Kidney Versus Islet Allograft Survival After Induction of Mixed Chimerism in Nonhuman Primates
Transplant Center, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B38
Keywords: Islets, Kidney transplantation, Mixed chimerism, Primates
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Cell Transplantation and Cell Therapies
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, May 3, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Background: We have previously reported a successful induction of mixed chimerism and the long-term acceptance of renal allografts in MHC-mismatched nonhuman primates. In this study, we extended our approach for tolerance induction to islet allografts in cynomolgus monkeys.
Methods: Eight recipients underwent combined kidney and bone marrow transplantation with a nonmyeloablative conditioning regimen that consisted of low dose total body (TBI) and thymic irradiation (TI), horse ATG (Atgam), six doses of anti-CD154 monoclonal antibody (mAb) and a one month course of calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) (Kidney-A). Nine cynomolgus monkeys received MHC mismatched islet allografts after induction of diabetes by streptozotocin. In Islet-A, four recipients were treated with the same conditioning regimen used in Kidney-A. In Islet-B, CNI was replaced with anti-CD8 mAb. In Islet-C, Atgam was also removed in addition to CNI.
Results: The majority of kidney recipients who received the Kidney-A regimen achieved long-term renal allograft survival, after induction of transient chimerism. In Islet-A, however, prolonged islet survival was not achieved despite induction of comparable levels of chimerism. In order to rule out islet allograft loss due to CNI toxicity, three recipients received anti-CD8 mAb in place of CNI. All three recipients developed significantly improved mixed chimerism and islet allograft survival (61, 103, and 113 days). However, islet allografts were lost soon after the disappearance of chimerism. In Islet-C, prolonged chimerism and islet survival were not observed (30 and 40 days).
Conclusion: Significant improvement of mixed chimerism induction and islet allograft survival were achieved without CNI by addition of anti-CD8 mAb with Atgam. However, unlike the kidney allograft, islet allograft tolerance was not induced with transient chimerism. Induction of more durable mixed chimerism may be necessary for induction of islet allograft tolerance.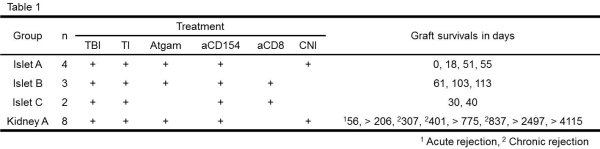
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Oura T, Ko D, O'Neil J, Boskovic S, Nadazdin O, Hotta K, Kawai K, Cosimi B, Kawai T. Kidney Versus Islet Allograft Survival After Induction of Mixed Chimerism in Nonhuman Primates [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/kidney-versus-islet-allograft-survival-after-induction-of-mixed-chimerism-in-nonhuman-primates/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
