Impact of Cold Ischemic Time (CIT) and Distance Traveled (DT) on Shipped Kidneys in the OPTN/UNOS Kidney Paired Donation (KPD) Pilot Program (PP)
1Univ Hosp Case Med Ctr, Cleveland, OH
2UNOS, Richmond, VA
3Carnegie Mellon Univ, Pittsburgh, PA
4Yale Univ, New Haven, CT.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 301
Keywords: Graft function, Graft survival, Ischemia, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney: Living Donor Issues II
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, May 4, 2015
Session Time: 4:00pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 4:48pm-5:00pm
Presentation Time: 4:48pm-5:00pm
Location: Terrace IV
Background: The success of a national KPD program is predicated on excellent early kidney function and graft survival (GS). As other KPD programs have reported increased delayed graft function (DGF) with CIT >8 hours (hrs), we assessed CIT and early outcomes (GS, DGF) for KPDPP kidneys and other living and deceased donor kidney transplants (tx). We also examined DT for KPDPP transplants.
Methods: DGF and Kaplan-Meier GS rates for KPDPP tx (n=111) performed between 10/2010-9/2014 were compared to other kidney tx: KPD (intra- and inter-hospital) (n=1,927); other living donor (LD) (n=20,431); and deceased donor (DD) (n=41,424). Additionally, DGF by CIT was assessed for all shipped LD kidneys (n=1,582). Shipped kidneys were those with different recovery vs. transplant hospital. An exact likelihood ratio chi-squared test was used to compare DGF rates. Results are based on OPTN data as of Nov 7.
Results: GS at 6 months for KPDPP tx was statistically no different from other KPD tx (p=0.59) and other LD tx (p=0.30), despite higher median CIT (8 hrs v 2.2 hrs v 1 hr). Of KPDPP tx, 103 (89%) kidneys were shipped (74% interregionally) including 49 (48%) >500 miles and 13 (13%) >1000 miles. Median CIT was 8 hrs (range: <1 to 26 hrs) and 2 kidneys (1.8%) experienced DGF (Table 1). Zero hospitals reported DGF for any KPDPP shipped kidneys with CIT ≥8 hours (n=55). Though statistical significance was borderline (p=0.05), this contrasted with a 5.8% DGF rate for other shipped LD tx with CIT ≥ 8 hrs. However, the DGF rate for shipped LD kidneys was markedly less than in DD tx (DGF=12.8% at 0-4 hrs; 26.7% at 16-20 hrs).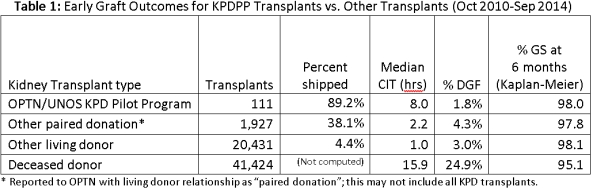
Conclusions: Shipped KPD kidneys are a safe option for LD tx even when the CIT will exceed 8 hours and DT >1000 miles, having a substantially lower DGF rate than DD tx. Additionally, shipped LD tx have equivalent GS at 6 months compared with non-shipped LD tx.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aeder M, Stewart D, Leishman R, Callahan LRobbins, Kucheryavaya A, Sandholm T, Formica R. Impact of Cold Ischemic Time (CIT) and Distance Traveled (DT) on Shipped Kidneys in the OPTN/UNOS Kidney Paired Donation (KPD) Pilot Program (PP) [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-cold-ischemic-time-cit-and-distance-traveled-dt-on-shipped-kidneys-in-the-optnunos-kidney-paired-donation-kpd-pilot-program-pp/. Accessed July 2, 2025.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
