Predicting Post Liver Transplant 30-Day Readmission Using Deep Neural Network Model
1Psychiatry & Psychology, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL, 2Enterprise Analytics, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, 3Health Sciences Research, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL, 4GI & Hepatology, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL, 5Psychiatry & Psychology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, 6Health Services Research, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL, 7Transplantation, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D2
Keywords: Economics, Liver transplantation, Methodology, Psychiatric comorbidity
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Quality Assurance Process Improvement & Regulatory Issues
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Liver transplantation (LT) is a complex, expensive process and requires multidisciplinary care. A significant portion of the estimated $735,000 LT cost can be attributed to post LT 30-day readmissions rates of 25-50%. The aim of this study was to develop a predictive Post-LT Re-Admission model.
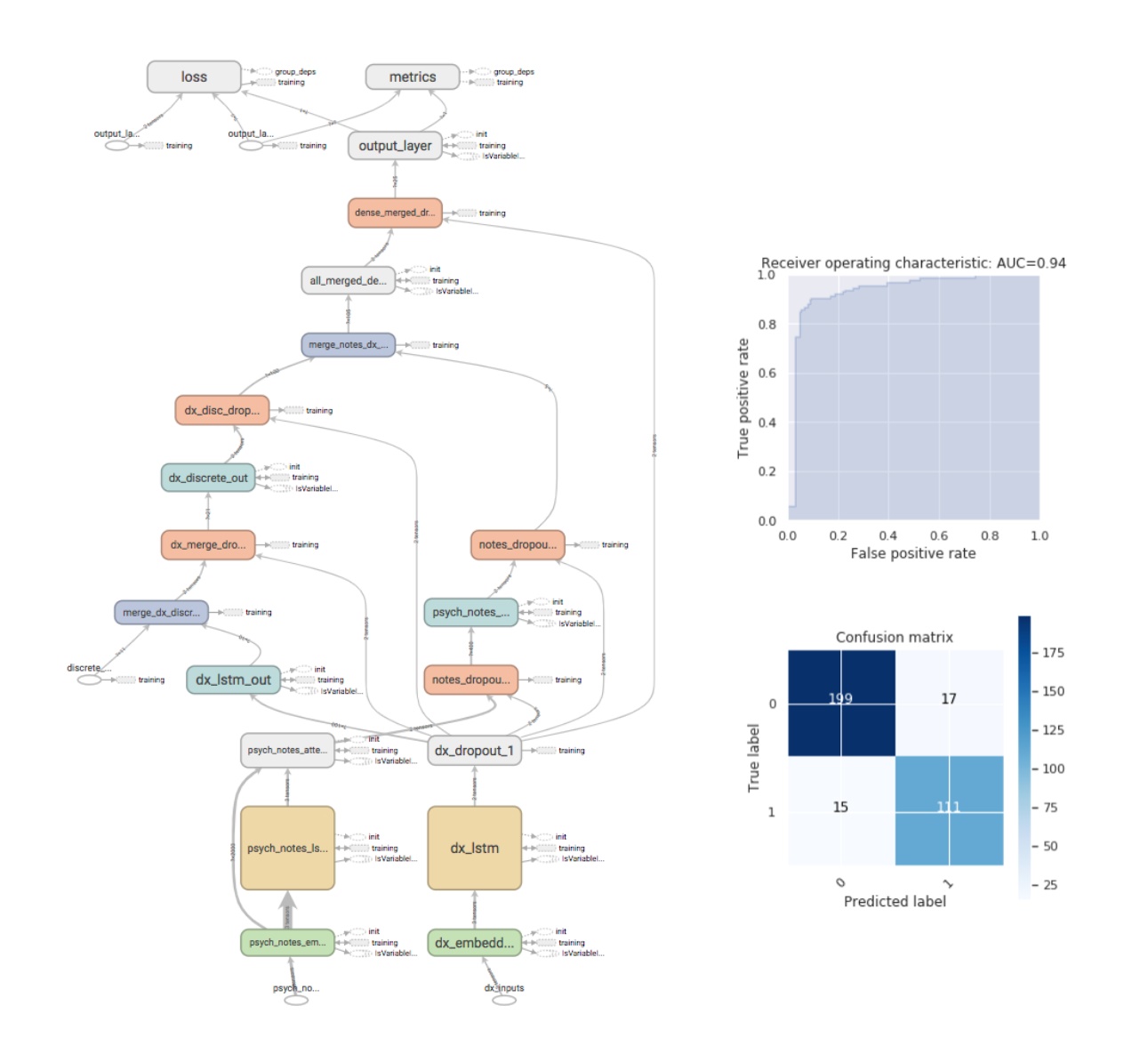
*Methods: A deep neural network model was trained from a randomly chosen sample of LT recipients based upon the following variables: Psychiatric notes, diagnosis description, Karnofsky score, age, sex, body mass index, creatinine, glucose, length of stay, surgery duration minutes, scheduled surgery duration and surgery duration difference. Data in Psychiatry notes were processed by removing common stop-words and punctuation and terms were tokenized with 10000 words of vocabulary. Based on the average number of words in Psychiatry notes, the number of words in each note was limited to 2,000. Notes with less than 500 words were dropped. Diagnosis descriptions were processed in a similar way but with 200 words of vocabulary, 50-word limit, and no drop for shorter descriptions. The model was structured with two layers of dense network/feed forward neural network fed by the concatenation of the two stacks of embedding layer, recurrent neural network, and dense network which convert sentences to five and ten-dimensional vectors for notes and diagnosis descriptions respectively and all other numerical/binary variables. Shorter notes (less than 2,000 but more than 500 words) were zero-padded with proper treatments in recurrent neural network. Dropout as a regularization was employed for most layers. (Figure) All work was done using Keras, Python Deep Learning library, on a GPU-powered cluster.
*Results: Among total of 1,656 LT recipients between 2011 and 2017, 20% were held out for testing and 1,858,291 parameters were trained on the remainder 1,325 LT recipients. After the training of 500 epochs, the model was tested with the data from 342 patients, held out from the training set. As a result, 90.6% (310/342) prediction accuracy, specificity of 0.92 (199/216), and sensitivity of 0.88 (111/126) were attained for 30-day readmission prediction. Additional iterations of model are being developed that improve the prediction accuracy even further.
*Conclusions: At a single large LT center, deep neural network model employed on data from comprehensive Pre-LT psychiatric assessment along with surgical variables was able to accurately predict Post-LT 30-day readmissions. Validation of model in other LT centers is needed for wider use.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Niazi SK, Park HO, Carter RE, Keaveny A, Schneekloth T, Spaulding A, Harnois D, Moreno-Franco PF, Vargas E, Rummans T, Taner C. Predicting Post Liver Transplant 30-Day Readmission Using Deep Neural Network Model [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/predicting-post-liver-transplant-30-day-readmission-using-deep-neural-network-model/. Accessed July 12, 2025.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress