Multicenter Validation of a Molecular Diagnostic for Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Human Renal Allograft Biopsies
1University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada
2Imperial College, London, United Kingdom.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 80
Keywords: Antibodies, Biopsy, Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Alloantibodies and Rejection: Animal Models
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, May 3, 2015
Session Time: 4:00pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 4:48pm-5:00pm
Presentation Time: 4:48pm-5:00pm
Location: Room 118-AB
Background: In 2013, the Banff classification adopted molecular diagnostics as an adjunct for the diagnosis of antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR) in renal allografts. The NanoString gene expression platform is unique in its ability to use formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples. We aimed to utilize this method to assess the validity of molecular ABMR diagnostics in routine renal allograft biopsies.
Design: NanoString was used to quantify expression of a literature-derived 34-gene set in a training cohort of 105 archival FFPE renal allograft biopsies. Gene set expression was correlated with serologic and histologic data and a diagnostic threshold for ABMR was determined with receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. This was applied in a blinded fashion to a validation cohort of 45 biopsies from a second institution. In addition, for these 45 biopsies, expression of 11 overlapping genes was assessed by rtPCR on corresponding non-FFPE samples.
Results: Gene set expression in the training cohort correlated with donor-specific antibodies (r=0.51, p<0.001) and histologic lesions of microcirculation injury (r=0.24-0.45, p<0.01). Increased gene set expression was seen in cases classified by Banff 2013 serohistologic criteria as ABMR, suspicious for ABMR, and mixed ABMR/T-cell mediated rejection (TCMR), compared with those called TCMR only, normal, or other (Figure 1). Using the ROC-derived diagnostic cut-off, gene set diagnosis of ABMR in the validation cohort showed the following compared to Banff 2013: sensitivity 0.60, specificity 0.77, PPV 0.43, NPV 0.87, and accuracy 0.73. Five cases classified as suspicious for ABMR by Banff 2013 would be upgraded to ABMR with the addition of gene set testing. Gene expression by NanoString showed variable correlation with rtPCR (r=-0.18-0.66, mean=0.25, p<0.001).
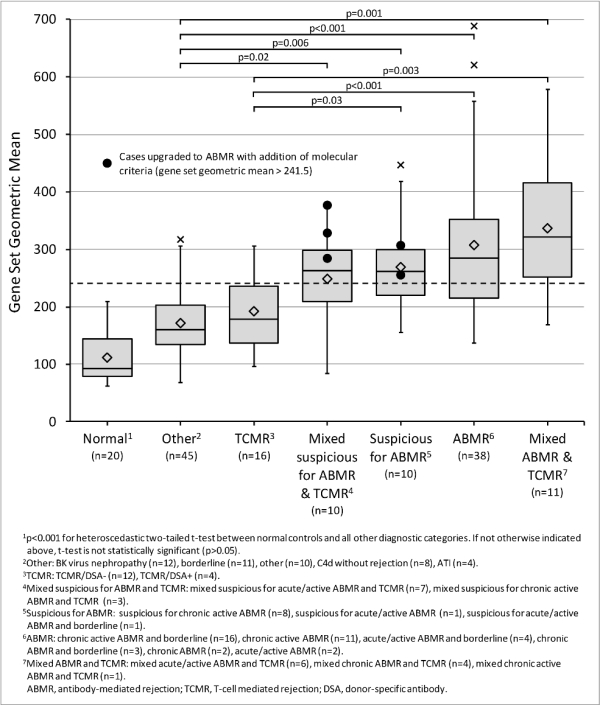
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate the feasibility of multiplexed gene expression quantification from FFPE renal allograft biopsies. These data suggest a method for molecular diagnostics to be introduced into clinical transplantation pathology.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Adam B, Afzali B, Shah N, Dominy K, Gill R, Hidalgo L, Campbell P, Roufosse C, Mengel M, Sis B. Multicenter Validation of a Molecular Diagnostic for Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Human Renal Allograft Biopsies [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/multicenter-validation-of-a-molecular-diagnostic-for-antibody-mediated-rejection-in-formalin-fixed-paraffin-embedded-human-renal-allograft-biopsies/. Accessed July 1, 2025.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
