Single Cell Sequencing of Human Kidney Allograft
1Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, 2Rockefeller University, New York, NY
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 34
Keywords: Biopsy, Gene expression, Graft function, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Technical
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:42pm-2:54pm
Presentation Time: 2:42pm-2:54pm
Location: Room 304
*Purpose: Transcriptome-based clustering of individual cells within the kidney allograft may help identify cell type-specific injury and has the potential to redefine the current histopathology-based classification of allograft rejection/injury.
*Methods: We obtained kidney tissue at the time of core needle biopsy from 3 subjects; 1 healthy kidney donor and 2 kidney allograft recipients (NK1-donor biopsy prior to transplantation, TK1-allograft biopsy with minimal/non-specific biopsy findings 9 mo after active antibody mediated rejection, and TK2-allograft biopsy with transplant glomerulopathy and fibrosis 42 months after transplantation). We digested the biopsy tissues and generated single cell suspensions. We used droplet-based 10X Chromium platform (10X Genomics) to capture single cells in emulsion, followed by cDNA synthesis, sequencing, and data analysis.
*Results: We obtained 2813 (NK1), 2657 (TK1), and 2207 (TK2) high-quality scRNA-seq profiles and identified 13, 13, and 11 major cell clusters, respectively (Figure 1)
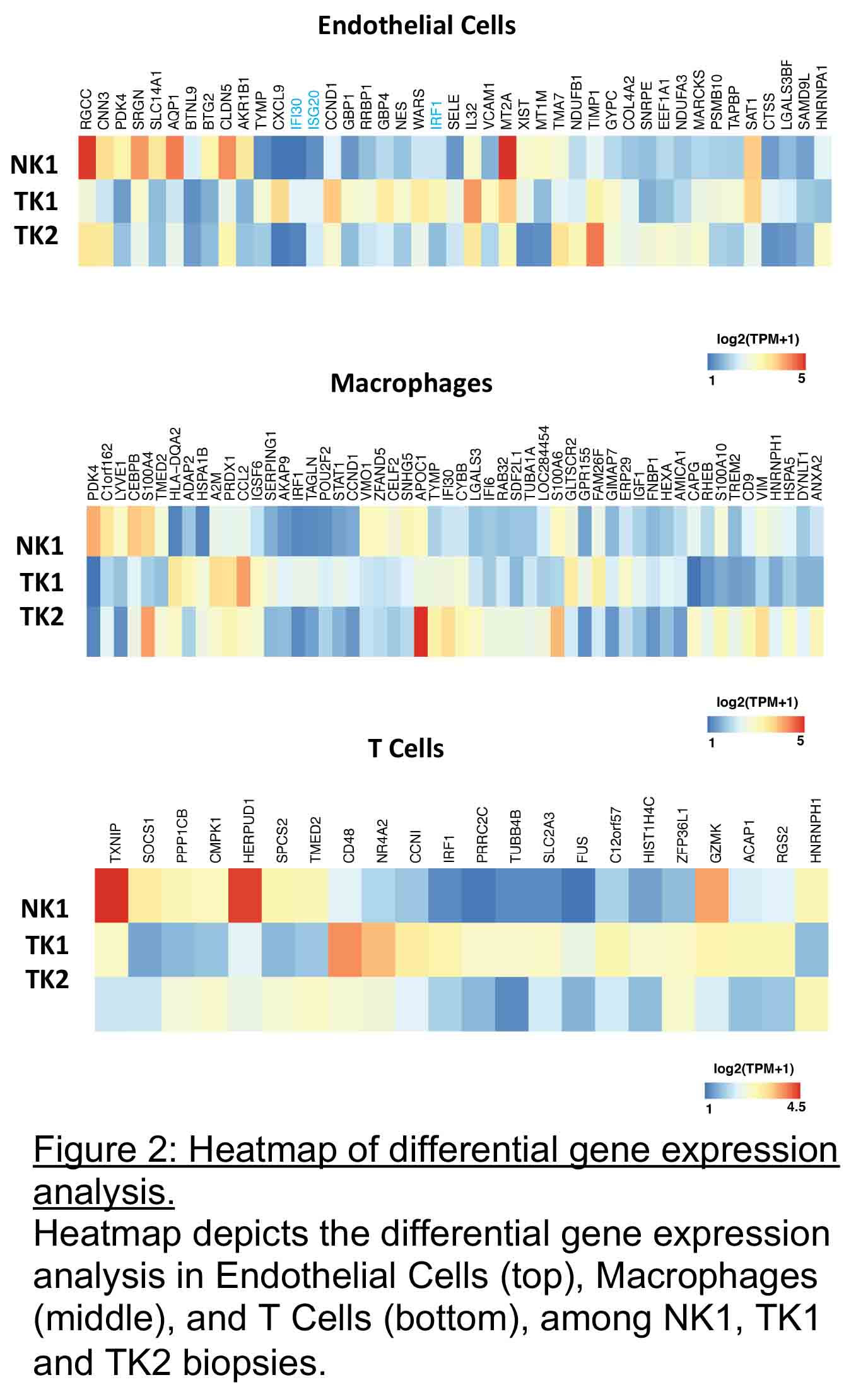
In both biopsies, T cells (27% TK1 and 24% TK2) were abundant despite the differences in histopathology findings. In TK1, infiltrating immune cells constituted more than 50% of the cells. Compared to NK1, TK1 showed altered gene expression pattern in endothelial cells and T cells whereas TK2 showed altered gene expression in macrophages (Figure 2)
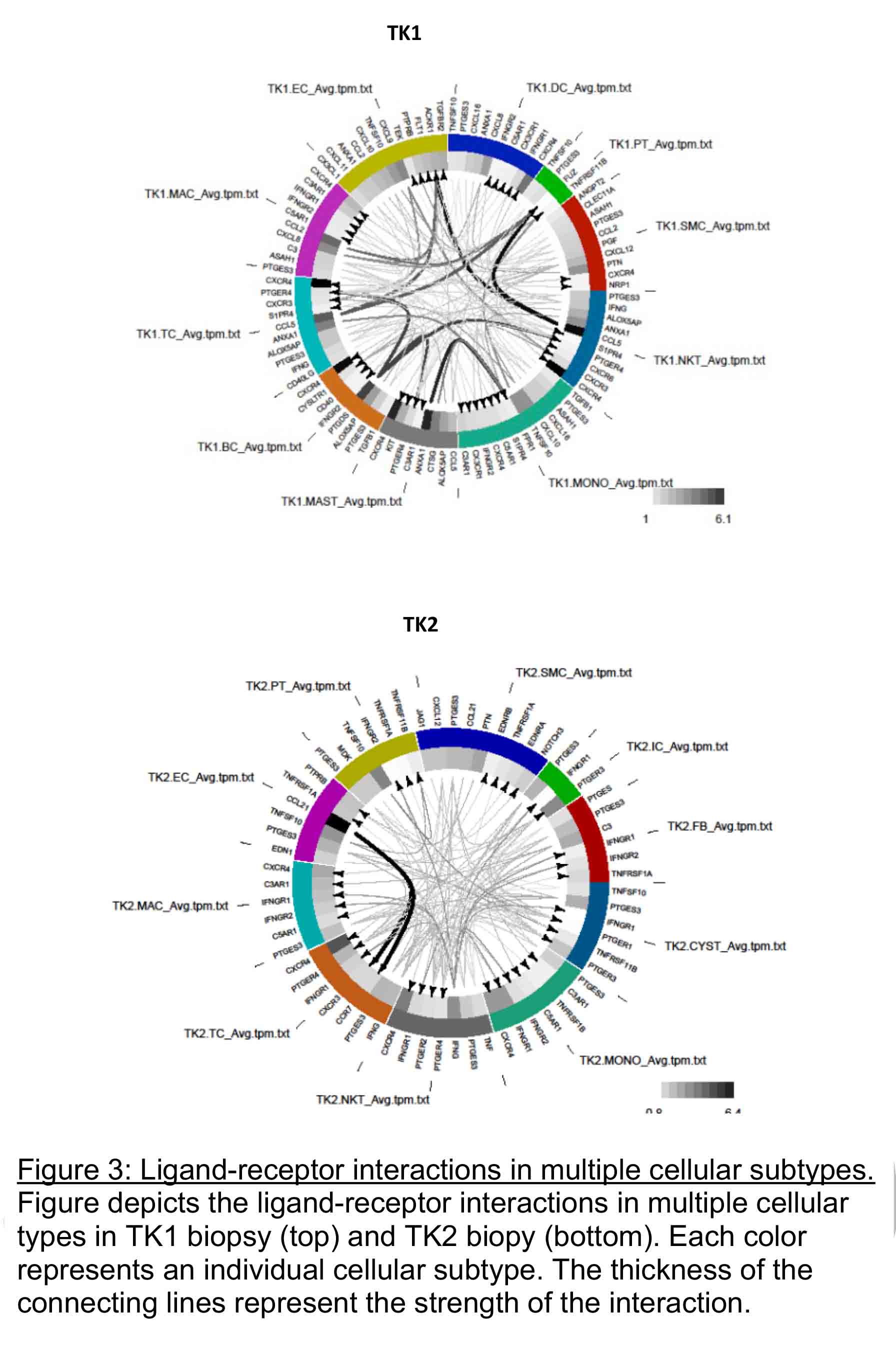
Analysis of ligand-receptor interactions revealed increased cellular activity in multiple cellular subtypes in TK1 (Figure 3)
*Conclusions: Our single cell expression atlas of human kidney allograft has deciphered the complex cellular microenvironment of kidney allograft. Single cell RNA sequencing is a valuable technique that provides a powerful step towards better understanding of the cellular basis of kidney allograft dysfunction.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yang H, Suryawanshi H, Lagman M, Lubetzky M, Alonso A, Seshan S, Tuschl T, Suthanthiran M, Muthukumar T. Single Cell Sequencing of Human Kidney Allograft [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/single-cell-sequencing-of-human-kidney-allograft/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress