Longitudinal Analysis of the Lung Microbiome and Immune Status in Lung Transplant Recipients
Y. Zhao, P. Zhang, Y. Su, Y. Zhu, L. Shen
Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital, Shanghai, China
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 49
Keywords: Donors, unrelated, IgG, Lung transplantation, Lymphocytes
Topic: Clinical Science » Lung » 64 - Lung: All Topics
Session Information
Session Name: Infectious Considerations for Lung Transplantation
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 3:30pm-5:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:50pm-5:00pm
Presentation Time: 4:50pm-5:00pm
Location: Hynes Room 210
*Purpose: The dynamic remodeling of lung flora structure and the association between microbial community dynamics and immune status after lung transplantation (LTx) remain unclear.
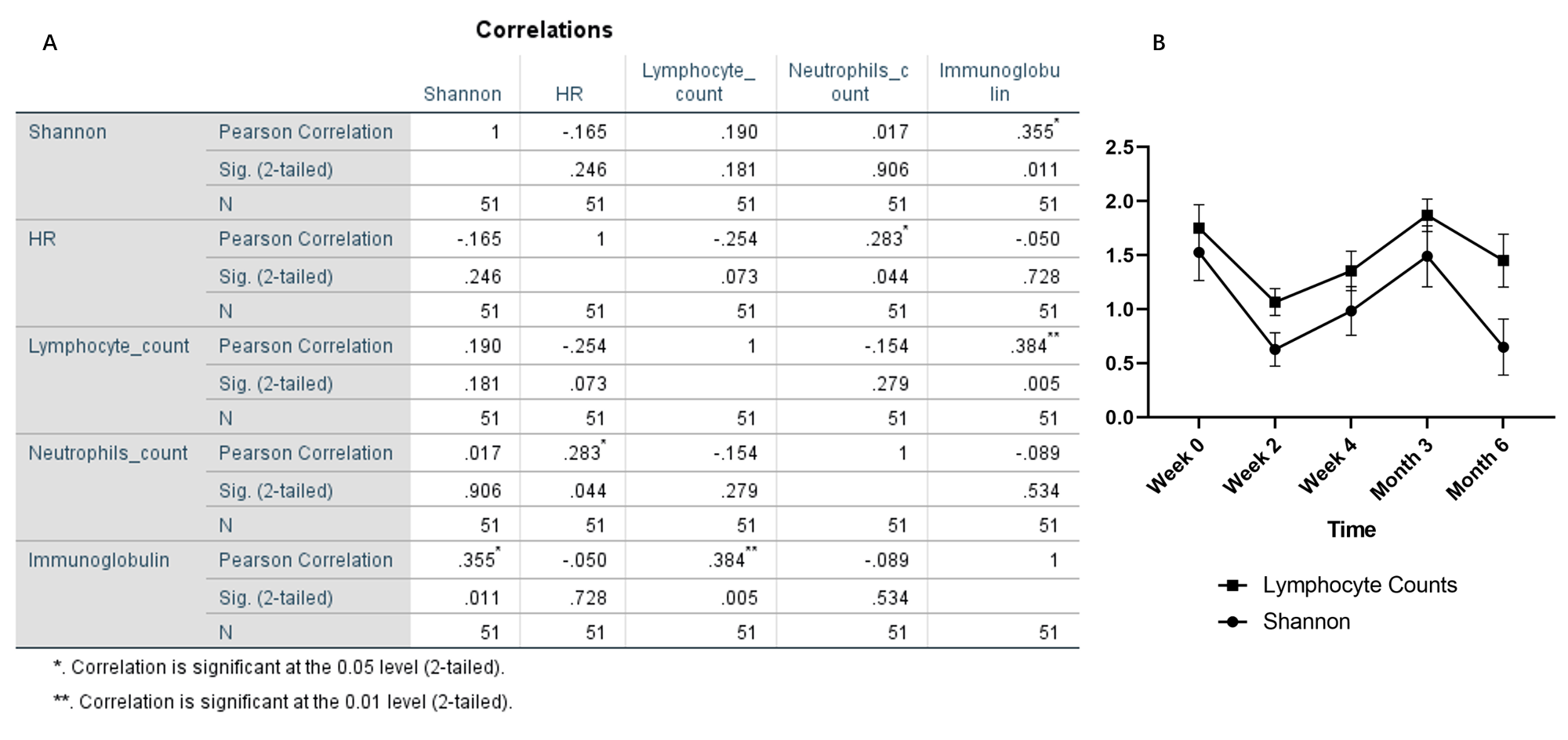
*Methods: Fourteen LTx recipients were included in the study. Fifty sputum samples were collected from 13 donors and 14 recipients. Microbial DNA was extracted and subjected to metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS). The sputum samples were also subjected to analysis via routine microbial culture. The clinical characteristics of recipients and data regarding immune status as well as pulmonary function were retrospectively collected. The correlation between the lung microbiome and immune status was analyzed using Spearman’s correlation tests.
*Results: Compared to culture, mNGS identified 24.4% more specimens as positive. The distribution of microorganisms in LTx recipients varied over time post-surgery, with dominant Gram-negative bacteria at the early stage after LTx and dominant Gram-positive bacteria as well as viruses at 6 months after LTx. The microbial community structure at 6 months post-transplantation not only differed from that in donors, but also exhibited great differences among recipients. An increased abundance of Rothia and Streptococcus as well as a decreased abundance of Klebsiella and Enterococcus were noted in recipients, in parallel to improved pulmonary function and immune status at 6 months after LTx. Furthermore, a significant positive correlation was observed between the pulmonary microbiota and immune status.
*Conclusions: The microbial community structure dynamically changed after LTx, and these compositional changes were associated with immune status of LTx recipients, indicating the potential role of microbiome-immune interactions in manifestation, progression, and clinical therapy of LTx recipients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhao Y, Zhang P, Su Y, Zhu Y, Shen L. Longitudinal Analysis of the Lung Microbiome and Immune Status in Lung Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/longitudinal-analysis-of-the-lung-microbiome-and-immune-status-in-lung-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress