Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Identifies the Changes of Human Normal Kidney After Transplantation
1Organ Transplant Center, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China, 2Department of Pathology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1298
Keywords: Gene expression, Inflammation, Kidney transplantation, T cell activation
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 16 - Biomarkers: -omics and Systems Biology
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers: -omics and Systems Biology
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: We found that in all studies about kidney transplantation and single cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), the native kidney rather than the transplanted kidney was used as a control. However, there are huge differences between the native kidney and the transplanted kidney. scRNA-seq was used to explore the difference between native kidney and stable transplanted kidney.
*Methods: scRNA-seq profiles were generated from two samples of normal transplanted kidney and matched with 6 native kidney data. Cell-cell communication analysis, trajectory analysis, and gene-set variation analysis were used to explore the difference of proximal tubule (PT) cells, T cells and macrophages. The expression of NR4A1, WARS1, JUND, ALDH2 was identified by immunohistochemistry.
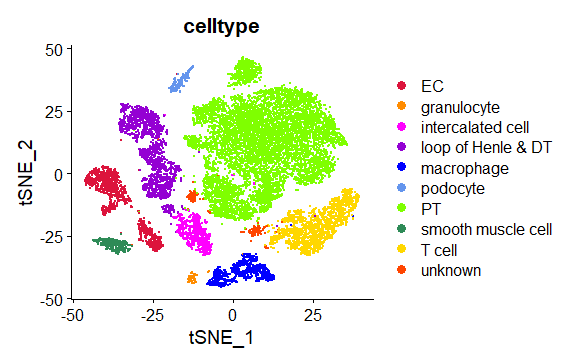
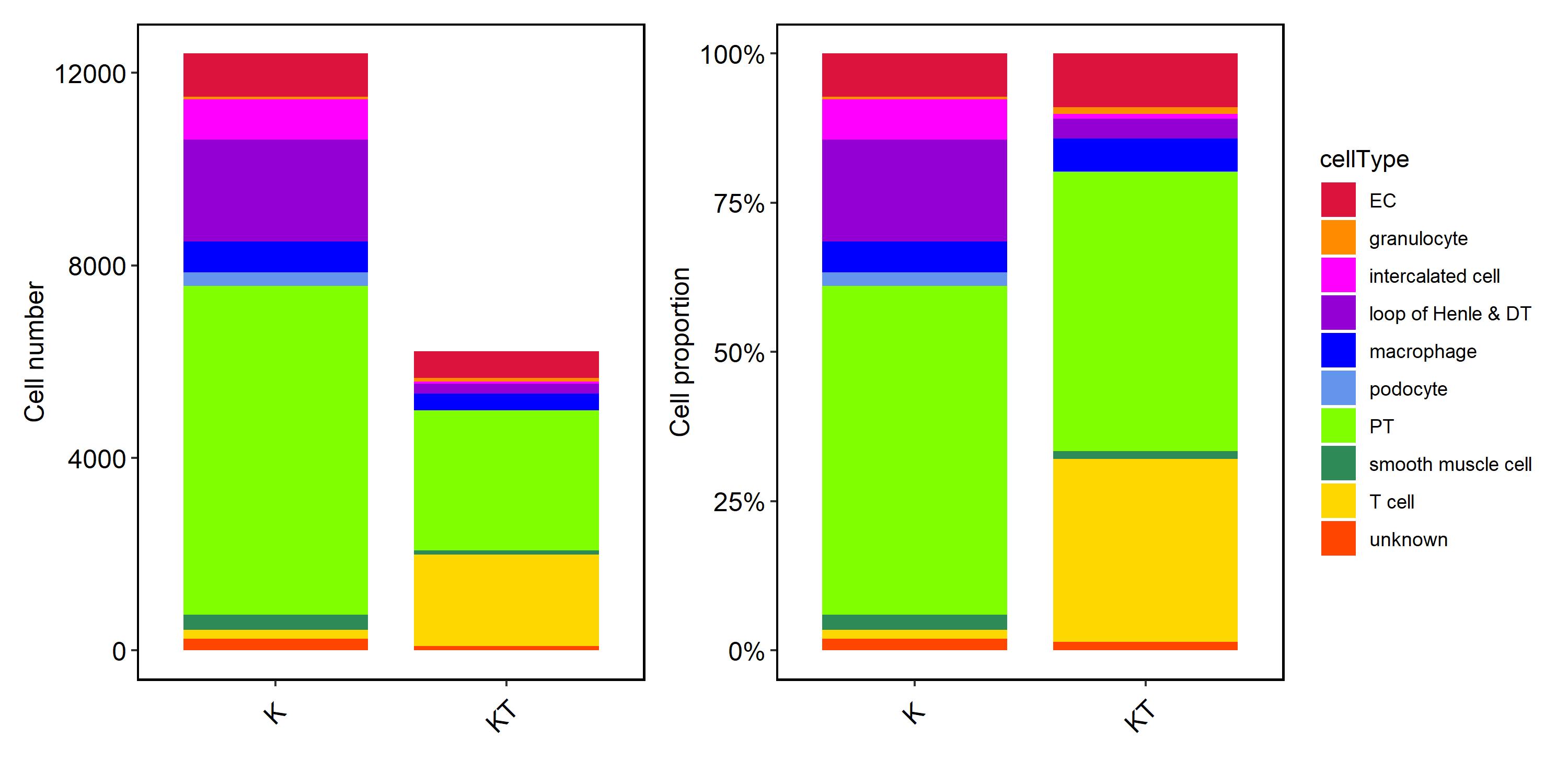
*Results: Nine main cell clusters were identified, including endothelial cells (EC), granulocyte, intercalated cell, PT cells, loop of Henle & distal tubule (DT), NK/T cells, mononuclear/macrophages, smooth muscle cells, podocytes. Intercellular and Molecular Interactions elevate in stable transplanted kidney. T cells increased in stable transplanted kidney and NKT cells accounted for the largest proportion. NR4A1, WARS1, JUND content increased and WNT signaling pathway, Jak-STAT signaling pathway and signal of PRRs were activated in macrophage of the transplanted kidneys. PT cells in transplanted kidneys were involved in higher metabolism signaling with the increasing of ALDH2.
*Conclusions: Our study demonstrates the differences between normal transplanted kidney and native kidney in cell communication and gene enrichment, which need to be aware of when researching kidney transplant complications.
| Age | Sex | Time after surgery | eGFR(ml/min/1.73m2) | Proteinuria | Global glomerulosclerosis | Interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy | Arterial and arteriolar sclerosis |
| 28 | Male | 2 months | 46.35 | No | No | 5% | No |
| 36 | Female | 2 months | 88.75 | No | 1/9 | 5% | No |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Huang G, Zhang H, Chen X, Zhao G, Luo J, Yang S, Qiu J. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Identifies the Changes of Human Normal Kidney After Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/single-cell-rna-sequencing-identifies-the-changes-of-human-normal-kidney-after-transplantation/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress