Profound Effect of HDAC2 Deletion on Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Is Intrinsic to the Kidney and Includes Protection Against Cold Ischemia
1Department of Surgery, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA
2Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA
3Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA
4Department of Surgery, The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D70
Keywords: Preservation, Renal dysfunction, Renal injury, Warm ischemia
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Innate Immunity in Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 5, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Introduction: Histone/protein deacetylases (HDACs) regulate gene expression by modifying chromatin accessibility and protein acetylation. We have previously found that deletion of HDAC2 protects from renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) and wished both to determine the tissue specificity of the HDAC2 deletion on renal IRI tolerance and to evaluate its influence in a transplant model of cold ischemia.
Methods: We transplanted renal isografts from C57BL/6 (B6) mice with inducible HDAC2 gene deletion into wild type B6 mice (HDAC2KO->B6), from B6 into inducible HDAC2 deletion mice (B6->HDAC2KO), or B6 into B6 mice (B6->B6). To assess warm IRI tolerance, mice underwent native nephrectomy, tamoxifen-induced HDAC2 deletion, and standardized 25-minute warm IRI with clamping of the transplanted renal pedicle. To evaluate cold IRI tolerance, kidneys were procured from gene-deleted mice, stored on ice for 18 hours before implantation, and transplanted.
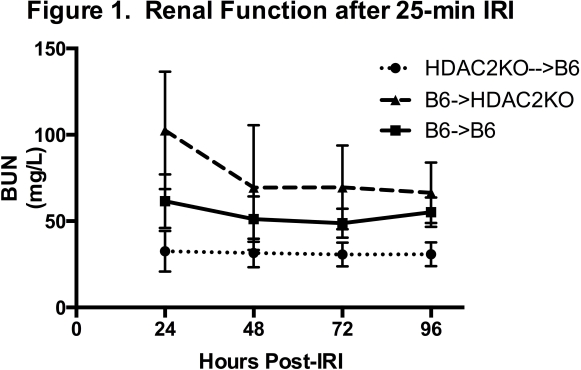
Results: HDAC2KO->B6 mice (n =10) demonstrated significant improvement in warm IRI tolerance with lower daily BUN levels over the 4 days following IRI compared to B6->HDAC2KO mice (n=5, p=0.0001) and B6->B6 mice (n=5, p=0.0003) (Figure 1) and significant reduction in renal fibrosis by Sirius Red staining at 28-days post-injury compared to both other groups (p=0.0128 and p=0.0136). HDAC2KO->B6 mice displayed significantly improved BUN (p=0.0187) and Cr (p=0.0012) compared to B6->B6 controls following renal transplant with 18 hours of cold ischemic time and had a trend towards improved survival (80% vs. 67%, p=0.43).
Conclusion: The profound effect of HDAC2 deletion on renal IRI is intrinsic to the kidney and extends to decreased renal injury post-cold ischemia and renal transplantation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aufhauser D, Wang Z, Cheraghlou S, Bhatti T, Hancock W, Levine M. Profound Effect of HDAC2 Deletion on Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Is Intrinsic to the Kidney and Includes Protection Against Cold Ischemia [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/profound-effect-of-hdac2-deletion-on-renal-ischemia-reperfusion-injury-is-intrinsic-to-the-kidney-and-includes-protection-against-cold-ischemia/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
