Outcome of Renal Transplantation in Systemic Amyloidosis
1Renal Medicine, Royal Free Hospital, London, United Kingdom, 2UCL Division of Medicine, National Amyloidosis Centre, London, United Kingdom
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C57
Keywords: Graft failure, Graft function, Graft survival, Recurrence
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Complications: Late Graft Failure
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Systemic amyloidosis accounts for approximately 0.8% of end stage renal disease (ESRD) in the UK. Outcomes following renal transplantation in systemic amyloidosis were historically poor, but there is a paucity of data on renal transplant outcomes following recent therapeutic advances which have benefited patients with systemic amyloidosis generally. We sought to determine renal allograft and patient survival in UK patients with ESRD from systemic amyloidosis.
*Methods: Outcomes following renal transplantation among 94 patients with systemic AA and AL amyloidosis being followed at the UK National Amyloidosis Centre (NAC) who underwent renal transplantation between 1989 and 2018 were compared with those of age-matched renal transplant recipients with diabetic and non-diabetic nephropathy recipients held in the NHSBT database.
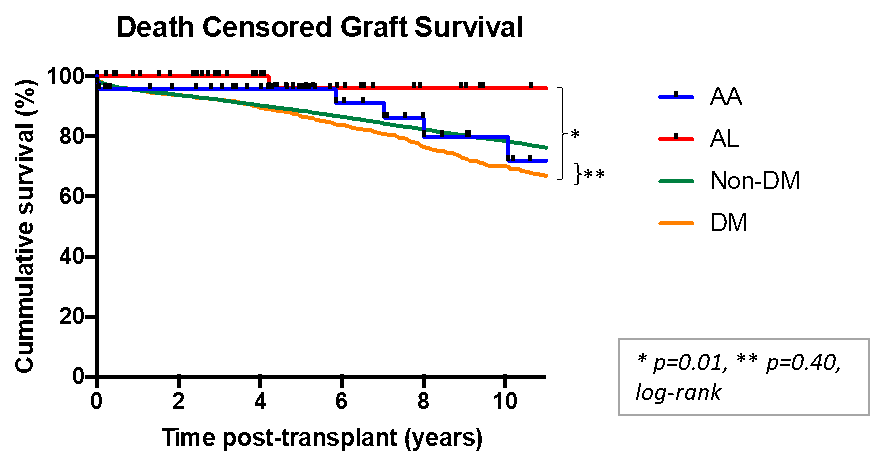
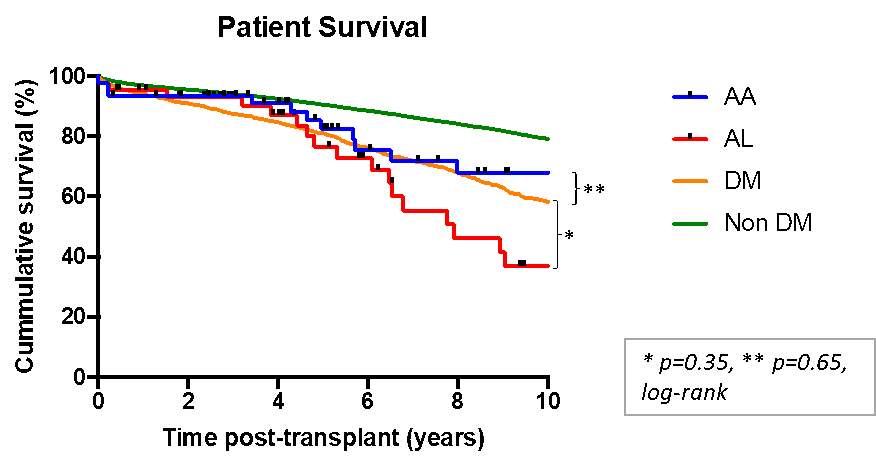
*Results: See Graphs 1 and 2
Death-censored graft survival was 96%, 96%, 96% and 81% in AA, and 98%, 98%, 93% and 93% in AL amyloidosis at 1,3, 5 and 10 years respectively. Overall patient survival was 92%, 92%, 81% and 68% in AA and 95%, 93%, 76%, 34% in AL amyloidosis at 1, 3, 5, and 10 years respectively. Twenty-five amyloidosis patients died with a functioning renal allograft and 9 suffered allograft loss, 3 within a month due to operative complications or rejection, 3 from recurrent amyloid (all AA) and 3 multifactorial but with recurrent amyloid (1AL, 2AA).
*Conclusions: Patient and renal allograft survival following renal transplantation in AA amyloidosis is similar to that in diabetic nephropathy. Despite excellent death-censored renal allograft survival in AL amyloidosis, reflecting prevention of recurrence of amyloid in renal allografts due to successful suppression of the underlying clonal dyscrasia with chemotherapy, patient survival following renal transplantation in this cohort was inferior to age-matched diabetic controls. This data indicates that carefully selected patients with systemic amyloidosis can achieve good outcomes following renal transplantation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Law S, Helen L, Resk T, Wechalekar A, Gillmore J, Motallebzadeh R. Outcome of Renal Transplantation in Systemic Amyloidosis [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/outcome-of-renal-transplantation-in-systemic-amyloidosis/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress