Attenuation of Warm Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition.
1Surgery, Dumont-UCLA Translant Center, Los Angeles, CA
2Pathology, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C135
Keywords: B cells, Ischemia, Liver grafts, Neutrophils
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Ischemia Reperfusion Injury and Organ Preservation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) is a central player in multiple signaling pathways in lymphoid and myeloid cells, including neutrophils. Neutrophils are crucial effectors in the pathophysiology of organ ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI). BTKB66 is a highly selective, irreversible inhibitor of Btk. In this study, we tested this small molecule in in vitro and in vivo assays of neutrophil activation and hypothesized that it would reduce warm hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI). BTKB66 was tested in an in vitro model of LPS-mediated neutrophil activation. To further assess its efficacy in vivo, BTKB66 was administered for seven days to mice in their drinking water prior to subjecting them to 90 minutes of warm hepatic ischemia followed by 6 or 24 hours of reperfusion. Clinical and pathologic features of these mice were examined following IRI, including AST, ALT, and a panel of cytokines and chemokines. BTKB66 potently inhibited LPS-mediated activation of bone-marrow derived neutrophils at 1 M. It also reduced the amount of IRI as determined by AST and ALT levels, as well as in immunohistochemical analyses, at a dose of 60 mg/kg/day. 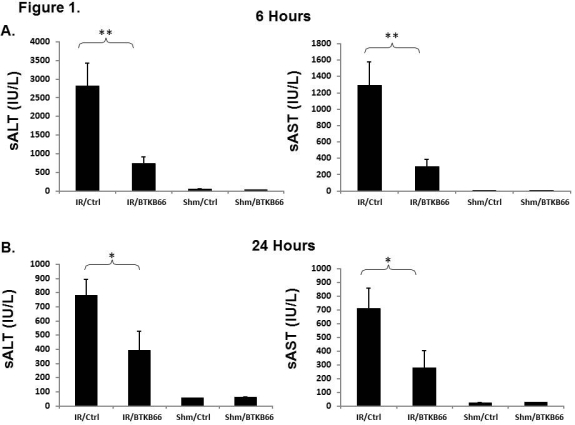 There were significant decreases in markers of inflammation in the liver, such as CXCL1, CXCL2, and CXCL10. There were also significant decreases in serum markers of the activation of myeloid cells, such as CCL5, CCL11, and CXCL5. BTKB66 is effective in inhibiting warm hepatic IRI. These finding confirm that neutrophil recruitment and activation plays a large role in injury during IRI and that targeting Btk activity could provide a useful approach for preventing liver IRI and improving overall outcomes in liver transplantation.
There were significant decreases in markers of inflammation in the liver, such as CXCL1, CXCL2, and CXCL10. There were also significant decreases in serum markers of the activation of myeloid cells, such as CCL5, CCL11, and CXCL5. BTKB66 is effective in inhibiting warm hepatic IRI. These finding confirm that neutrophil recruitment and activation plays a large role in injury during IRI and that targeting Btk activity could provide a useful approach for preventing liver IRI and improving overall outcomes in liver transplantation.
CITATION INFORMATION: Zarrinpar A, Palumbo T, Nakamura K, Lassman C, Busuttil R, Kupiec-Weglinski J. Attenuation of Warm Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zarrinpar A, Palumbo T, Nakamura K, Lassman C, Busuttil R, Kupiec-Weglinski J. Attenuation of Warm Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/attenuation-of-warm-hepatic-ischemia-reperfusion-injury-by-brutons-tyrosine-kinase-inhibition/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
