Intragraft MicroRNA Transcriptome of Acute Antibody Mediated Rejection of Human Kidney Allografts
1Weill Cornell Medicine, New York
2Rockefeller University, New York.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A21
Keywords: Biopsy, Gene expression, Polymerase chain reaction (PCR), Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Biomarkers, Immune Monitoring and Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 2, 2018
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Background
MicroRNAs (miRNA) are master regulators of gene expression and are potential therapeutic targets. Intragraft miRNA transcriptome of acute antibody rejection (AMR) of human kidney allograft has not been characterized by RNA-sequencing.
Aims
To characterize the global intragraft miRNA expression profile of AMR in human kidney allografts.
Methods
We did small RNA-sequencing of 22 kidney allograft biopsy tissues obtained from 22 kidney allograft recipients who had either a clinically-indicated biopsy for graft dysfunction (AMR, N= 9 and acute cell-mediated rejection [ACR], N=7) or a surveillance/protocol biopsy (Normal, N=6). Barcoded cDNA libraries were multiplexed and sequenced on a HiSeq-2500. Differential abundance analysis of the miRNAs was done by edgeR, a Bioconductor package, based on negative binomial distribution of the count data. We quantified the miRNA abundance using a standard curve-based qRT-PCR assay.
Results
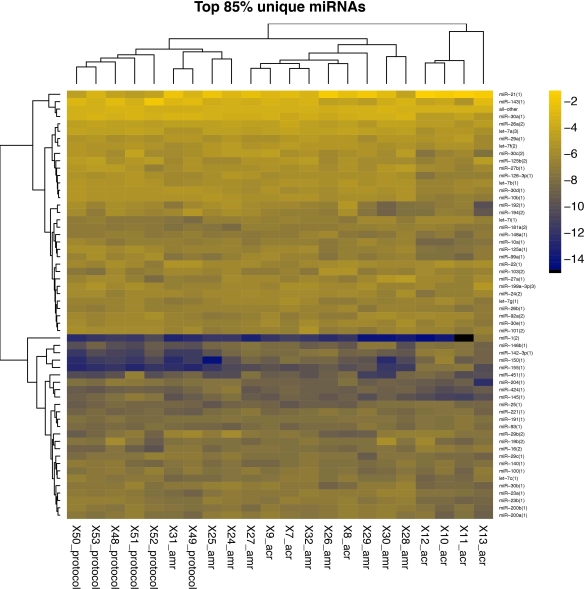
Hierarchical clustering of the top 85% of the miRNAs is shown.
Twenty-five miRNAs were different between AMR and Normal biopsies at FDR-P value <0.1. miR-21 was the most abundant miRNA in AMR (25% of total miRNA) and in Normal (9%) biopsies. The abundance of 20 of 25 miRNAs were similar between AMR and ACR.
We next measured the absolute quantity of a select (miRNA frequency of >0.005% in at least one group, Fold Change of ≥2.5 and FDR-P value <0.1) panel of miRNAs by a customized amplicon-based qRT-PCR assays and successfully verified the differential abundance.
Conclusions/Implications
Global miRNA profiling by RNA-sequencing of kidney allografts with AMR reveals miRNA transcripts that are unique and those shared with ACR. Further characterization of the miRNAs will help develop novel biomarkers and elucidate potential therapeutic targets.
CITATION INFORMATION: Yang H., Akat K., Li C., Snopkowski C., Khan Z., Dadhania D., Tuschl T., Suthanthiran M., Muthukumar T. Intragraft MicroRNA Transcriptome of Acute Antibody Mediated Rejection of Human Kidney Allografts Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yang H, Akat K, Li C, Snopkowski C, Khan Z, Dadhania D, Tuschl T, Suthanthiran M, Muthukumar T. Intragraft MicroRNA Transcriptome of Acute Antibody Mediated Rejection of Human Kidney Allografts [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/intragraft-microrna-transcriptome-of-acute-antibody-mediated-rejection-of-human-kidney-allografts/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress