Post Heart Transplant Outcomes of Desensitized Durable Mechanical Circulatory Support Patients
1Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 2Heart Vascular Stroke Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 3Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital, Daegu, Korea, Republic of, 4Department of Cardiology, Smidt Heart Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, 5Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Smidt Heart Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 144
Keywords: Heart/lung transplantation, Sensitization, Ventricular assist devices
Topic: Clinical Science » Heart » 63 - Heart and VADs: All Topics
Session Information
Session Name: Heart and VADs: All Topics I
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:10pm-6:20pm
Presentation Time: 6:10pm-6:20pm
Location: Hynes Room 210
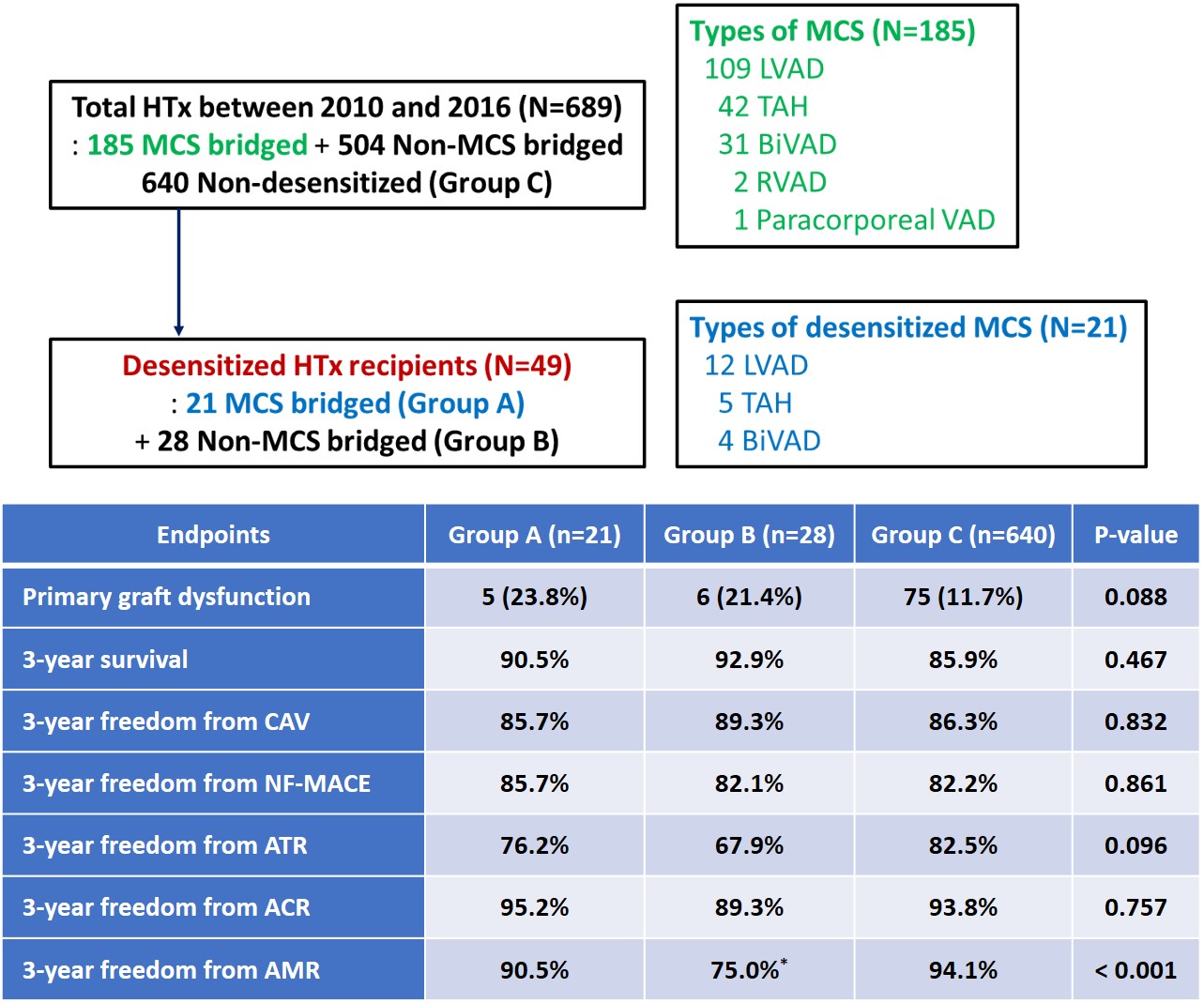
*Purpose: Desensitization therapy (DST) is considered to increase the chances of a negative crossmatch, to expand the number of suitable donors, and to improve post-transplant outcomes. However, post-transplant outcome of consecutively enrolled desensitized durable mechanical circulatory support (MCS) patients are not well known. We aimed to investigate the post-transplant outcome of desensitized MCS patients.
*Methods: Among 689 consecutively enrolled heart transplant (HTx) recipients between 2010 and 2016, we categorized them into Group A (desensitized MCS patients, n = 21), Group B (desensitized non-MCS patients, n = 28) and Group C (all non-desensitized patients, n = 640). Post-transplant outcome included the incidence of primary graft dysfunction (PGD), 3-year survival, freedom from cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV), non-fatal major adverse cardiac events (NF-MACE), any treated rejection (ATR), acute cellular rejection (ACR), and antibody mediated rejection (AMR). Infectious complications were evaluated for Groups A and B.
*Results: The types of DST in both groups were similar and included combinations of rituximab/IVIG and plasmapheresis/bortezomib. Group A, compared with Group B, showed significantly higher pre-DST PRA (92.2 ± 9.8 vs. 83.3 ± 15.6, P = 0.007) and higher PRA reduction after DST (-22.2 ± 26.9 vs. -6.3 ± 7.5, P = 0.015). Groups A and C showed comparable PGD, 3-year survival, freedom from CAV, NF-MACE, ATR, ACR and AMR. Group A compared to Group B showed a numerically higher 3-year freedom from AMR. Infectious complications within 3 years were not different between Groups A and B.
*Conclusions: DST for MCS patients showed significant PRA reduction, resulting in an expansion of the donor pool. Post-transplant outcome of desensitized MCS patients showed comparable clinical outcome to all non-desensitized control patients in the same study period, revealing the safety and efficacy of DST.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Youn J, Kim D, Choi J, Kim K, Kim I, Kransdorf E, Chang D, Kittleson M, Patel J, Cole R, Moriguchi J, Ramzy D, Esmailian F, Kobashigawa JA. Post Heart Transplant Outcomes of Desensitized Durable Mechanical Circulatory Support Patients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/post-heart-transplant-outcomes-of-desensitized-durable-mechanical-circulatory-support-patients/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress