P2X7R Inhibition Impairs In Vitro Training of Macrophages
1Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, 2Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, 3Oncological Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, 4Center for Transplantation Sciences, Department of Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1237
Keywords: Inflammation, Leukocytes, Mice, Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 08 - Innate Immunity; Chemokines, Cytokines, Complement
Session Information
Session Name: Innate Immunity; Chemokines, Cytokines, Complement
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
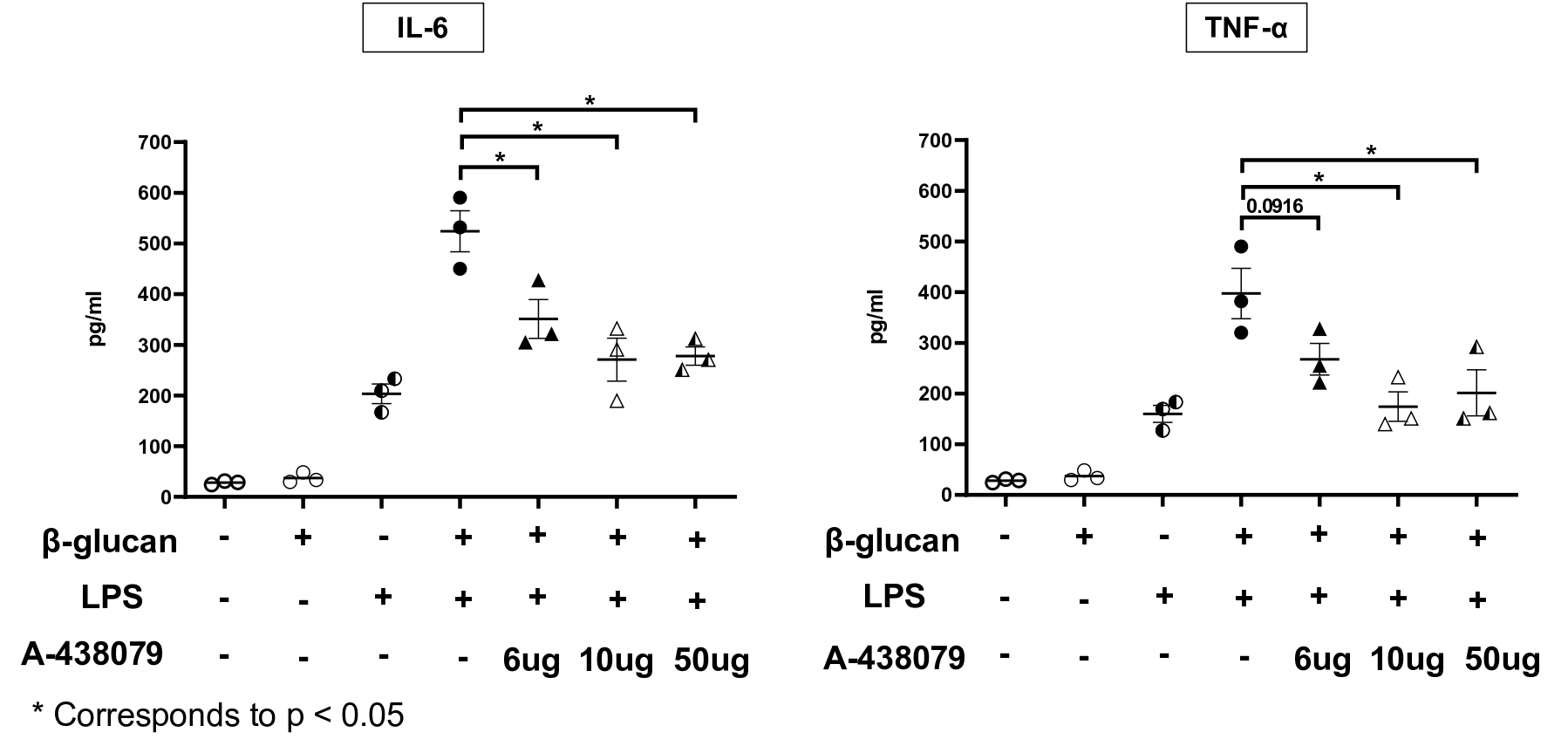
*Purpose: Macrophage training and ATP-mediated P2X7R signaling are unrelated key elements of the innate immune response associated with allotransplant rejection. In the present study, we studied whether inhibition of P2X7R signaling impacts macrophage training in vitro.
*Methods: Mouse bone marrow were collected and cultured with macrophage-colony stimulating factor for 7 days. The purity of bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) was > 98%. Next, BMDM were trained with 10ug/mL of β-glucan with or without a P2X7R inhibitor (A-438079) for 24h. After, 5 days of resting, BMDM were restimulated with 10 ng/mL of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 24h. The effect on P2X7R inhibition on trained immunity was tested by measuring the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNFα by BMDM.
*Results: As shown in Figure1. inhibition of P2X7R signaling using A-438079 significantly suppressed macrophage training induced with β-glucan + LPS, as we observed that P2X7R inhibition suppressed IL-6 and TNFαproduction by macrophages in vitro. (p < 0.05) in vitro.
*Conclusions: Inhibition of P2X7R signaling prevents training on macrophages in vitro, indicating that ATP plays a critical role in train immunity. This also suggests that strategies designed to suppress P2X7R signaling and subsequent NLRP3 inflammasome may represent a promising strategy to prevent macrophage training in transplantation and prolong allograft survival.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lancia HH, Sanchez R, Lellouch AG, Cetrulo CL, Ochando J, Benichou G. P2X7R Inhibition Impairs In Vitro Training of Macrophages [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/p2x7r-inhibition-impairs-in-vitro-training-of-macrophages/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress