Development of a Novel Multidrug Combination to Defat Steatotic Rat Liver via Normothermic Machine Perfusion
1Surgery, Washington University, St. Louis, MO, 2Pathology and Immunology, Washington University, St. Louis, MO
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D-298
Keywords: Donors, marginal, Liver, Machine preservation, Rat
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Cellular Therapies, Tissue Engineering / Regenerative Medicine
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Hepatic steatosis is now the leading cause of liver discards in deceased donors. Previous studies (Yarmush et al., Y defatting) have successfully reduced the fat content by treating rat steatotic livers with a multidrug combination using GW7647, GW501516, Hypericin, Scoparone, Forskolin, and Visfatin on extracorporeal normothermic machine perfusion (NMP). However, several studies linked the use of GW compounds to an increased risk of carcinogenesis as evidenced by increased cell proliferation signaling in the AKT and ERK pathways. We aimed to develop a novel pharmacologic intervention with an improved safety profile while preserving defatting efficacy. We developed a novel multidrug combination by removing the GW compounds and adding two polyphenols, Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (E) and Resveratrol (R), which are natural plant products that have been shown to promote lipid metabolism by activating the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway.
*Methods: Sixteen rat livers were placed on NMP and assigned to control, Y defatting, Y+E+R defatting, or Y’-GW+E+R defatting groups (Y’=dose-reduced Y defatting, n=4/group).
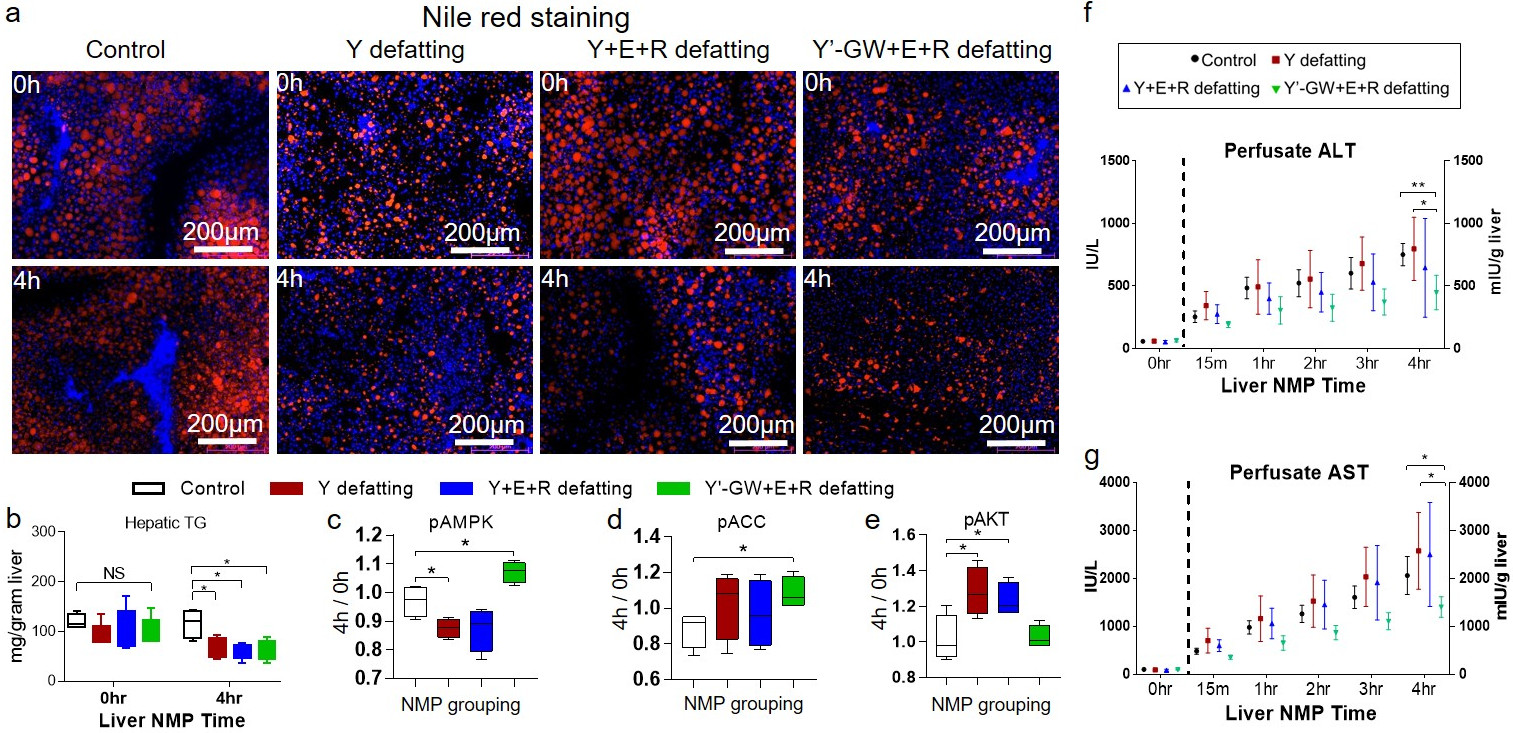
*Results: The viability of the livers after NMP in all groups were evidenced by increased glucose utilization and lactate clearance to 2.2 mmol/L after 2hrs of NMP. All livers in the defatting groups had significant decreases in hepatic TG content at the end of the experiment (Fig. a, b). However, livers treated with our novel Y’-GW+E+R combination had evidence of increased metabolism, and less hepatocyte damage and carcinogenic potential. Our Y’-GW+E+R combination had increased markers of metabolism, shown by increased phosphorylation of AMPK (P=0.019) and Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (P=0.023) compared with control (Fig. c, d ); these were not increased in Y+E+R, and actually decreased in the Y groups. Furthermore, the Y’-GW+E+R group had less evidence of carcinogenic potential with no increase in AKT phosphorylation compared to control (P=0.089); the Y (P=0.031) and Y+E+R (P=0.035) groups had striking increases in AKT phosphorylation in comparison (Fig. e). Finally, our Y’-GW+E+R showed less evidence of hepatocyte damage with significantly lower perfusate ALT (P=0.007) and AST (P=0.014) levels (Fig. f, g).
*Conclusions: We have developed a novel multidrug combination demonstrating promising defatting efficacy via activation of the AMPK pathway with an optimized safety profile and reduced hepatotoxicity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Xu M, Zhou F, Ahmed O, Upadhya G, Jia J, Lee C, Xing J, Ye L, Shim S, Zhang Z, Byrnes K, Wong B, Kim J, Lin Y, Chapman W. Development of a Novel Multidrug Combination to Defat Steatotic Rat Liver via Normothermic Machine Perfusion [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/development-of-a-novel-multidrug-combination-to-defat-steatotic-rat-liver-via-normothermic-machine-perfusion/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress