Regulatory T Cells Expanded by Activated iNKT Cells Facilitate Migration of Donor Dendritic Cells Into the Recipient Thymus and Subsequent Establishment of Clonal Deletion
1Department of Urology, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan
2Laboratory for Vaccine Design, RINEK Center for IMS, Yokohama, Japan.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 282
Keywords: Co-stimulation, Mixed chimerism, Thymic tolerance, Tolerance
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Immune Regulation and Graft Survival
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, May 4, 2015
Session Time: 4:00pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:12pm-5:24pm
Presentation Time: 5:12pm-5:24pm
Location: Room 119-B
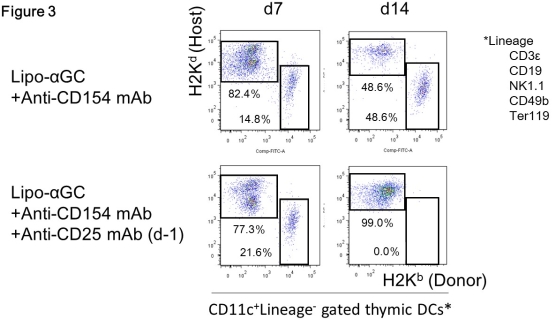
We previously reported that combination therapy using liposomal α-galactosylceramide (lipo-αGC) and anti-CD154 mAb could expand regulatory T cells (Tregs) in vivo through activation of the regulatory potential of invariant natural killer T cells and establish mixed hematopoietic chimerism in sublethally irradiated bone marrow (BM) transplant recipients. Although the importance of Tregs in our model has been demonstrated, the mechanism by which these Tregs established mixed chimerism is still elusive. In the current study, both euthymic and thymectomized (Tx) BALB/c mice were transplanted with C57BL/6 or AKR BM with lipo-αGC plus anti-CD154 mAb after 3-Gy total body irradiation. Tx recipients failed to establish mixed chimerism. CD8+ T cells isolated from chimeric mice and adoptively transferred into SCID mice that received donor and third-party skin grafts showed donor-specific hyporesponsiveness, whereas those from Tx mice did not (Fig. 1), suggesting that thymic deletion has an integral role in tolerance induction. Early engraftment of donor-derived dendritic cells (DCs) was observed in recipient thymi on day 7 and became robust on day 14 (Fig. 3) accompanied with a sequential reduction in donor-reactive Vβ-TCR repertoire (Fig. 2). Because Treg depletion precluded induction of chimerism and expansion of donor DCs in the thymus as well as the reduction in donor-reactive T cells, Treg help might be required for thymic donor DCs to expand and complete clonal deletion. Taken together, these data show that central tolerance could be established through peripheral mechanisms enhanced by lipo-αGC plus anti-CD154 mAb therapy.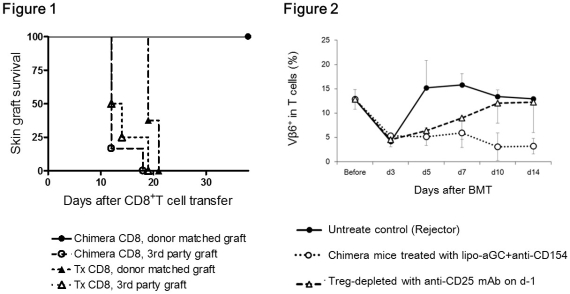
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hirai T, Shibahara R, Miyairi S, Ikemiyagi M, Omoto K, Ishii Y, Tanabe K. Regulatory T Cells Expanded by Activated iNKT Cells Facilitate Migration of Donor Dendritic Cells Into the Recipient Thymus and Subsequent Establishment of Clonal Deletion [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/regulatory-t-cells-expanded-by-activated-inkt-cells-facilitate-migration-of-donor-dendritic-cells-into-the-recipient-thymus-and-subsequent-establishment-of-clonal-deletion/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
