QSant, a Novel Urine Test Monitors Recovery of Allograft Injury After DGF
1Nephrosant, Brisbane, CA, 2Hospital do Rim, Sao Paolo, Brazil
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 653
Keywords: Immunogenicity, Inflammation, Kidney transplantation, Renal ischemia
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 14 - Ischemia Reperfusion
Session Information
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: We evaluate urine QSant assay to non-invasively monitor recovery of allograft injury, post delayed graft function(DGF).
*Methods: 65 HLA-DR matched, renal allograft recipients, on TAC/MMF/prednisone and no induction, had serial urine sampling for the multianalyte QSant assay(Yang et al., STM 2020). Sampling was across 8 visits over the initial 2 months post transplantation. 49% of the cohort had DGF; 12% had biopsy confirmed acute rejection(AR; 5 TCMR, 3 bAR, 0 ABMR). QSant measures 6 urinary biomarkers(cfDNA, methylated cfDNA, clusterin, total protein, creatinine and CXCL10) and provides a ML-based scaled(0-100) QScore for risk prediction of AR(QScore >32); immunequiescence is designated by a QScore <32. A QScore time-series analysis followed by PCA was done to explore biomarker contributions in patients with DGF, and graft function recovery over time.
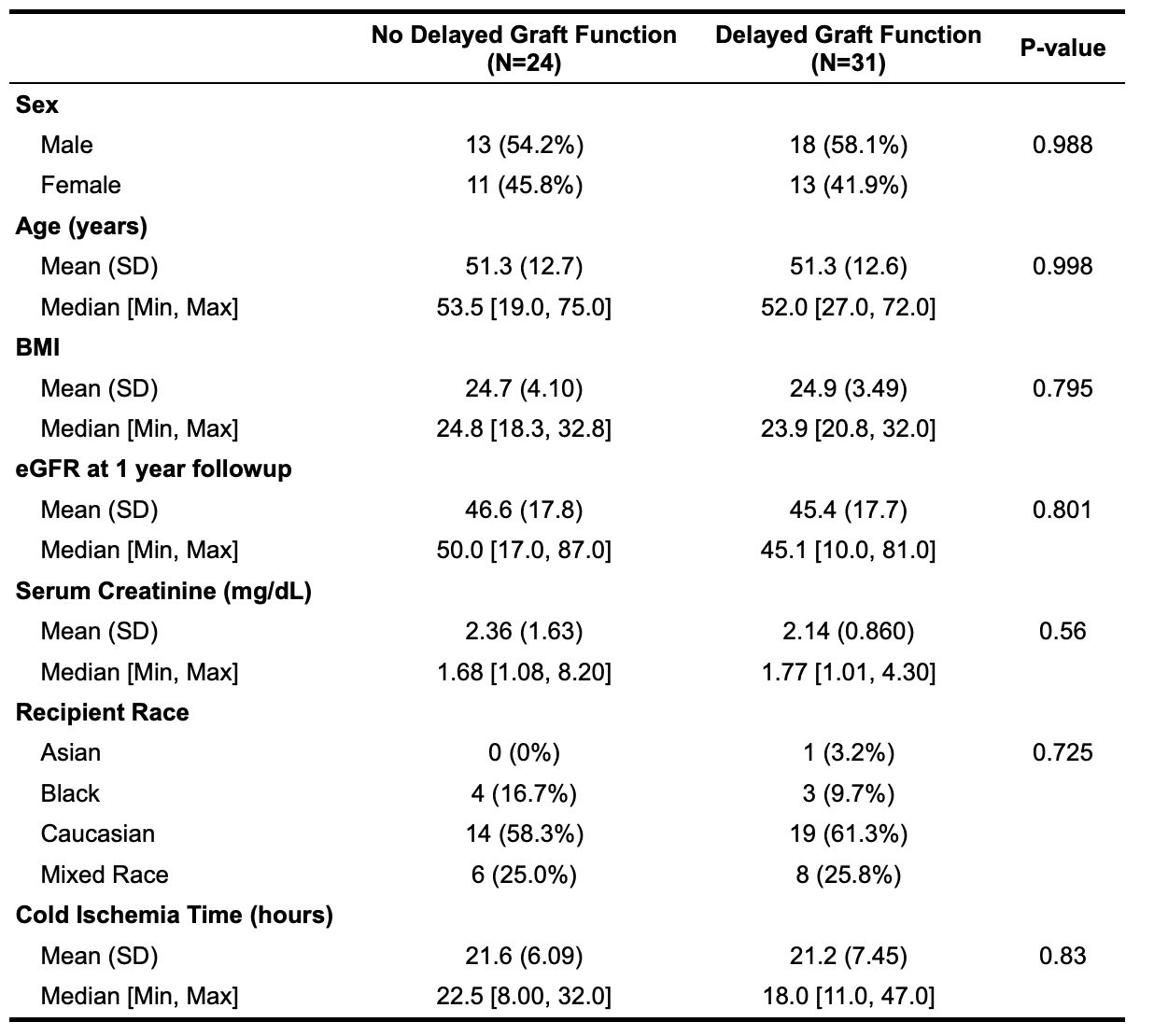
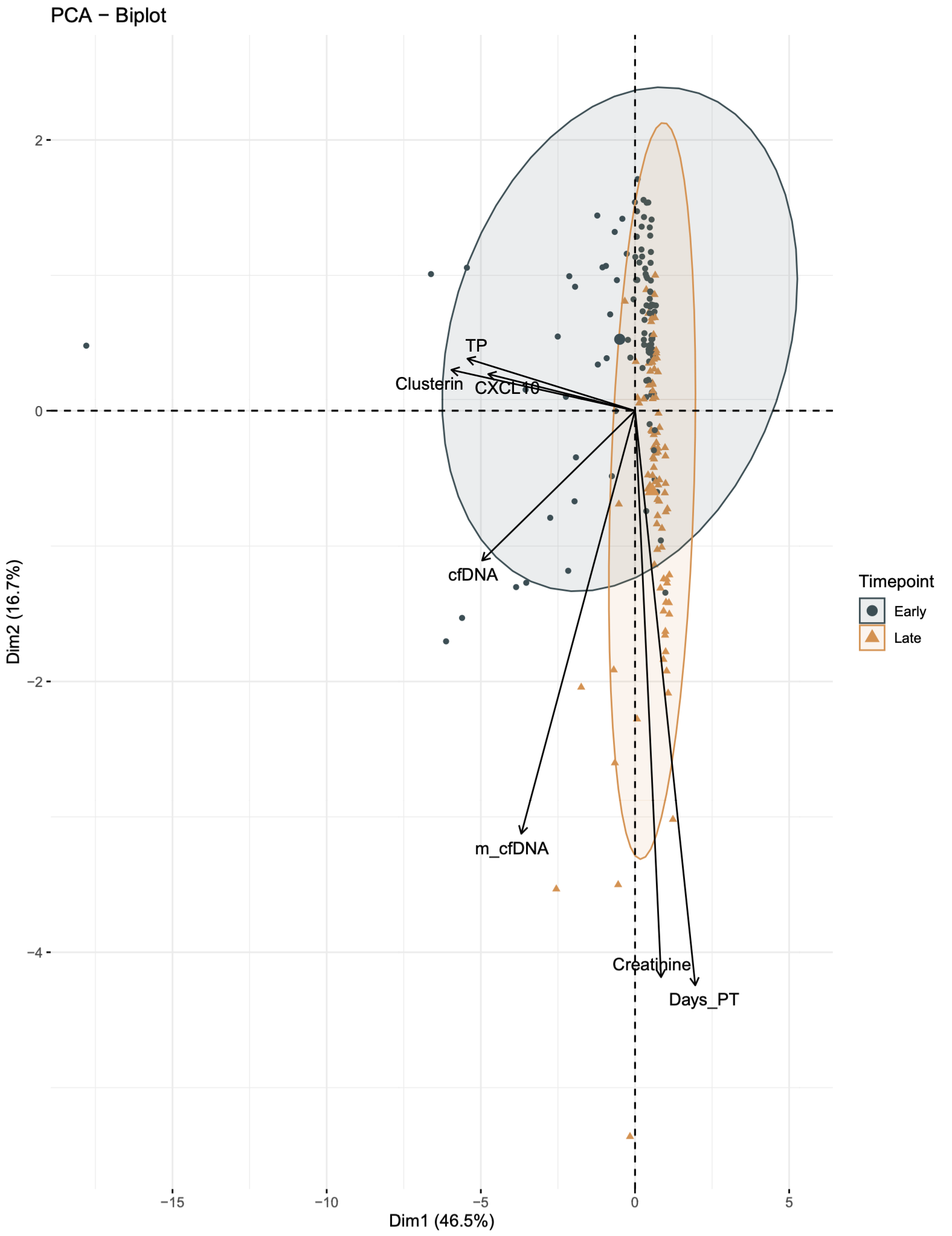
*Results: No statistical significance was observed for the examined clinical variables in patients with and without DGF(Table 1). The QScore time-series analysis showed a statistically significant (p=2.5e-7) mean decline in rejection risk with QScore dropping into immunequiescence range (<32) by 2 months post-transplant(visit 8: median 60 days post-transplant), irrespective of DGF. The limit of immunequiescence was first achieved at visit 3(median:12 days) with median QScore of 32.8. In comparison to visit 1(median: 4 days), the decline in rejection risk at visit 3 was significant(p=0.037). PCA of the DGF population over the early(visits 1-3) versus late(visits 5-8) timepoints elucidate patient segregation and quantify the contribution of the QSant urinary biomarkers with DGF recovery(Fig.1). Clusterin explains 46.5% of the variance followed by total protein, cfDNA and CXCL10 at 16.7%-12.2%.
*Conclusions: Overall, there is good recovery of renal function, irrespective of DGF. The study shows serial urine biomarker-based monitoring captures the progression and potential resolution of DGF-related renal injury. Also highlights the variable contribution of the biomarkers in the QSant assay relating to tubular injury and immune activation, consistent with underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms of injury in IRI and DGF.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ghosh S, Tedesco H, Sarwal R, Titzler N, Yazar W, Nakamura M, Pestana J, Sarwal M. QSant, a Novel Urine Test Monitors Recovery of Allograft Injury After DGF [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/qsant-a-novel-urine-test-monitors-recovery-of-allograft-injury-after-dgf/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress