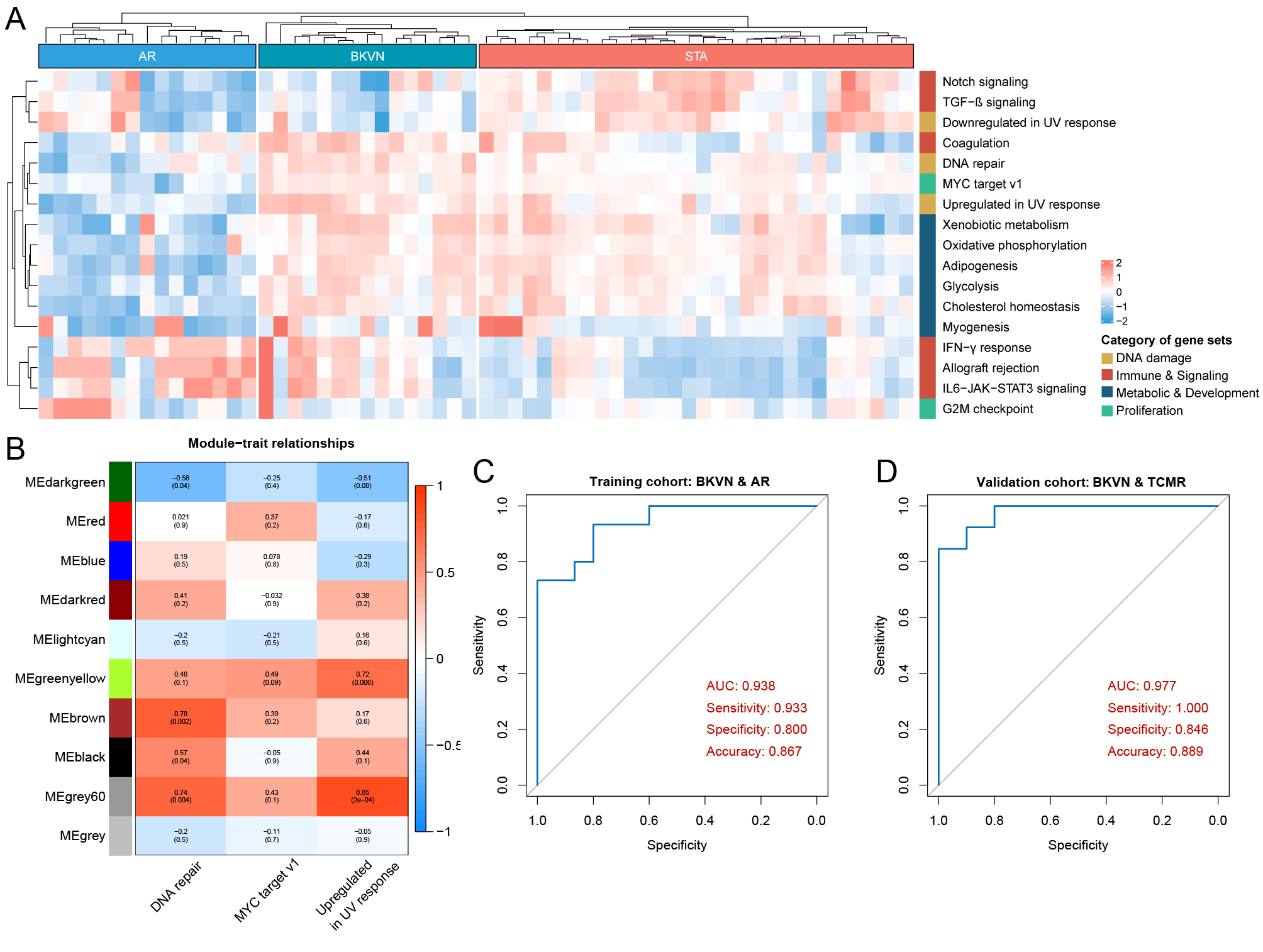
*Purpose: BK virus-associated nephropathy (BKVN) remains a major infectious complication of kidney transplantation, and its histologic appearance can mimic rejection, leading to a diagnostic dilemma with significant implications in patient management. The current study aims to apply machine learning methods to identify molecular biomarkers in renal biopsy to distinguish BKVN from rejection.
*Methods: We collected gene expression profiles of 169 kidney biopsies taken from BKVN, rejection and stable functioning (STA) allografts included in two independent transplantation cohorts from Gene Expression Omnibus database. Based on single sample gene set enrichment analysis, the performances of 50 hallmark biological states or processes were estimated and random forest algorithm was then applied to detect specific hallmark activities in BKVN. Subsequently, we utilized weighted gene co-expression network analysis to select the most relevant gene module associated with BKVN-specific hallmarks. Genes in the corresponding module were employed to support vector machines (SVM) algorithm to choose biomarkers with promising and robust diagnostic ability.
*Results: Three hallmarks associated with DNA damage and proliferation activities were detected as BKVN-specific hallmarks and they were most positively correlated with grey60 gene module. RBBP7 was then screened out based on SVM approach in the training cohort with acute rejection samples (AUC = 0.938) and it exhibited higher accuracy in the validation cohort with T-cell mediated rejection samples (AUC = 0.977). Moreover, RBBP7 showed better diagnostic ability in comparison with other biomarkers proposed by previous studies.
*Conclusions: We identified and validated RBBP7 as a robust and promising biomarker with high accuracy for distinguishing BKVN from rejection states in renal transplant patients. The current study provided a molecular biomarker contributing to BKVN diagnosis thus benefiting patient management in clinical practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yicun W, Yuxuan W, Xiaopeng H. RBBP7 as a Novel Biomarker for the Molecular Diagnosis of BK Virus-Associated Nephropathy [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/rbbp7-as-a-novel-biomarker-for-the-molecular-diagnosis-of-bk-virus-associated-nephropathy/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress