Normothermic Ex Situ Liver Perfusion with Different Clinical Perfusates and Their Effect on Pig Liver Transplant Outcomes in a Donation after Circulatory Death Model
Toronto General Hospital, Toronto, ON, Canada
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A115
Keywords: Apoptosis, Endothelial cells, Machine preservation, Perfusion solutions
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Ischemia Reperfusion & Organ Rehabilition
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Human-albumin/Dextran (HA-D), Bovine-gelatin (BG) and packed red blood cells plus plasma have been used in European and North-American clinical trials of normothermic ex-situ liver perfusion. We compared the effects of these perfusates in a porcine model during ex-situ perfusion and after transplantation.
*Methods: Porcine livers were retrieved 30mins following circulatory death. After 5hrs of normothermic ex-situ perfusion, grafts were transplanted. Three groups (n=6) were assessed [HA-D vs BG vs whole blood (WB)]. One group of static cold storage was evaluated for comparison with the perfusion groups. Hemodynamic variables, liver, and endothelial injury and function were assessed during ex-situ perfusion and post-transplantation.
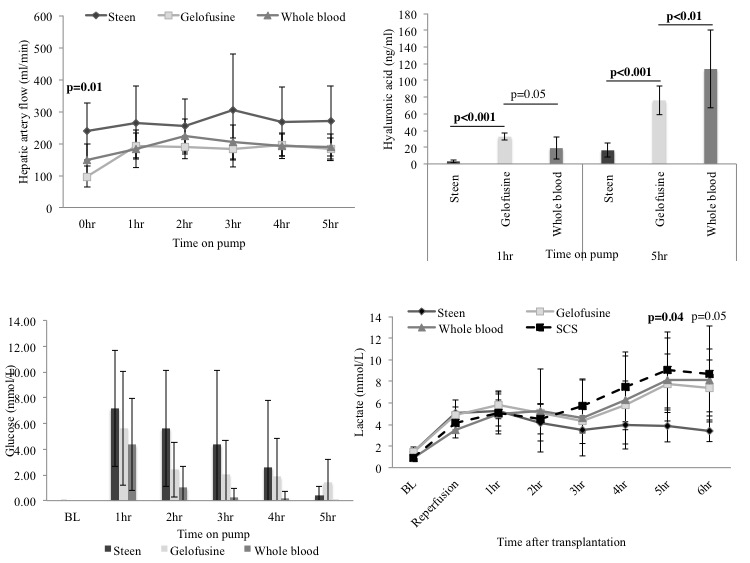
*Results: Hepatic artery flow was higher since the beginning of ex-situ perfusion in the HA-D vs BG vs WB group (238±90ml/min vs 97±33ml/min vs 148±49ml/min;p=0.01). Hyaluronic-acid was lower in the HA-D vs BG vs WB group at the end of perfusion (16.28±7.59ng/ul vs 76.05±15.30ng/ul vs 114±46ng/ul;p<0.001). After transplant, aspartate aminotransferase was lower in the HA-D group when compared with BG, WB and static cold storage group (444±226IU/L vs 1033±694IU/L vs 616±444IU/L vs 2235±1878IU/L). At 5hr after transplant, lactate was lower in the HA-D vs BG vs WB vs static cold storage group (3.88±1.49mmol/L vs 7.79±2.68mmol/L vs 8.16±3.86mmol/L vs 9.06±3.54mmol/L;p=0.04). INR was improved in HA-D group compared with BG, WB and static cold storage grafts (1.23±0.30 vs 1.63±0.20 vs 1.50±0.31 vs 1.97±1.55;p=0.03) after transplantation. In the BG vs HA-D vs WB group lower ex-situ perfusion aspartate aminotransferase (142±52IU/L vs 183±53IU/L vs 285±74IU/L;p=0.01) and cleaved-caspase-3 staining (0.95±1.14% vs 2.05±0.73% vs 1.74±0.54%) were found. The bile from the WB vs HA-D vs BG displayed higher pH (7.59±0.18 vs 7.54±0.11 vs 7.34±0.37) and lower glucose levels (0±0mmol/L vs 0.38±0.75mmol/L vs 1.42±1.75mmol/L) at the end of perfusion.
*Conclusions: HA-D, BG and WB perfusates have different effects on graft function and hepatocyte, biliary and endothelial injury. Optimization of the perfusates based on the characteristics of these solutions will potentially improve the outcomes with the use of normothermic ex-situ liver perfusion in marginal grafts.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Linares-Cervantes I, Kollmann D, Goto T, Echeverri J, Kaths M, Hamar M, Urbanellis P, Mazilescu L, Rosales R, Bruguera C, Oquendo F, Ganesh S, Adeyi O, Yip P, Selzner N, Selzner M. Normothermic Ex Situ Liver Perfusion with Different Clinical Perfusates and Their Effect on Pig Liver Transplant Outcomes in a Donation after Circulatory Death Model [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/normothermic-ex-situ-liver-perfusion-with-different-clinical-perfusates-and-their-effect-on-pig-liver-transplant-outcomes-in-a-donation-after-circulatory-death-model/. Accessed February 20, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress