Noninvasive Quantization of Intra-Renal Allograft C4d Deposition with Targeted Ultrasound Imaging
1Organ Transplantation Research Institute, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
2Department of Medical Ultrasound, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D269
Keywords: Biopsy, Image analysis, Rat, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Late Breaking
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 5, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) has emerged as the major cause of renal allograft dysfunction. C4d, a specific marker of AMR diagnosis, was strongly recommended for routine surveillance. However, currently, C4d detection is dependent on tissue biopsy, which is invasive and only provides local semi-quantitative data. Targeted ultrasound (US) with high sensitivity and specificity has been extensively used for noninvasive and real-time diagnosis, which makes it possible to visualize C4d deposition in vivo. We designed a serial dilution of C4d-targeted microbubbles (MBC4d) using a streptavidin-biotin conjugation system (binding rate: 91.0±2.5%). A rat model of AMR was established by pre-sensitization with skin transplantation. After MBC4d injection, it was then qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed using the destruction-replenishment method with a clinical US imaging system and analyzed by software  . Finally, through this noninvasive procedure, we successfully obtained the qualitative images of C4d deposition in a wide renal allograft section, which, for the first time, reflected real-time C4d distribution. Moreover, normal intensity difference (NID) was used for quantitative analysis and exhibited a nearly linear correlation with the grade of C4d deposition according to the pathologic evidence
. Finally, through this noninvasive procedure, we successfully obtained the qualitative images of C4d deposition in a wide renal allograft section, which, for the first time, reflected real-time C4d distribution. Moreover, normal intensity difference (NID) was used for quantitative analysis and exhibited a nearly linear correlation with the grade of C4d deposition according to the pathologic evidence 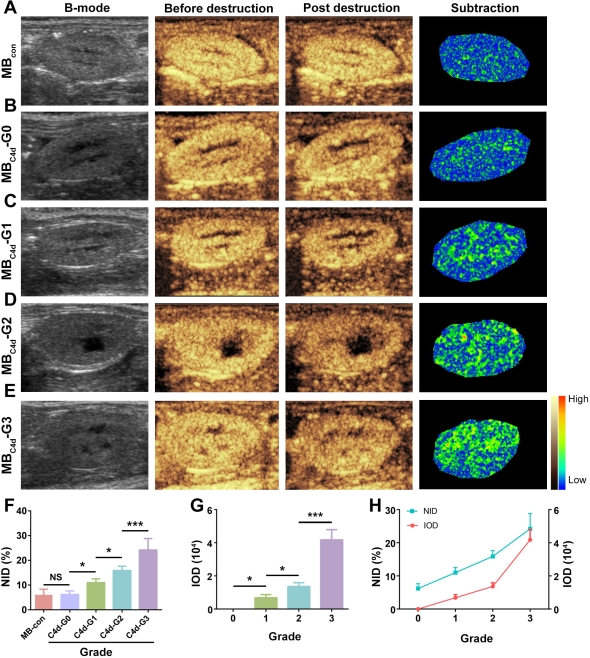 . In addition, MBC4d injection did not affect the survival and pathologic features, which demonstrates its safety. In conclusion, this study demonstrated a simple, noninvasive, quantitative and safe evaluation method for C4d and the utility of this approach may prevent numerous patients from having to undergo an invasive biopsy.
. In addition, MBC4d injection did not affect the survival and pathologic features, which demonstrates its safety. In conclusion, this study demonstrated a simple, noninvasive, quantitative and safe evaluation method for C4d and the utility of this approach may prevent numerous patients from having to undergo an invasive biopsy.
CITATION INFORMATION: Liao T., Zhang Y., Ren J., Zheng H., Zhang H., Liu X., Yin T., Sun Q. Noninvasive Quantization of Intra-Renal Allograft C4d Deposition with Targeted Ultrasound Imaging Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liao T, Zhang Y, Ren J, Zheng H, Zhang H, Liu X, Yin T, Sun Q. Noninvasive Quantization of Intra-Renal Allograft C4d Deposition with Targeted Ultrasound Imaging [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/noninvasive-quantization-of-intra-renal-allograft-c4d-deposition-with-targeted-ultrasound-imaging/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
