iNKT Cell Activation Plus Veto Cell Transfer Yields Complete Chimerism in a Murine Sub-Lethal Bone Marrow Transplant Model.
1Department of Urology, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan
2Cluster for Industry Partnerships (CIP), RIKEN, Yokohama, Japan
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A38
Keywords: Bone marrow transplantation, Graft survival, Graft-versus-host-disease, Tolerance
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Cellular & Bone Marrow Transplantation Session I
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, April 29, 2017
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall D1
Transplant tolerance induction makes it possible to preserve functional grafts for a lifetime without immunosuppressants. We have previously established a novel method for mixed chimera generation using sublethal irradiation, CD40-CD40L blockade (MR1), and iNKT cell activation with a liposomal α-galactosylceramide (lipo-aGC) in murine model. However, numerous bone marrow cells (BMCs) that are required to achieve stable chimerism make it difficult to apply this model for the clinical setting. Here, we implemented an alterativestrategy: additional transfer of donor T cells as veto cells to facilitate donor BMCs engraftment. B6 (H2b) BMCs (5 [times] 106) followed by lipo-aGC plus MR1 were administered to 3 Gy-irradiated BALB/c (H2d) recipient mice. Skin grafts from B6 and C3H (H2k) mice were transplanted on the recipient mice. In this number of BMCs, all mice rejected both B6 and C3H grafts. However, when 5 [times] 105 splenic T cells obtained from an H2b+GFP-Tg donor were administered, complete chimerism was established and the skin allograft were accepted permanently in an H2b-specific manner, even with one-fourth of the BMCs used in our original method. The complete chimeric mice did not show any characteristics of graft versus host reaction in vivo and in vitro. The transferred GFP+ T cell population expanded as CD8+ T cells, showing veto cell-like characteristics, and expressed CCR7, LFA1 and FasL. Since veto CD8+ T cells induce apoptosis in donor-reactive host CD8+ T cells through the phosphorylation of MAPK/ERK, we administered an ERK1/2 inhibitor before BMT. The blockade of MAPK/ERK signaling resulted in increase in the number of host-derived CD8+ T cells and chimerism brake. Moreover, only donor-derived splenic CD8+ T cells, but not donor CD4+ or third party-derived T cells, could contribute to the establishment of complete chimerism in our model. These results indicate that donor-derived splenic CD8+ T cells having veto activity play a role in the depletion of host-derived CD8+ T cells and the facilitation of complete chimerism.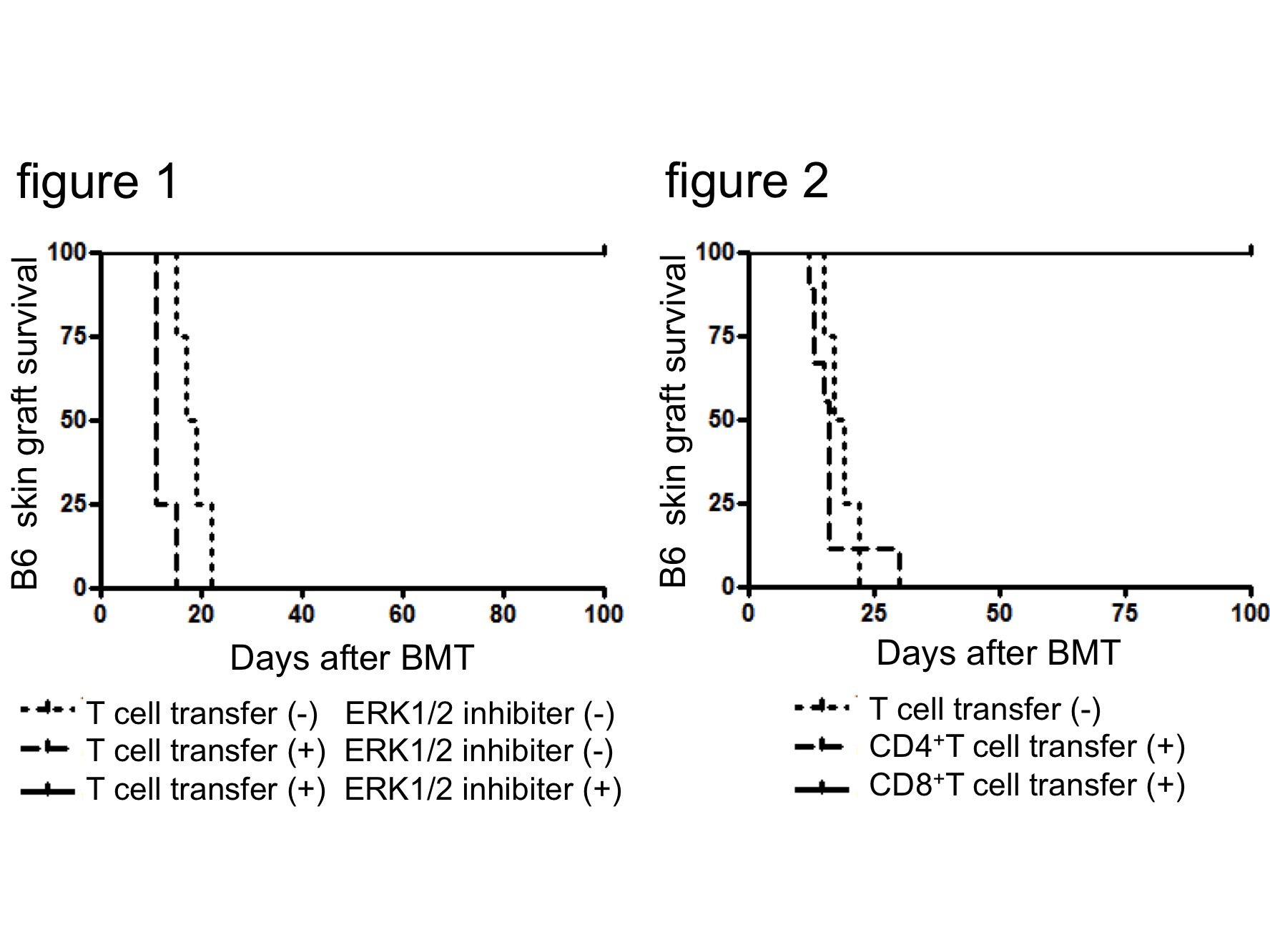
CITATION INFORMATION: Ishii R, Hirai T, Ishii Y, Okumi M, Tanabe K. iNKT Cell Activation Plus Veto Cell Transfer Yields Complete Chimerism in a Murine Sub-Lethal Bone Marrow Transplant Model. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ishii R, Hirai T, Ishii Y, Okumi M, Tanabe K. iNKT Cell Activation Plus Veto Cell Transfer Yields Complete Chimerism in a Murine Sub-Lethal Bone Marrow Transplant Model. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/inkt-cell-activation-plus-veto-cell-transfer-yields-complete-chimerism-in-a-murine-sub-lethal-bone-marrow-transplant-model/. Accessed February 21, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
