Autologous Expanded Tregs Promote Bone Marrow Engraftment and Donor Kidney Survival in Non-Human Primate Chimerism Model
1Columbia Center for Translational Immunology, Columbia University, New York City, NY, 2Department of Pathology and Cell Biology, Columbia University, New York City, NY
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A-381
Keywords: Graft survival, Kidney transplantation, T cells, Tolerance
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Tolerance / Immune Deviation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
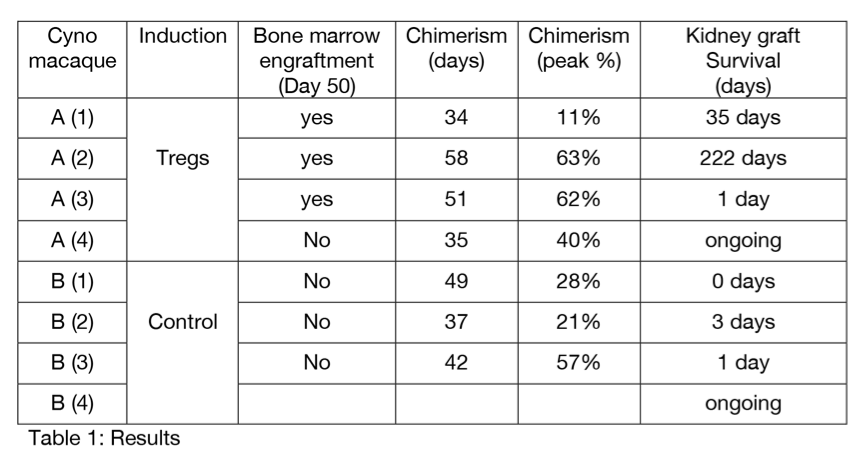
*Purpose: Mixed chimerism (MC) induced with non-myeloablative conditioning in monkeys and humans induces tolerance to 70% of kidney grafts transplanted at the time of BMT. We use ex vivo expanded, polyclonal host Tregs to improve MC induction. To test tolerance, we waited 120 days before grafting donor kidneys in the abscence of immunosuppression (IS), as such grafts are routinely rejected by animals receiving BMT without Tregs.
*Methods: Host Tregs were grown from sorted (CD4+ CD25hi) PBMCs and cryopreserved. Conditioning included total body irradiation (125cGy), thymic irradiation (7Gy), anti-CD154 mAbs, horse ATG, loCD2 mAbs, followed by allogeneic MHC-mismatched BMT and 1 month of rapamycin, after which all immunosuppression (IS) was withdrawn. 8 cynomolgous macaques underwent this regimen, of which 4 received Treg infusions and donor kidney grafted on day 120.
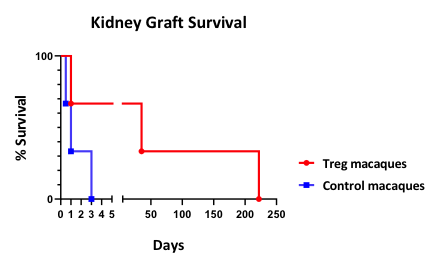
*Results: Transient peripheral blood macrochimerism was seen in all animals for 30 to 60 days after BMT. Treg animals showed bone marrow engraftment on day 50, anti-donor hyporesponsiveness in MLR and Elispot, an overall higher level of peak chimerism and no signs of graft-versus-host disease. In the longest survivor, MLR assays showed antidonor hyporesponsiveness that was restored in CD25-depleted MLR. This animal also showed a larger Treg population in proliferating anti-donor T cells versus anti-third party T cells in a CFSE stained MLR. Treg animals had kidney graft survival up to 222 days without IS. In contrast, control animals demonstrated donor-specific antibodies and rejected their kidney graft within 3 days.
*Conclusions: Autologous, ex vivo expanded Tregs in combination with iliac crest BMT results in prolonged survival of donor kidneys grafted after peripheral chimerism is lost. Ex vivo expanded, polyclonal Tregs given at the time of BMT not only enhance donor chimerism but may induce a regulatory environment that is associated with robust operational tolerance to the donor.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bruestle K, Alonso-Guallart P, Sakai H, Fredriksson F, Piegari B, Lopes E, Pierre G, Shou A, Ekanayake-Alper D, Weiner J, Iuga A, Coley SM, Sykes M, Griesemer A. Autologous Expanded Tregs Promote Bone Marrow Engraftment and Donor Kidney Survival in Non-Human Primate Chimerism Model [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/autologous-expanded-tregs-promote-bone-marrow-engraftment-and-donor-kidney-survival-in-non-human-primate-chimerism-model/. Accessed July 9, 2025.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress