The Increase of Serum MiR-142-3p Level in Acute Cardiac Rejection as a Reflection of Exosome-Mediated Genetic Exchange Between T Cells and Endothelial Cells.
1Cardiology, Lund University, Lund, Sweden
2PROOF Center of Excellence, Vancouver, Canada.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B9
Keywords: Graft failure, Heart/lung transplantation, T cell activation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Allograft Rejection, Tolerance, and Xenotransplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Introduction
In the recent years, microRNAs has emerged as the popular biomarker candidate in the field of solid organ transplantation due to their expression patterns reflect both physiological underlying pathological conditions in humans. It is known from the previous study that immune cells are communication experts that exchange information in several ways. Recent evidence reveals that miRNA transport is a new way in cell communication and that genetic exchange of miRNA in T cells can be accomplished through exosome-mediated transfer.
Methods
This study included heart transplant recipients with biopsy-proven acute rejection (n = 26) and without rejection (n = 38) from 6 Canadian transplant centers. Each local research ethics board approved the study. We assessed the expression of miR-142-3p from the serum samples of each patients groups by extracting the RNA and performing qPCR Analysis on Pick and Mix microRNA PCR Panel. For the in vitro experiment, we collected PBMC (Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells) from healthy volunteer donors (n = 6) and stimulated them using human T cells mitogen, phytohemagglutinin (PHA). HUVEC cells was used to study uptake mechanism of miR-142-3p by endothelial cells.
Results
MiR-142-3p level was increased in the serum samples of heart-transplanted patients with acute rejection and the in vitro activation of PBMC showed the release of miR-142-3p 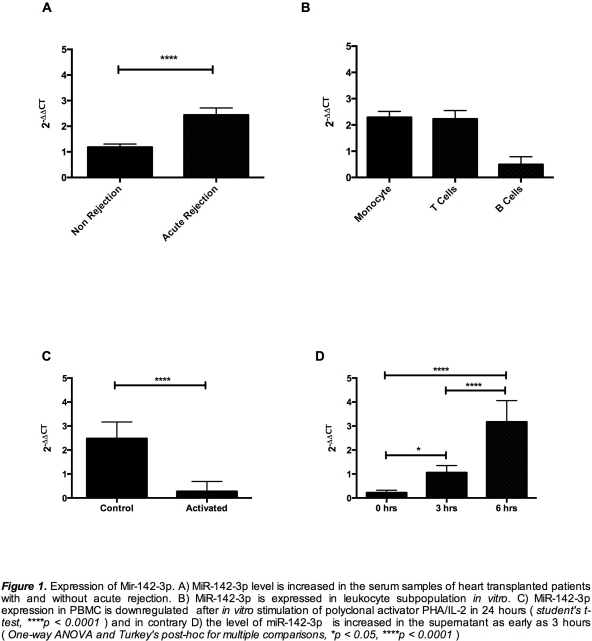
Under inflammatory activation, MiR-142-3p was transported from T cells to endothelial cells, mediated by exosomes 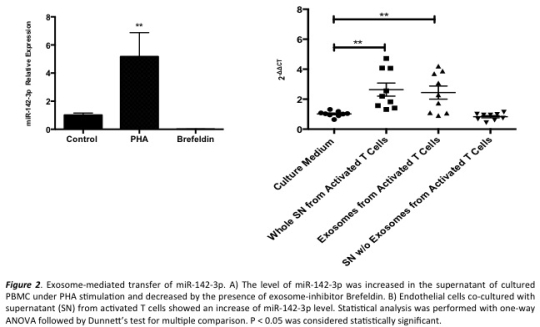 .
.
Conclusion
Serum miR-142-3p level increased during acute cardiac rejection. The increase of circulating microRNA was a reflection of exosome-mediated microRNA transport between T cells and endothelial cells.
CITATION INFORMATION: Dewi I, Hollander Z, McManus B, Gidlöf O, Öhman J. The Increase of Serum MiR-142-3p Level in Acute Cardiac Rejection as a Reflection of Exosome-Mediated Genetic Exchange Between T Cells and Endothelial Cells. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dewi I, Hollander Z, McManus B, Gidlöf O, Öhman J. The Increase of Serum MiR-142-3p Level in Acute Cardiac Rejection as a Reflection of Exosome-Mediated Genetic Exchange Between T Cells and Endothelial Cells. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-increase-of-serum-mir-142-3p-level-in-acute-cardiac-rejection-as-a-reflection-of-exosome-mediated-genetic-exchange-between-t-cells-and-endothelial-cells/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
