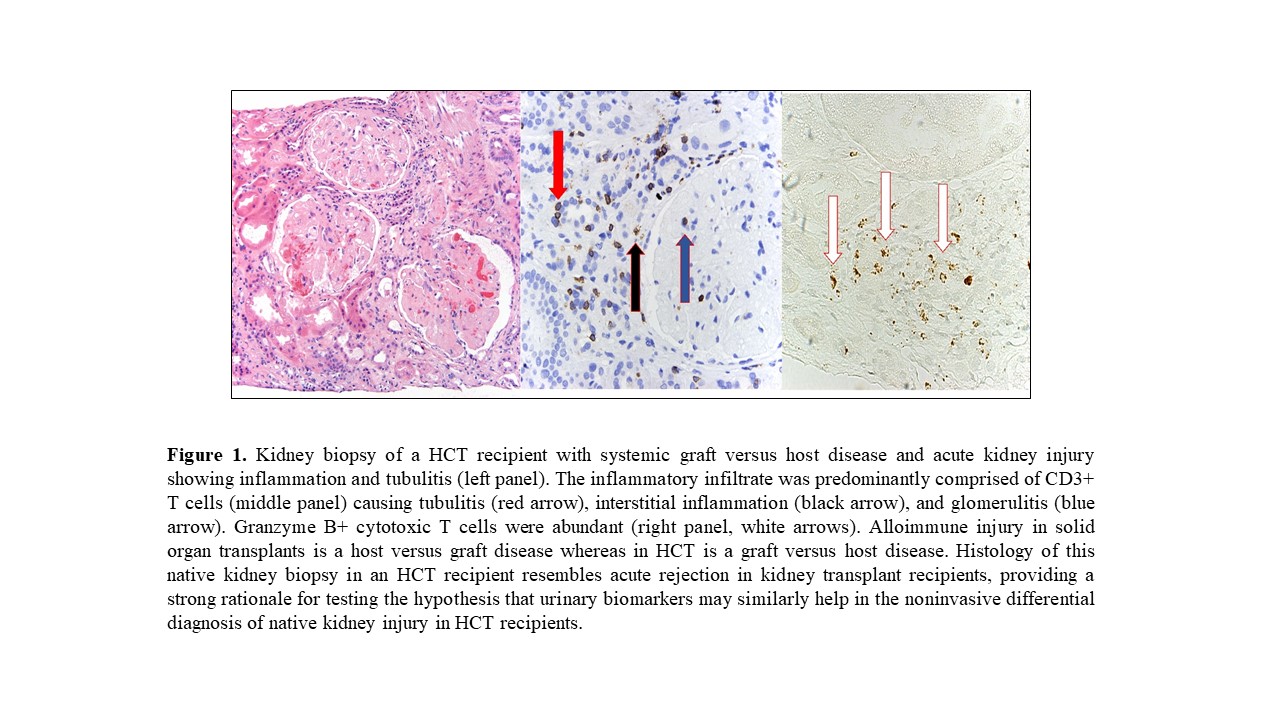
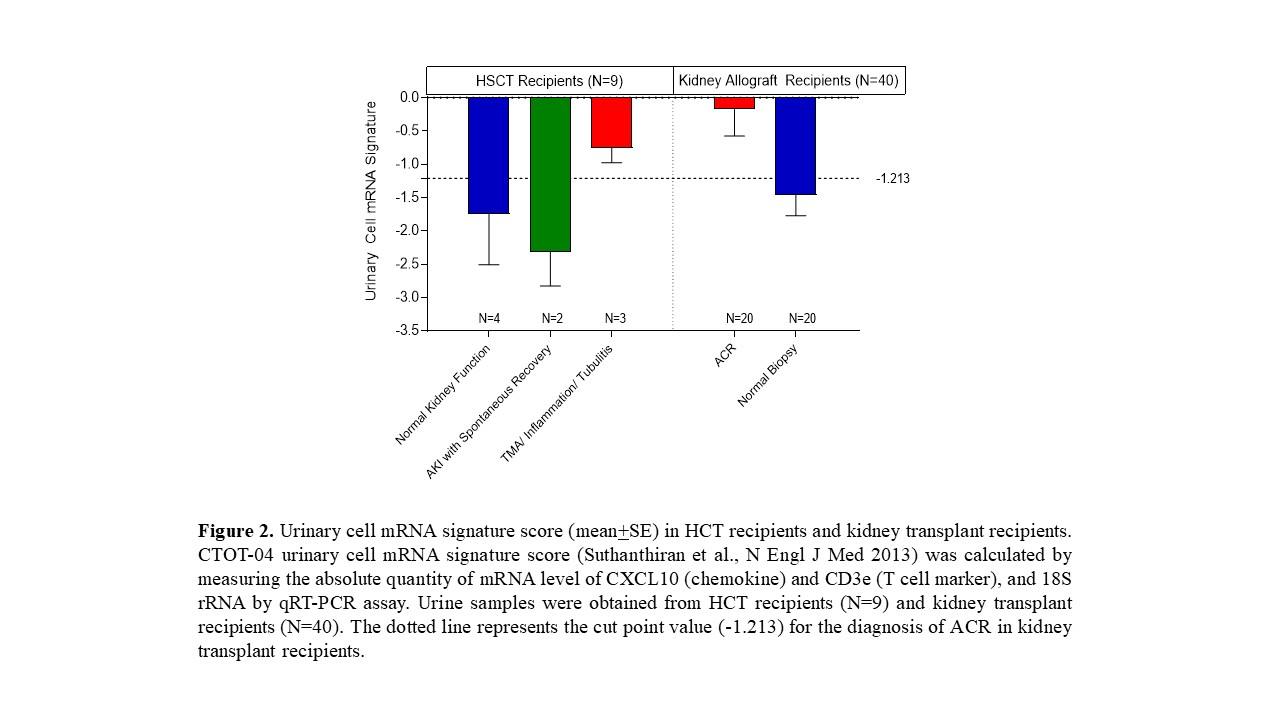
Kidney Injury in Hematopoietic Cell Transplant (HCT) Recipients: Urinary Biomarkers to the Rescue
1NY Presbyterian- Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY, 2Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, 3University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 671
Keywords: Bone marrow transplantation, Graft-versus-host-disease, Kidney, Renal injury
Topic: Clinical Science » Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Kidney injury is common in HCT recipients and can be the result of graft versus host/kidney disease. However, this has not been well characterized, mainly due to limitations in performing kidney biopsies in these patients. Alloimmune injury in solid organ transplants is a host versus graft disease whereas in HCT is a graft versus host disease. Urinary cell mRNA has been validated as a noninvasive biomarker for the diagnosis of acute rejection in kidney transplant recipients. In an analogous fashion, urinary biomarkers may help in the noninvasive diagnosis of native kidney injury in HCT recipients.
*Methods: We obtained urine samples from 9 HCT recipients: 3 with acute kidney injury (AKI) and native kidney biopsy showing tubulitis and interstitial inflammation (Figure 1), 2 with AKI that resolved spontaneously, and 4 with normal kidney function. We also obtained urine samples from 40 kidney allograft recipients: (i) 20 with biopsy diagnosis of acute cellular rejection (ACR) and (ii) 20 with stable graft function and normal/no rejection biopsies. We isolated total RNA from urinary cells, reverse transcribed to cDNA, and measured the absolute quantity of mRNA level of CXCL10 (chemokine) and CD3e (T cell marker), and 18S rRNA by qRT-PCR assay. We calculated the CTOT-04 urinary cell mRNA signature score for each recipient (Suthanthiran et al, N Engl J Med 2013).
*Results: Of the 3 HCT recipients with AKI who had a kidney biopsy, 2 had significant inflammation that stained positive for CD3 and/or Granzyme B in the interstitium and tubules (Figure 1). The urinary cell CTOT-04 signature score was higher in HCT recipients with AKI/tubulitis and interstitial inflammation in the native kidney and resembled ACR of kidney allograft recipients (Figure 2).
*Conclusions: We herein confirm our hypothesis and demonstrate the feasibility and utility of urinary cell molecular profiling as a noninvasive tool for the diagnosis of kidney injury in recipients of HCT.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Salinas T, Snopkowski C, Li C, Chen K, Lubetzky M, Salvatore S, Besien KVan, Jaimes E, Hingorani S, Seshan S, Muthukumar T. Kidney Injury in Hematopoietic Cell Transplant (HCT) Recipients: Urinary Biomarkers to the Rescue [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/kidney-injury-in-hematopoietic-cell-transplant-hct-recipients-urinary-biomarkers-to-the-rescue/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress