Interrogation of Plasma Cell-Rich Acute Rejection in Human Kidney Allografts by Whole Transcriptome Sequencing
Weill Medical College of Cornell University, New York.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B252
Keywords: Gene expression, Genomics, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Translational Genetics and Proteomics in Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, May 3, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Plasma cell-rich acute rejection (PCRAR, plasma cells constituting >20% of the allograft infiltrating cells) portends poor prognosis.
To gain better mechanistic insights and develop diagnostic biomarkers, we performed next generation sequencing of kidney allograft biopsies classified as PCRAR (n=7), Banff acute cellular rejection (ACR, n=7), Banff acute antibody mediated rejection (AMR, n=8) and Banff normal (Normal, n=5).
We isolated total RNA from the 27 kidney allograft biopsies obtained from 27 recipients (mean[SD] age in years, PCRAR: 50[15]; ACR: 47[18]; AMR: 40[15] and Normal: 45[12]; Median time from transplantation to biopsy: 39, 13, 8 and 6 months, respectively; Median creatinine at biopsy: 2, 2.63, 3.16 and 1.2 mg/dl, respectively). Total RNA yield (mean[SD]): 1927ng[784ng]; RNA integrity number: 7.4[0.6]. The cDNA libraries were subjected to 100bp single-end sequencing on a HiSeq 2000 sequencer. We used Goby, our next-gen data management framework (Campagne et al, PLoS ONE 2013) for data analyses.
Principal component analysis of intragraft mRNA expression patterns showed clear separation of the PCRAR biopsies (Figure 1).
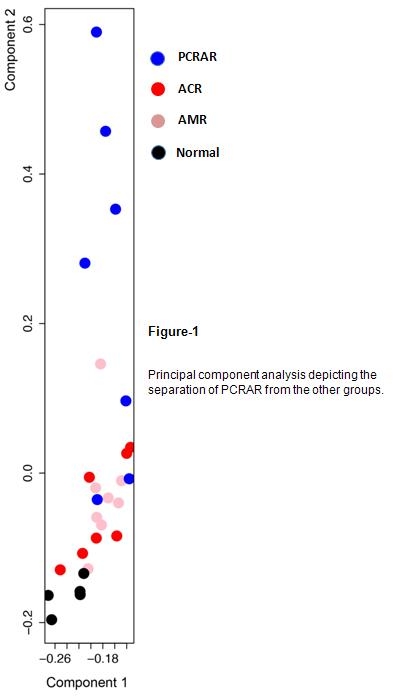
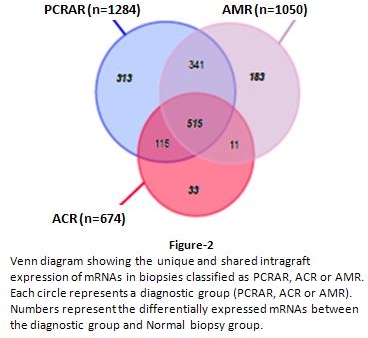
In an analysis restricted to mRNAs expressed by renal parenchymal cells and excluding mRNA expressed by graft infiltrating cells, 1284 mRNAs were expressed in PCRAR, 1050 in AMR and 674 in ACR biopsies. Importantly, 515 mRNAs were shared among the groups (Figure 2). Pathway analysis of the mRNAs unique to PCRAR revealed predominance of tryptophan metabolism pathway.
Our investigation represents the first characterization of intragraft mRNA transcriptome by sequencing of human allograft biopsies. Our study, in addition to discovering mRNA expression pattern unique to PCRAR, suggests targeting of metabolites of tryptophan pathway may improve outcome following PCRAR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mesnard L, Campagne F, Yang H, Dadhania D, Lee J, Seshan S, Suthanthiran M, Muthukumar T. Interrogation of Plasma Cell-Rich Acute Rejection in Human Kidney Allografts by Whole Transcriptome Sequencing [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/interrogation-of-plasma-cell-rich-acute-rejection-in-human-kidney-allografts-by-whole-transcriptome-sequencing/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
