AT1R Antibody Analysis: High Proportion of Non-Specific Reactivity?
1Dept of Pediatrics, U of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada
2Dept of Medicine, U of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada
3Dept of Lab Medicine & Pathology, U of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada
4ATI, , Canada
5CNTRP, , Canada.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A41
Keywords: Antibodies, Autoimmunity, Immunoadsorption, Methodology
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Biomarkers, Immune Monitoring and Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 2, 2018
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall 4EF
INTRODUCTION:
The angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) is expressed on vascular endothelium. AT1R antibodies (Ab) have been studied to examine their relevance in renal and adult cardiothoracic transplantation but these Ab have not been studied in pediatric cardiac patients. Our aim is to measure the frequency of AT1R Ab in this patient population and controls and to assess for non-specific reactivity.
METHODS:
Patients for whom pre and post-transplant sera data were available were included (n=42 patients and 154 samples). AT1R Ab were measured by ELISA (distributed by One Lambda ThermoFisher). Age-matched, sex-balanced, non-transplant controls (n=27) were collected from a local cardiac-catheterization laboratory. A subset of sera with positive results (n=52 sera from 20 patients) as well as the assay's positive control were re-tested following adsorption for non-specific reactivity using a commercially available product (Adsorb Out).
RESULTS:
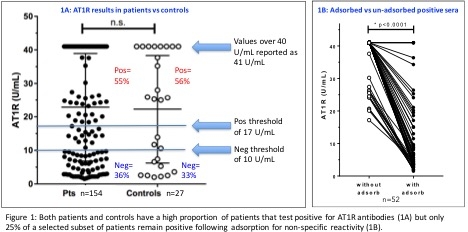
No significant difference was observed between patient and control AT1R Ab results: 55 and 56% of each group tested positive (Figure 1A). Adsorbed sera had significantly decreased AT1R Ab values vs non-adsorbed sera (Figure 1B) whereas known standards remained positive for AT1R antibodies. In the UN-adsorbed sera, 57% of the pre-transplant sera and 64% of the post-transplant sera were positive for AT1R Ab. In contrast, using ADSORBED sera, only 21% and 15% (respectively) tested positive.
CONCLUSION:
Non-specific binding is a known issue in ELISA immunoassays and may result in an overestimation of AT1R Ab detection; this may be overcome by the absorption method used here. The pediatric heart transplant population may be especially prone to method interferences due to high frequency of thymectomy and mechanical circulatory support t and this study should be replicated in other patient populations. To avoid possible false positive results and facilitate a clearer understanding of the clinical implication of AT1R Ab, future studies should routinely include a step to assess non-specific reactivity.
CITATION INFORMATION: Halpin A., Abou-Zeki S., Larsen I., Campbell P., Urschel S., West L. AT1R Antibody Analysis: High Proportion of Non-Specific Reactivity? Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Halpin A, Abou-Zeki 5S, Larsen I, Campbell P, Urschel 5S, West1 L. AT1R Antibody Analysis: High Proportion of Non-Specific Reactivity? [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/at1r-antibody-analysis-high-proportion-of-non-specific-reactivity/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress