Orthotopic Liver Transplantation of Xenogeneic Livers Repopulated with Autologous Hepatocytes: Proof of Normal Function and Consistent Survival.
Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 477
Keywords: Graft function, Liver transplantation, Waiting lists, Xenotransplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Xenotransplant
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, May 2, 2017
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:06pm-3:18pm
Presentation Time: 3:06pm-3:18pm
Location: E351
Background
Generation of transplantable patient-like organs in pigs will solve the problem of organ shortage and potentially extend the indications for liver transplantation. However, the efficacy of this approach is yet to be demonstrated even in preclinical studies involving small animals. We challenged this idea by transplanting mouse-rat chimeric livers into baby rats, in orthotopic position. Grafts and animals survival was assessed along with liver synthetic function
Methods
Chimeric livers were created by transplanting Lewis rat hepatocytes into FRG® mice (C57Bl/6 Fah-/-Rag2-/-Il2rg-/-). The organs obtained were transplanted into 3-week old female Lewis rats (45±3g) without or with immunosuppression (Tacrolimus 0.6mg/kg/day, during 56 days). The intensity of rejection was assessed by weekly graft biopsies and peripheral blood immune cells activation. Rat and mouse albumin production was measured once a week. Wild type C57Bl/6 mice were used as control donors
Results
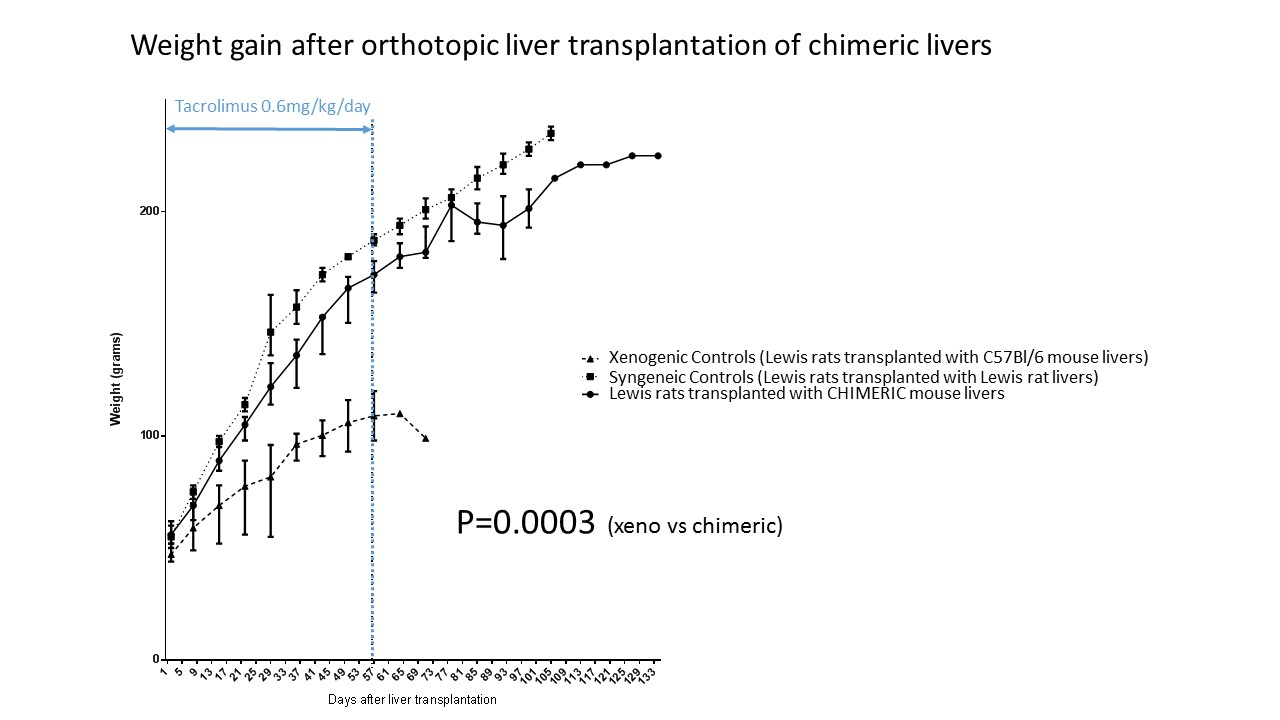
All non-immunosuppressed recipients experienced acute rejection and died between day 8 and 11 after transplantation. Under calcineurin inhibitor monotherapy all chimeric liver recipients survived in good health, having normal development and weight gain. Banff score was 2-3, rejection being mostly driven by cholangiocytes. Rat albumin production was within physiologic ranges. By contrast, pure xenogeneic controls showed impaired growth (p=0.0003) and died before or shortly after the immunosuppression was stopped (p=0.0014) 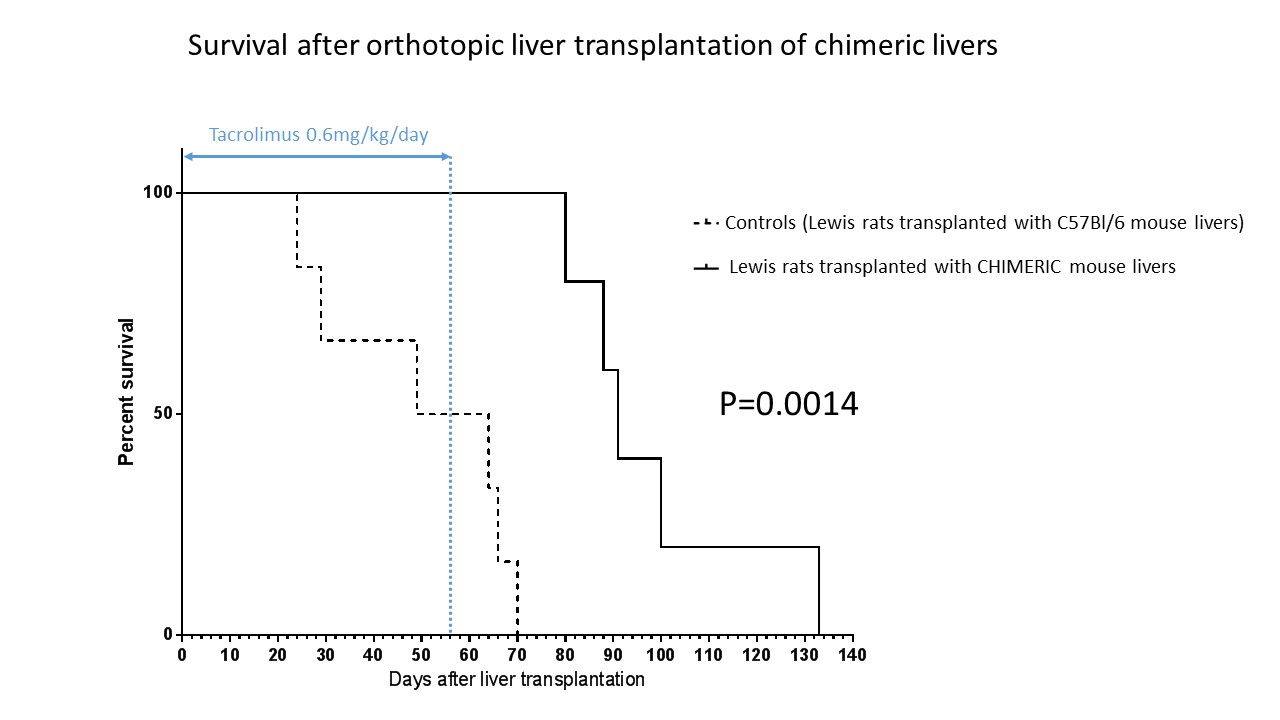
 Banff score was never inferior to 6, rejection involving all epithelia
Banff score was never inferior to 6, rejection involving all epithelia
Conclusion
This is the first report showing robust survival of orthotopically transplanted chimeric livers. Moreover, the transplanted organs sustained and were able to follow normal animal growth and development after transplantation.
CITATION INFORMATION: Oldani G, Lacotte S, Orci L, Delaune V, Toso C. Orthotopic Liver Transplantation of Xenogeneic Livers Repopulated with Autologous Hepatocytes: Proof of Normal Function and Consistent Survival. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Oldani G, Lacotte S, Orci L, Delaune V, Toso C. Orthotopic Liver Transplantation of Xenogeneic Livers Repopulated with Autologous Hepatocytes: Proof of Normal Function and Consistent Survival. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/orthotopic-liver-transplantation-of-xenogeneic-livers-repopulated-with-autologous-hepatocytes-proof-of-normal-function-and-consistent-survival/. Accessed March 1, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
