Long-Term Rejection Free Renal Allograft Survival with Fc-Modified Anti-cd154 Antibody Monotherapy in Nonhuman Primates
MGH Center for Transplantation Sciences, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 172
Keywords: Co-stimulation, Graft survival, Immunosuppression, Preclinical trails
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 12 - Immunosuppression & Tolerance: Preclinical & Translational Studies
Session Information
Session Name: Immunosuppression and Tolerance: Preclinical and Translational Studies
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:20pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 6:20pm-6:30pm
Location: Hynes Ballroom A
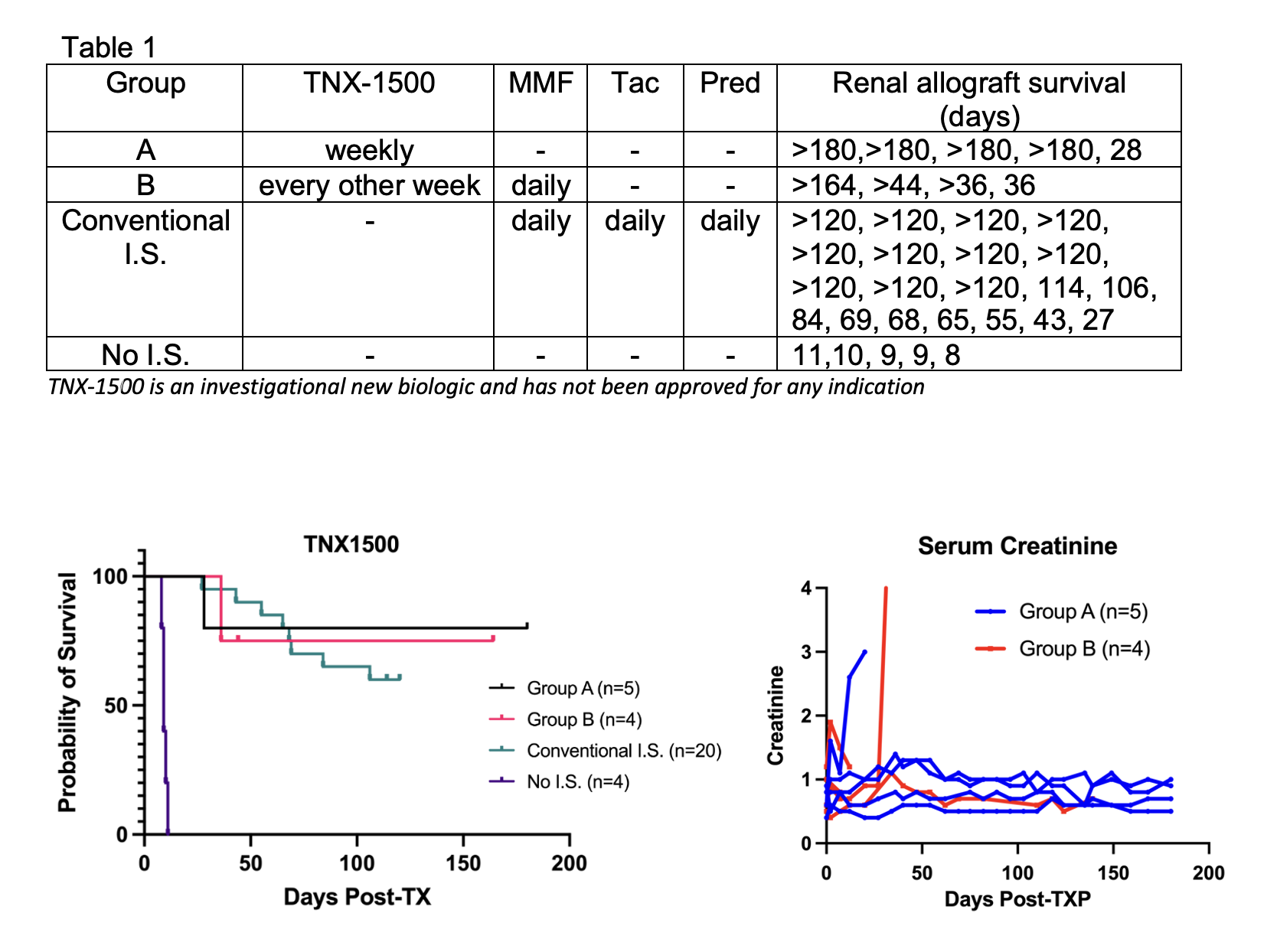
*Purpose: Belatacept is currently the only FDA approved costimulatory blockade (CB) used as an alternative to calcineurin inhibitors in kidney transplantation. However, it has been associated with higher rates of acute cellular rejection (ACR) and more effective CB has been sought. Blockade of the CD154/CD40 pathway with anti-CD154 antibody (αCD154) has been shown to be more effective in inhibiting alloimmune responses than CTLA4Ig. Despite the efficacy shown in humans and animals, clinical application of αCD154 with human IgG1 Fc was abandoned due to its prothrombotic property which appears have been mediated by FcγRIIA receptor-dependent platelet activation. To address this problem, an Fc-modified αCD154 (TNX-1500), in which Fc was modified by protein engineering to decrease binding to FcγRII, has been developed. In the current study, we have evaluated TNX-1500 for its efficacy to prevent kidney allograft rejection in NHPs.
*Methods: Nine cynomolgus macaques received MHC mismatched kidney allografts with either TNX-1500 monotherapy 20mg/kg weekly (Group A) or every two weeks with daily mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) (Group B). The results were compared with our historic results with no immunosuppression (No IS, n=5) or conventional immunosuppression (Conventional IS, n=20) with tacrolimus (Tac), MMF and methylprednisolone (Pred).
*Results: Without [ketorolac] prophylaxis, no thromboembolic complication was observed in any of the nine recipients of TNX-1500. Renal allograft survival at 6 month was 80% in Group A (n=5). Histopathology at 6 months of 4/5 recipients showed no evidence of rejection (g0,i0,t0,v0,ptc0,cg0,ci0,ct0,cv0, C4d0). One recipient was lost on day 28 with ACR2b. Four recipients have so far been tested in Group B. Although one recipient developed rejection on day 36, three other recipients in this group are currently in progress with normal kidney function at days 164, 44 and 36. Renal allograft survival at four months in Conventional I.S. was 52% (p=0.33 vs. Group A) and all five recipients without I.S. rejected their kidney allografts by day 11 (p=0.0018 vs. Group A).
*Conclusions: Excellent renal allograft survival was achieved with TNX-1500 monotherapy without thromboembolic complications. The optimal dosage of TNX-1500 remains to be defined.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lassiter G, Hirose T, D’Attilio A, Kawai T. Long-Term Rejection Free Renal Allograft Survival with Fc-Modified Anti-cd154 Antibody Monotherapy in Nonhuman Primates [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/long-term-rejection-free-renal-allograft-survival-with-fc-modified-anti-cd154-antibody-monotherapy-in-nonhuman-primates/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress