Successful Induction of Hematopoietic Chimerism by Dual Inhibition of Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 Without Myeloablative Treatments in Nonhuman Primates
Center for Transplantation Sciences, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 263
Keywords: Bone marrow transplantation, Mixed chimerism, Skin transplantation, Tolerance
Session Information
Session Name: Lymphocyte Biology and Tolerance
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Monday, June 7, 2021
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:30pm-6:35pm
Presentation Time: 6:30pm-6:35pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Induction of hematopoietic chimerism by donor bone marrow transplantation (BMT) is essential for achievement of allograft tolerance in clinical HLA mismatched kidney transplantation, while myelosuppressive toxicity of the radiation is yet to be solved. We have recently found that chimerism can be achieved with minimal total body irradiation in nonhuman primates (NHPs) by inhibiting Bcl-2 (anti-apoptotic protein) with Venetoclax (ABT-199). However, a minimal dose of TBI was still required for chimerism induction. Since Mcl-1, another member of the Bcl-2 family proteins, is highly expressed in hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) in bone marrow (BM), we hypothesized that Mcl-1 inhibition might delete the host HSC niche, thus facilitating donor bone marrow engraftment without TBI requirement.
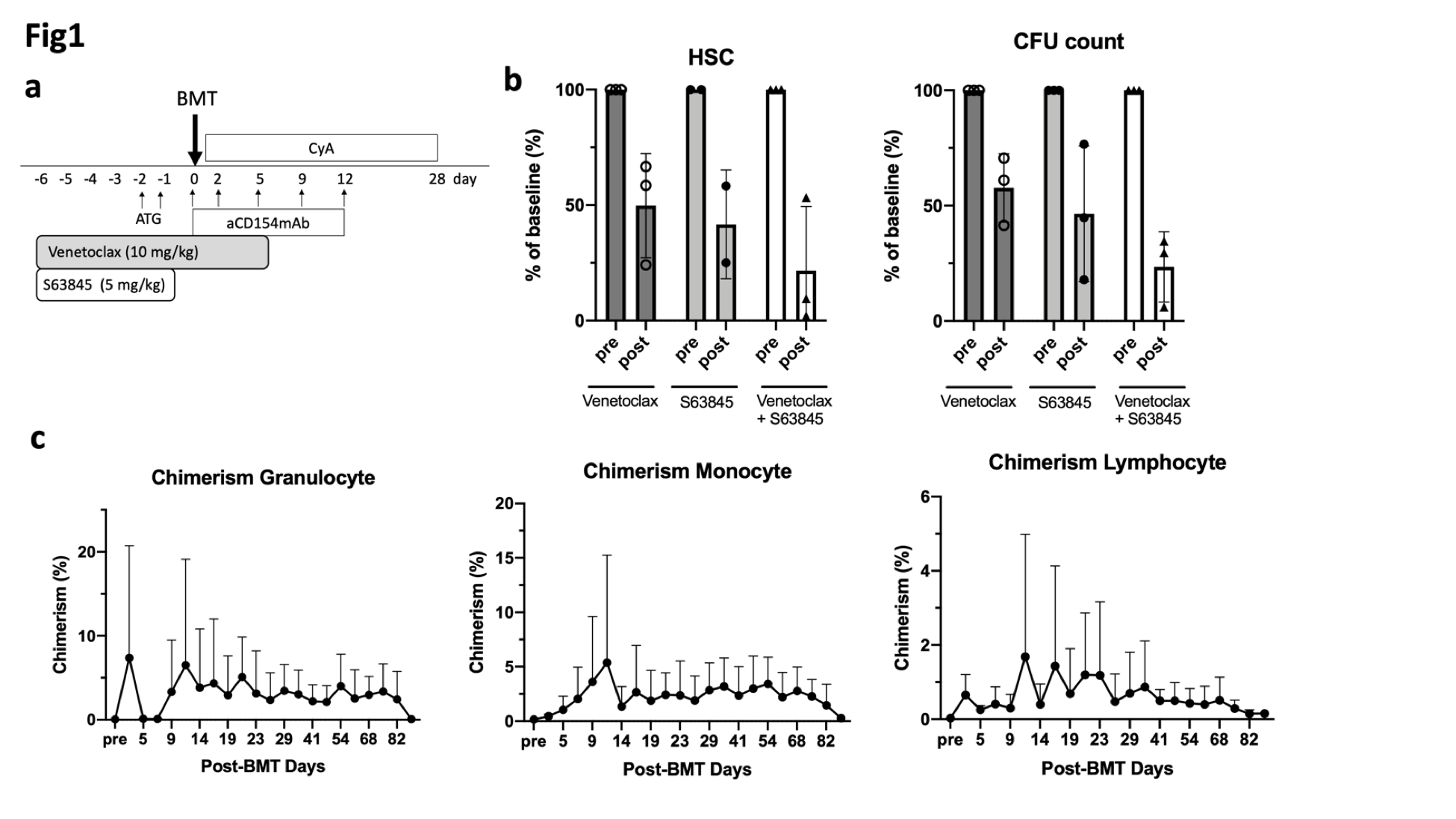
*Methods: HSC (CD34+CD90+CD45RA-) counts and Colony Forming Units (CFU) of BM aspirates were measured after treatment with ABT-199 (10mg/kg X11) alone (n=3), Mcl-1 inhibitor (S63845, 5mg/kg X 5) alone (n=3), or combination of both (n=3). In three recipients treated with the combination of S63845 and ABT-199, BMT from the MHC mismatched donor was performed. All BMT recipients were also treated with ATG (3 doses pre-transplant) and anti-CD154 and a 28 day-course of cyclosporine (CyA), all of which were included in our standard BM conditioning for NHPs (Fig. 1a). One NHP underwent skin transplantation after BMT.
*Results: Monotherapy of ABT-199 or S63845 depleted CD34+ BM cells to 50 ± 13% and to 42±17% of pre-treatment levels, respectively. CFUs were also suppressed to 58 ± 8.6% and to 46 ± 17%, respectively. Combining ABT-199 with S63845 depleted more HSCs (22 ± 11%) with near complete depletion in two animals. CFUs were also effectively suppressed to 23 ± 8%(Fig. 1b). Since dual inhibition of both Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 most effectively depleted HSCs, BMT was perfomred using the combination of S63845 and ABT-199 (Fig. 1a). After conditioning, all recipients successfully developed multilineage chimerism, which lasted for 3 months (Fig. 1c) despite discontinuation of CyA at one month. Transplanted donor skin was engrafted, while two grafts from different third-party were rejected.
*Conclusions: Dual inhibition of Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 effectively depleted BM HSC, leading to successful hematopoietic chimerism induction without myeloablative treatments and donor-specific tolerance. This approach may set the path for the development of a novel and clinically applicable protocol for induction of hematopoietic chimerism without myeloablative treatments.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hirose T, Ma D, Lassiter G, Kawai T. Successful Induction of Hematopoietic Chimerism by Dual Inhibition of Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 Without Myeloablative Treatments in Nonhuman Primates [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/successful-induction-of-hematopoietic-chimerism-by-dual-inhibition-of-mcl-1-and-bcl-2-without-myeloablative-treatments-in-nonhuman-primates/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress