Single-cell Transcriptomic Analysis Of Peripheral Blood Reveals The Disparate Subsets Of Innate Immune Cells In Kidney Transplant Recipient With BK Virus Infection
1Department of Biomedical Science, Graduate School, College of medicine, The Catholic university of Korea, Seoul, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s hospital, the Catholic University of Korea, seoul, Korea, Republic of, 3Catholic University Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul 137-040, Korea, Republic of
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 9079
Keywords: Genomic markers, Kidney transplantation, Nephropathy, Renal dysfunction
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Clinical Science » 17 - Biomarkers: Clinical Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers: Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: BK virus (BKV) infection is a common problem in kidney transplant recipients receiving immunosuppressive therapy, resulting in a serious complications including BKV-associated nephropathy and subsequent allograft loss. The purpose of this study was to characterize the disparate blood subsets in BKV infection/nephropathy at the single-cell transcriptional level.
*Methods: We isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells from three kidney transplant recipients with stable status, BK viremia and BK nephropathy. Single-cell libraries were generated using the 10x Genomics Chromium Platform. We analyzed multiplexing data in Cell-Ranger Pipeline and used R and “Seurat” packages for downstream analysis.
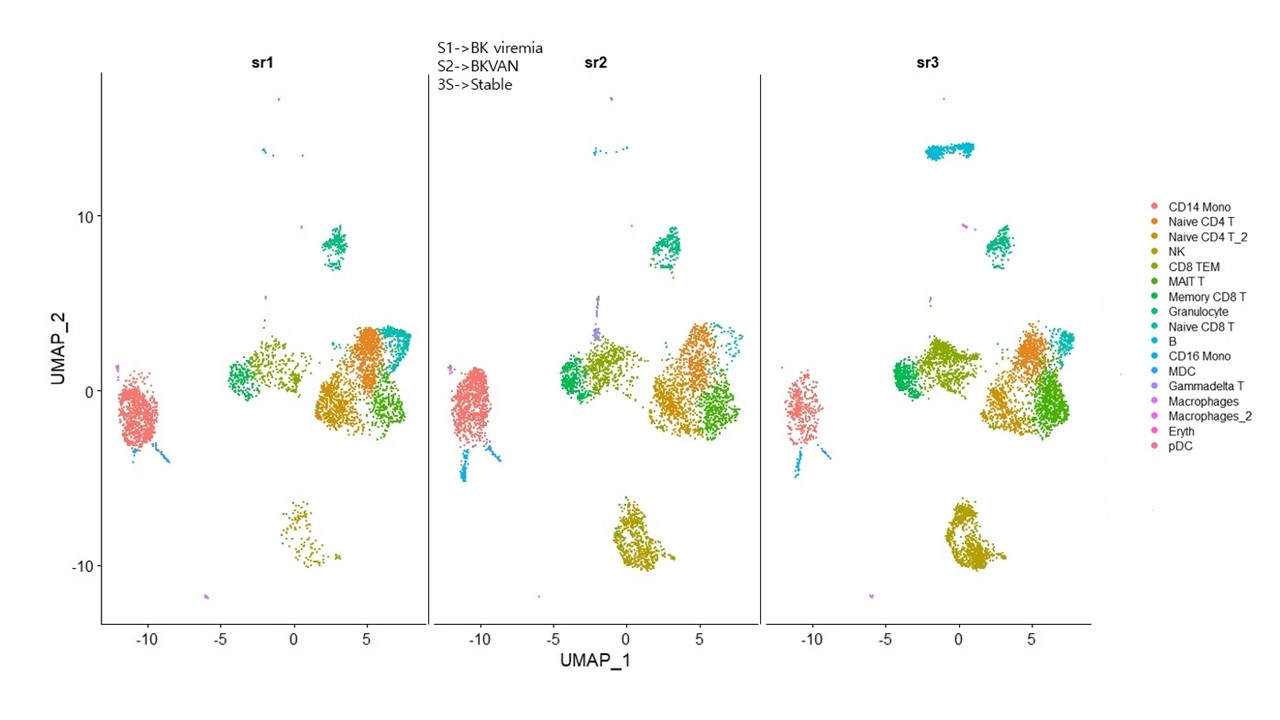
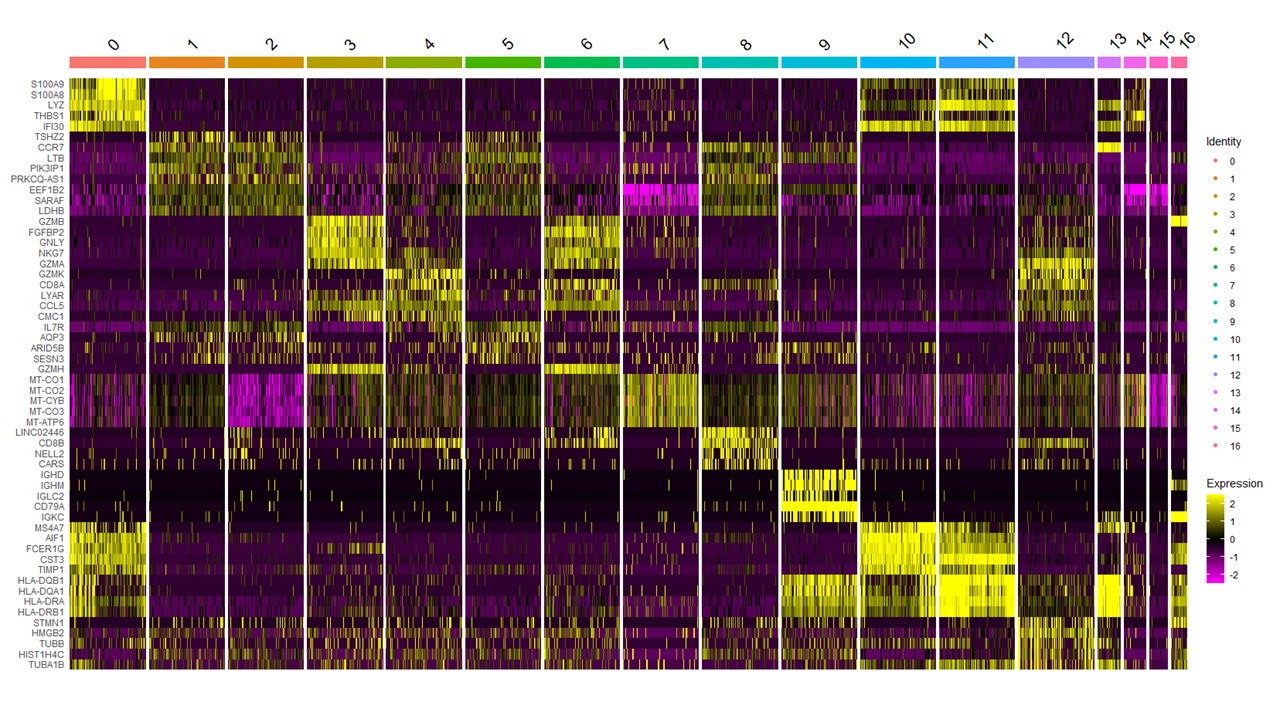
*Results: A total of 14,031 cells were analyzed, including 5473 cells from stable patients, 3976 cells from patients with BK viremia, and 4582 cells from patients with BK nephropathy obtained from Illumina HiSeq X. We characterized 17 distinct clusters representing different cell types. Of these, 13 clusters had differentially expressed transcripts for each sample, and the most differentially expressed markers were S100A8, CCR7, LTB, GNLY, GZMK, GZMH, MT-CO1, LINC02446, IGKC, AIF1, HLA-DRA, STMN1. Stable patient had more mRNA upregulated in B cells compared to patients with BK virus infection. In BK viremia, NK cells and monocytes were downregulated, whereas in BK nephropathy, mRNA expression was high in gamma delta T cells.
*Conclusions: Our study revealed that BK virus infection/nephropathy induce unique characteristics in lymphocytes, which could be confirmed through single-cell RNA analysis. Further studies are needed to characterize the innate immune cells involved in the progression of BK nephropathy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
BAE H, Ryu J, Jang J, Lee J, Ko G, PARK H, Oh E. Single-cell Transcriptomic Analysis Of Peripheral Blood Reveals The Disparate Subsets Of Innate Immune Cells In Kidney Transplant Recipient With BK Virus Infection [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/single-cell-transcriptomic-analysis-of-peripheral-blood-reveals-the-disparate-subsets-of-innate-immune-cells-in-kidney-transplant-recipient-with-bk-virus-infection/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress