Sialoadhesin Mediates the Adhesion of Human RBC to Porcine Macrophages from Genetically Engineered Pigs
1Center for Transplantation Sciences, Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, 2Revivicor, Blacksburg, VA, 3MassBiologics of UMMS, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A-275
Keywords: Immunogenicity, knockout, Leukocytes, Pig
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Xenotransplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: The sequestration of human RBC is prominent after liver and lung xenotransplantation. Rees et al previously implicated porcine sialoadhesin in adhesion of human RBC to WT pig macrophages in vitro and ex vivo. The role of this pathway in pigs lacking carbohydrate antigens, including the pig sialic acid Neu5Gc, has not previously been evaluated.
*Methods: Porcine alveolar macrophages were isolated from Wild Type (WT) GalTKO.hCD46, and TKO.hCD46.hCD55 (TKO: GalTKO, Neu5GCKO, β4GalKO) lungs and cultured in 96-well plates. Adherent macrophages were incubated with pig or human red blood cells alone, or in presence of a monoclonal antibody against porcine sialoadhesin antibody (1F1) or an isotype control antibody. Following incubation, wells were imaged to quantify the proportion of macrophages associated with erythrocyte rosetting (5-10 pictures/well at x10 magnification). The percentage of macrophages exhibiting erythrocyte rosetting (defined as >3RBC/mθ) was expressed as an average for each condition.
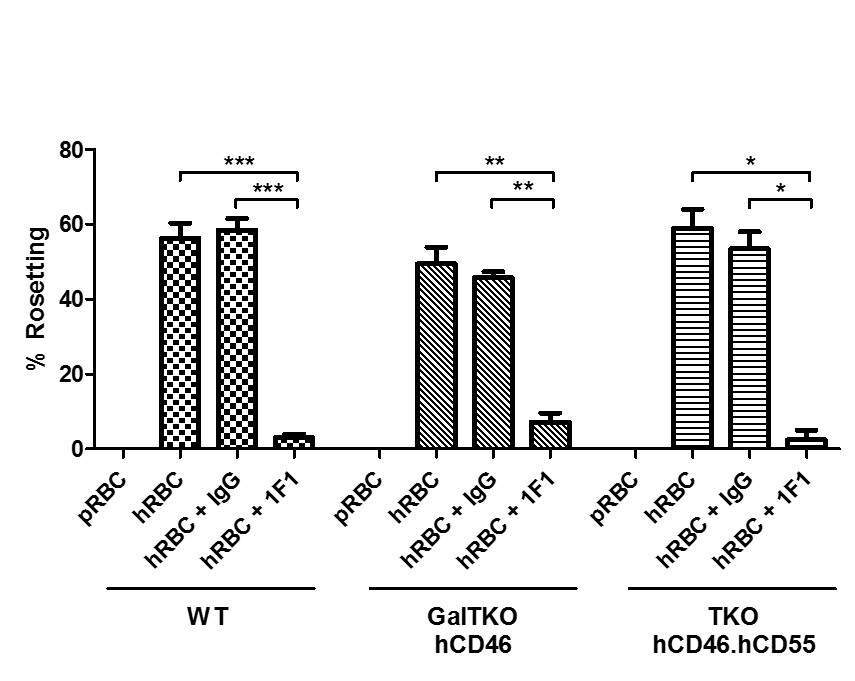
*Results: Pig RBC exhibited minimal adhesion to pig macrophages of all genotypes (allogeneic control; 0±0%). In contrast, a large proportion (56.3±4%) of WT macrophages formed rosettes with human RBC (Figure 1). Macrophages from genetically modified pigs exhibited similar levels (GalTKO.hCD46 49.5±4.4%, TKO 59±5%) of rosetting, not significantly different from WT. Rosetting was significantly abrogated (p<0.01) for all pig genotypes in presence of 1F1 relative to the isotype control Ab or no treatment, although some rosetting (2-8%) was still observed even at high 1F1 concentrations; no significant variation was observed between untreated and isotype control groups.
*Conclusions: Sialoadhesin mediates xenogeneic interactions between human erythrocytes and macrophages from pigs genetically modified to reduce antibody- and complement-mediated xenograft rejection. That macrophages in the presence of 1F1 are still able to form rosettes, albeit in small numbers, demonstrates residual binding via an alternate pathway. Current work is exploring a role for Fc-mediated adhesion as well as non-physiologic cross-species interactions between other pig lectins and their human ligand analogues.
Figure 1: Statistical significance was assessed using a two-tailed paired t test. *** = p<0.0001, ** = p<0.007, * = p≤0.01.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Petitpas K, Cerel B, Abady Z, Burdorf L, Ayares DL, Magnani DM, III RNPierson, Azimzadeh AM. Sialoadhesin Mediates the Adhesion of Human RBC to Porcine Macrophages from Genetically Engineered Pigs [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/sialoadhesin-mediates-the-adhesion-of-human-rbc-to-porcine-macrophages-from-genetically-engineered-pigs/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress