Noninvasive Prognostication of Renal Allograft Failure Following BK Virus Associated Nephropathy – A Validation Study.
Transplant Medicine, Weill Cornell Medicine, NY, NY
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 234
Keywords: Gene expression, Graft failure, Polyma virus
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney BK Virus
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:42pm-2:54pm
Presentation Time: 2:42pm-2:54pm
Location: E451a
Introduction. Identification of kidney transplant (KTx) recipients at risk for graft loss following BKVN diagnosis may allow personalization of immunosuppressive protocols. Previous study demonstrated that a composite signature of urinary cell levels of 18S rRNA normalized PAI-1 mRNA and serum creatinine, measured at the time of BKVN diagnosis, predicts 3 year graft loss (Dadhania et al. Txp. 2013) Herein, we determined whether the previously identified composite signature is prognostic of graft outcomes in an independent cohort of KTx recipients.
Methods. From 2008 to 2014, 26 of 33 newly diagnosed KTx recipients with BKVN were enrolled in our gene expression monitoring study and followed for 3 yrs. We measured 18S rRNA and PAI-1 mRNA levels in urine specimens collected at time of initial BKVN diagnosis. We examined whether the composite signature is prognostic of graft outcome in this replication study.
Results. Seven of 26 patients experienced graft loss (GL) post BKVN diagnosis. Serum creatinine levels (2.9± 0.8 vs. 1.9 ±0.6, P=0.005) and urinary cell PAI-1 mRNA levels (7.3±0.68 vs. 6.2±1.2 , P=0.02) were significantly higher in the GL vs. No GL group. The area under the curve (AUC) following ROC curve analysis was 0.85 (95% CI, 0.67-1.0) for serum creatinine; 0.80 (95% CI, 0.62-0.97) for PAI-1 mRNA; and 0.90 (95% CI, 0.78-1.0) for the combination of serum creatinine and PAI mRNA (Fig.1). Using the published composite signature, a comparison of the AUC of the original study with AUC observed in the current study showed that the AUCs are not different (P>0.05, De Long test, Table 1)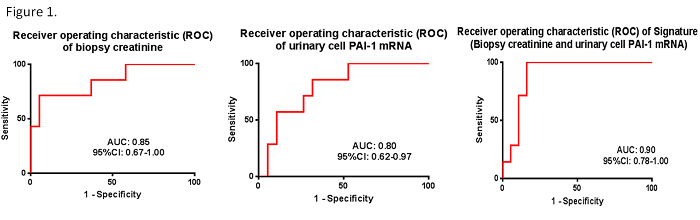
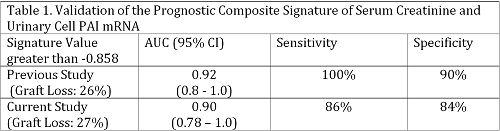 Conclusion. We have validated, using an independent cohort, that a composite signature of serum creatinine and PAI-1 mRNA is an accurate prognosticator of kidney allograft outcome following BKVN diagnosis.
Conclusion. We have validated, using an independent cohort, that a composite signature of serum creatinine and PAI-1 mRNA is an accurate prognosticator of kidney allograft outcome following BKVN diagnosis.
CITATION INFORMATION: Abuhelaiqa E, Snopkowski C, Li C, Lee J, Muthukumar T, Yang H, Suthanthiran M, Dadhania D. Noninvasive Prognostication of Renal Allograft Failure Following BK Virus Associated Nephropathy – A Validation Study. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Abuhelaiqa E, Snopkowski C, Li C, Lee J, Muthukumar T, Yang H, Suthanthiran M, Dadhania D. Noninvasive Prognostication of Renal Allograft Failure Following BK Virus Associated Nephropathy – A Validation Study. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/noninvasive-prognostication-of-renal-allograft-failure-following-bk-virus-associated-nephropathy-a-validation-study/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
