Anti- CD154 / CD40 Costimulation Blockade is Superior to Tacrolimus in Prolonging Survival in Pig-to-Nonhuman Primate Renal Xenotransplantation
1Emory Transplant Center, Emory University, Atlanta, GA, 2Yerkes National Primate Center, Emory University, Atlanta, GA, 3University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 269
Keywords: Co-stimulation, Preclinical trails, Primates, Xenoreactive antibodies
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Xenotransplantation
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:54pm-3:06pm
Presentation Time: 2:54pm-3:06pm
Location: Room 310
*Purpose: Costimulation blockade strategies targeting the CD40/CD154 pathway are highly effective in preventing xenograft rejection in pig-to-nonhuman primate (NHP) transplantation models. The aim of this study was to assess the relative therapeutic efficacy of tacrolimus, a clinically applicable immunosuppressive agent, compared to either anti-CD40 or anti-CD154 therapies.
*Methods: Rhesus macaques (n=17) with low pre-transplant xenoreactive antibody titers were selected following recipient screening. Selected recipients underwent bilateral nephrectomy and life-sustaining porcine renal xenotransplantation using GGTA1 KO/CD55 transgenic donor pigs (NSRRC, Columbia, MO). Animals underwent T cell depletion and were randomized to one of three maintenance treatment regimens: tacrolimus (target trough 8-12ng/mL), anti-CD40 (clone 2C10R4), or anti-CD154 (clone 5C8), plus mycophenolic acid and steroids.
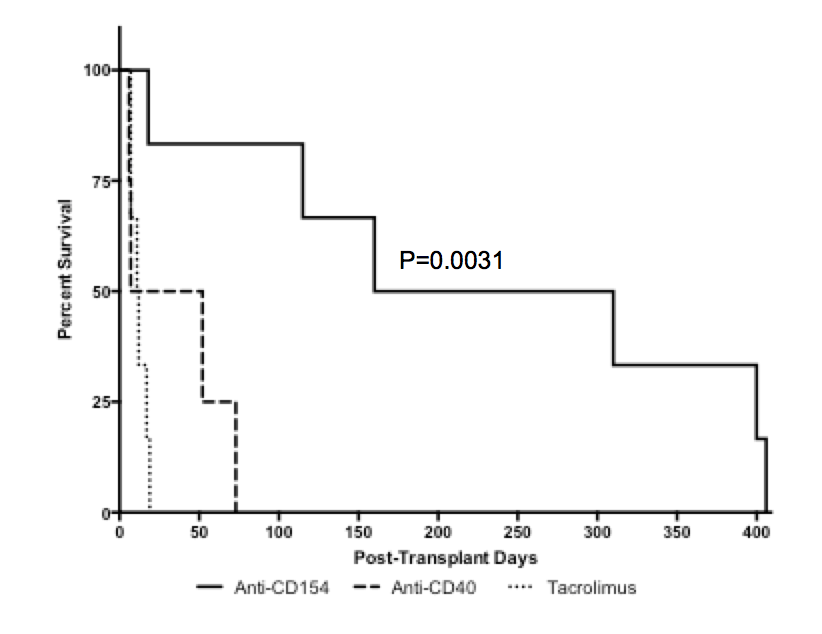
*Results: Recipients treated with anti-CD154 therapy (n=6) experienced the longest survival (MST=235 days, p=0.0031), including three rhesus macaques with survival over 300 days (406, 400, 310 days). Recipients treated with anti-CD40 therapy (n=4) exhibited a moderate prolongation in survival (MST=29.5 days) whereas tacrolimus-treated recipients (n=6) experienced the shortest survival (MST = 11.5 days). Graft failure was associated with an increase in serum creatinine.
*Conclusions: Here we demonstrate that immunosuppression with anti-CD154 or anti-CD40 therapy is associated with prolonged survival of kidney xenografts relative to tacrolimus in a porcine-to-NHP xenotransplantation model. These data provide further rationale for clinical translation of these costimulation blockade reagents which demonstrate the strongest survival benefit for xenotransplant recipients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lovasik BP, Matar AJ, Breeden C, Jenkins J, Tector J, Kim SC, Adams AB. Anti- CD154 / CD40 Costimulation Blockade is Superior to Tacrolimus in Prolonging Survival in Pig-to-Nonhuman Primate Renal Xenotransplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/anti-cd154-cd40-costimulation-blockade-is-superior-to-tacrolimus-in-prolonging-survival-in-pig-to-nonhuman-primate-renal-xenotransplantation/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress