Histocompatibility Findings in the First Xenotransplants from a Pig to Deceased Human Recipient
Transplant Institute, NYU Langone Transplant Institute, New York, NY
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 82
Keywords: Histocompatibility, knockout, Pig, Xenoreactive antibodies
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 13 - Xenotransplantation
Session Information
Session Time: 3:30pm-5:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:20pm-4:30pm
Presentation Time: 4:20pm-4:30pm
Location: Hynes Room 302
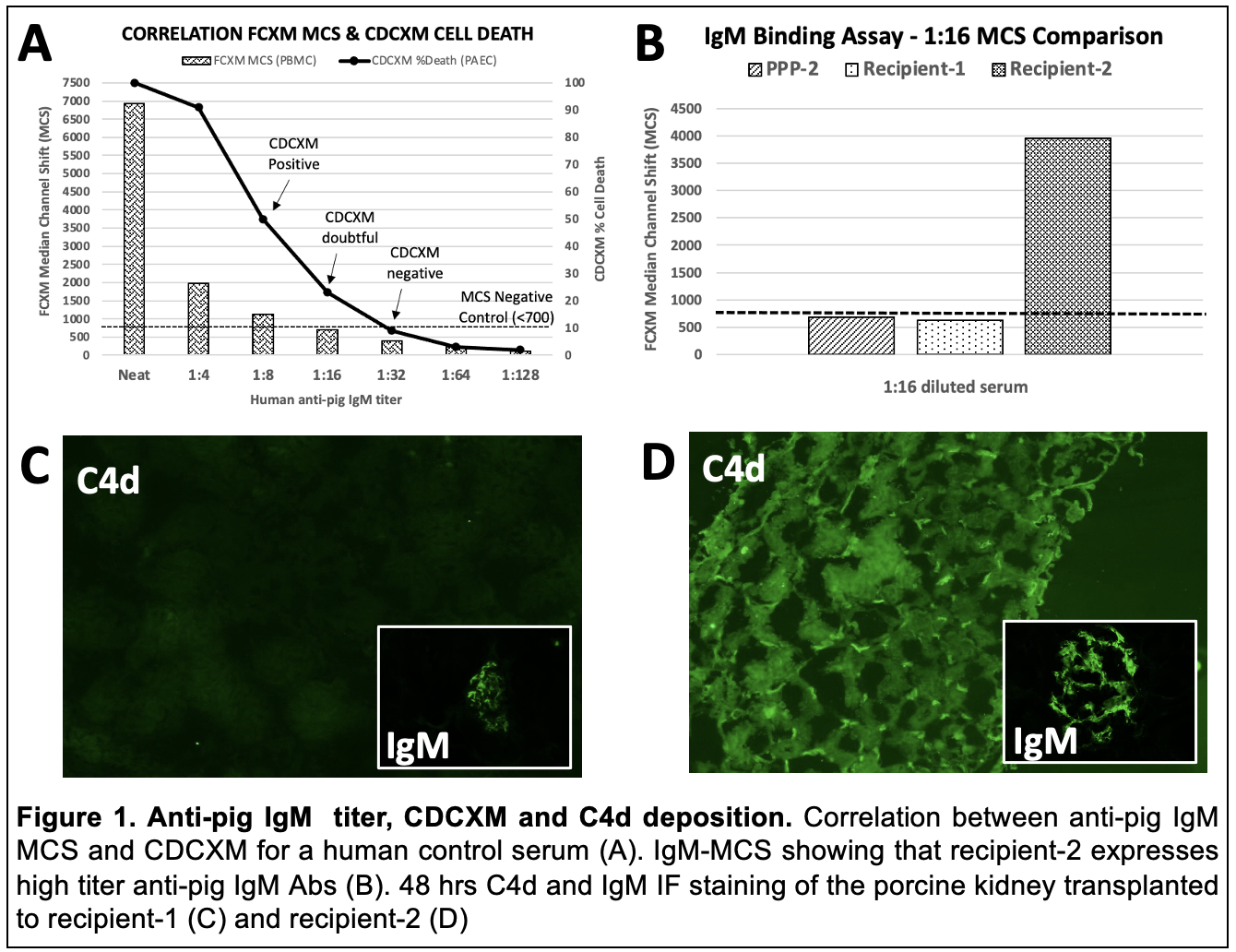
*Purpose: Humans lack α-1,3-Gal (α-gal) epitopes, and naturally occurring α-gal antibodies (Abs) cause hyperacute rejection of porcine xenografts. We conducted 2 successful xenotransplants in brain-dead decedents using kidneys from α1,3Galactosyltranserase knockout (GTKO) pigs. However, human sera may contain Abs reactive to other non-Gal epitopes with unknown in-vivo significance. We report the first in-vivo evidence in humans of the histologic phenotype of non-Gal anti-pig IgM Abs.
*Methods: We conducted 2 successful GTKO xenotransplants in decedents registered as research donors. Sera collected before transplant were tested for the presence of anti-pig IgM Abs by flow cytometry (FC) on pig PBMCs. To establish a correlation between FC and complement-dependent cytotoxicity crossmatch (CDCXM), a serially diluted positive control (PPP) was tested for the presence of anti-pig IgM Abs by FC on pig PBMC and by CDCXM on pig endothelial cells. The pre-transplant sera of both decedents were tested for the presence of anti-pig IgM Abs by FC, and the results compared to the observations from PPP. Biopsies of both porcine kidneys were assessed for C4d deposition by immunofluorescence (IF).
*Results: Testing on PPP indicate that anti-pig IgM Abs with FC median channel shift (MCS) <700 at 1:16 dilution correspond to a negative CDCXM on endothelial cells (Fig.1). Decedent’s sera were tested against the PBMCs of their pig donor at the same dilution. Recipient-1 MCS was +628, comparable to PPP and predictive of a negative CDCXM (Fig.1B). However, recipient-2 had a +3958 MCS, a 6.3-fold increase in IgM titer and predictive of a positive CDCXM (fig.1B). The 48 hrs C4d staining was significantly stronger in porcine kidney transplanted to recipient-2 (Fig.1D) compared to kidney transplanted to recipient-1 (Fig.1C). However, in both recipients there was no histologic evidence of acute AMR (ptc-itis, vasculitis, or glomerulitis), a phenotype that has been seen in human ABO-incompatible transplants.
*Conclusions: Our study demonstrates that strong non-Gal anti-pig IgM Abs in human recipients predict C4d deposition on kidney xenografts. However, C4d deposition does not correlate with histologic findings of acute AMR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mangiola M, Tatapudi V, Stern J, Lewis ZStewart, Lonze B, Ali N, Montgomery R. Histocompatibility Findings in the First Xenotransplants from a Pig to Deceased Human Recipient [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/histocompatibility-findings-in-the-first-xenotransplants-from-a-pig-to-deceased-human-recipient/. Accessed February 9, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress