Vendor-Specific Differences in Identical Strains of Mice Yield Dichotomous Result in Lung Allograft Rejection
Surgery, University of Virginina, Charlottesville, VA
Surgery, Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A425
Keywords: Lung transplantation, Rejection, T cells, Tolerance
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Tolerance / Immune Deviation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 2, 2018
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Intro: Orthotropic transplantation of murine lung allografts has paved the way for mechanistic studies of pulmonary tolerance and rejection but discrepancies have been reported by different groups.
Methods: We investigated the immune responses to minor antigen mismatched B10 to B6 lung transplants with donors and recipients obtained either from Jackson Labs or Envigo (formerly known as Harlan). Left single lung orthotropic transplants were performed as previously described and immune responses analyzed.
Results: Higher ISHLT histologic rejection grade was evident for B10 grafts from either Envigo or Jackson when transplanted into B6 Jackson recipients. B10 lung grafts transplanted into Envigo B6 recipients virtually free of inflammation.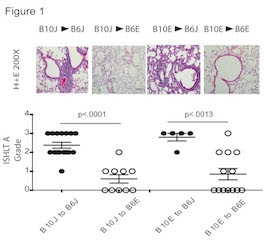 More CD8+, CD4+ T cells as well as CD4-CD8- T cells were evident in grafts of Jackson recipients.
More CD8+, CD4+ T cells as well as CD4-CD8- T cells were evident in grafts of Jackson recipients. 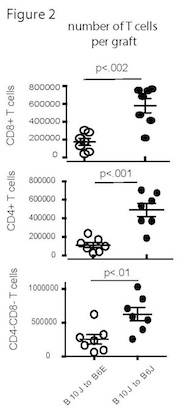 A higher proportion of regulatory T cells expressing the transcription factor Foxp3 (19.7+/-3.5 vs. 8.3+/1.7% p<.01) were evident in Enviro-derived mice explaining decreased inflammatory changes. Both CD4+ T cells and gamma delta T cells expressed Th17 polarization in Envigo recipient mice. As TGF-beta contributes to both Treg generation and Th17 polarization we next measured the levels of this cytokine in B6 mice from Envigo and Jackson Labs and defined a trend for higher TGF beta levels in Envigo mice (2.8+/- 0.09 vs 2.3+/- 0.2 pg/mg).
A higher proportion of regulatory T cells expressing the transcription factor Foxp3 (19.7+/-3.5 vs. 8.3+/1.7% p<.01) were evident in Enviro-derived mice explaining decreased inflammatory changes. Both CD4+ T cells and gamma delta T cells expressed Th17 polarization in Envigo recipient mice. As TGF-beta contributes to both Treg generation and Th17 polarization we next measured the levels of this cytokine in B6 mice from Envigo and Jackson Labs and defined a trend for higher TGF beta levels in Envigo mice (2.8+/- 0.09 vs 2.3+/- 0.2 pg/mg).
Summary: We now demonstrate that B6 recipient mice from different vendors manifest divergent immune responses to identical lung allografts. Our data can partially explain differences in acute and chronic rejection between different laboratories and provides an experimental platform to manipulate the immune response in different animal models.
CITATION INFORMATION: Guo Y., Wang Q., Onyema O., Gelman A., Kreisel D., Krupnick A. Vendor-Specific Differences in Identical Strains of Mice Yield Dichotomous Result in Lung Allograft Rejection Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Guo Y, Wang Q, Onyema O, Gelman A, Kreisel D, Krupnick A. Vendor-Specific Differences in Identical Strains of Mice Yield Dichotomous Result in Lung Allograft Rejection [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/vendor-specific-differences-in-identical-strains-of-mice-yield-dichotomous-result-in-lung-allograft-rejection/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
