Immune Checkpoints, Immune Cells, and MHC Expression in the Tumor Microenvironment of Resected Hepatocellular Carcinomas
1Scripps, La Jolla, CA, 2UCSD, San Diego, CA, 3University, Seville, Spain, 4Kaiser, San Diego, CA, 5USC, Los Angeles, CA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1096
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Liver transplantation, Major histocompatibility complex (MHC), T cells
Topic: Clinical Science » Liver » 56 - Liver: Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Other Malignancies
Session Information
Session Name: Liver: Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Other Malignancies
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Advances in tumor biology has shown the important role of the tumor microenvironment (TME) in tumor growth and metastasis. A better understanding of the interaction of tumor cells (TC) with host immune cells (IC) in the TME is essential to develop future immunotherapies. Aim: Analyze the expression of the IC, immune checkpoints (ICP), MHC-I and HLA-G in the TME of resected hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) specimens.
*Methods: A total of 175 patients with HCC who underwent either surgical liver resection (n =72) or liver transplant (n = 103) between 2008 and 2017 at Scripps and USC Transplant Centers were included in this retrospective study.The biomarkers expression of IC (CD4+, CD8+, NK-CD56, FoxP3-Treg), ICP (PD-1, PD-L1), MHC-I and HLA-G was assessed by immunohistochemistry in 175 surgically resected HCC specimens, 136 peritumoral, and 20 controls. The biomarkers expression was graded as G0:<5%, G1:5-25%, G2:26-50%, G3:>50%.The expression was compared using linear mixed-effects models and Spearman’s correlations were calculated.
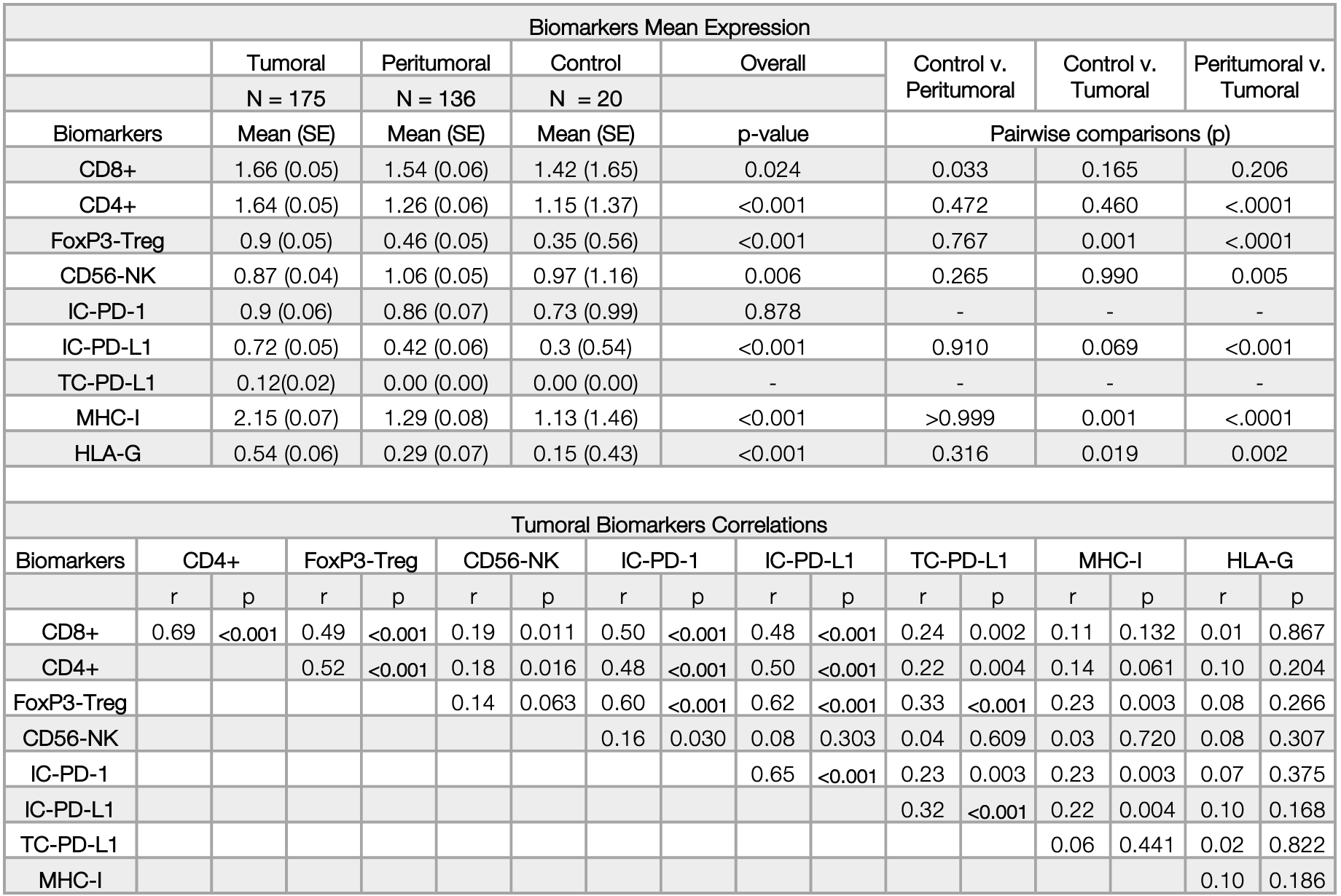
*Results: Patients mean age was 61.99 years old, 71.4% were male, and 70.1% had cirrhosis. The mean expression grades of the biomarkers in tumoral, peritumoral and control samples showed significantly different expression of all biomarkers, except IC-PD-1. (Table). The pairwise comparisons between control and peritumoral samples did not show significant differences in any biomarkers. However, the comparisons between control and tumoral revealed higher tumoral mean expression of FoxP3-Treg, MHC-I and HLA-G compared to controls. The comparisons between tumoral and peritumoral showed significantly higher expression of CD4+, FoxP3-Treg, IC-PD-L1, MHC-I and HLA-G in tumoral compared with peritumoral samples. In contrast, NK-CD56 expression was higher in peritumoral than in tumoral samples. The correlation between biomarkers in the tumoral samples showed that the strongest correlation was between CD8+ with CD4+, FoxP3-Treg with IC-PD-L1 and IC-PD-1, and IC-PD-1 with IC-PD-L1. HLA-G was not correlated with any biomarkers analyzed.
*Conclusions: Significantly higher expression of CD4+, FoxP3-Treg, IC-PD-L1, MHC-I and HLA-G was observed in tumoral versus peritumoral samples. In contrast, NK-CD56 expression was higher in the peritumoral tissues. The strongest correlation between tumoral biomarkers was CD8+ with CD4+, FoxP3-Treg with IC-PD-L1 and IC-PD-1, and IC-PD-1 with IC-PD-L1.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baquerizo A, Vavinskaya V, Bagsic S, Rojas A, Mhoyan A, Frenette C, Sher L, Romero M, Fisher J, Marsch C, Schaffer R. Immune Checkpoints, Immune Cells, and MHC Expression in the Tumor Microenvironment of Resected Hepatocellular Carcinomas [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/immune-checkpoints-immune-cells-and-mhc-expression-in-the-tumor-microenvironment-of-resected-hepatocellular-carcinomas/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress