Il-33 Induced Regulatory Macrophages Inhibit Transplantation Immune Rejection by Inducing Tregs
Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Beijing, China
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1274
Keywords: Graft survival, Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation, Tolerance
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 12 - Immunosuppression & Tolerance: Preclinical & Translational Studies
Session Information
Session Name: Immunosuppression & Tolerance: Preclinical & Translational Studies
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
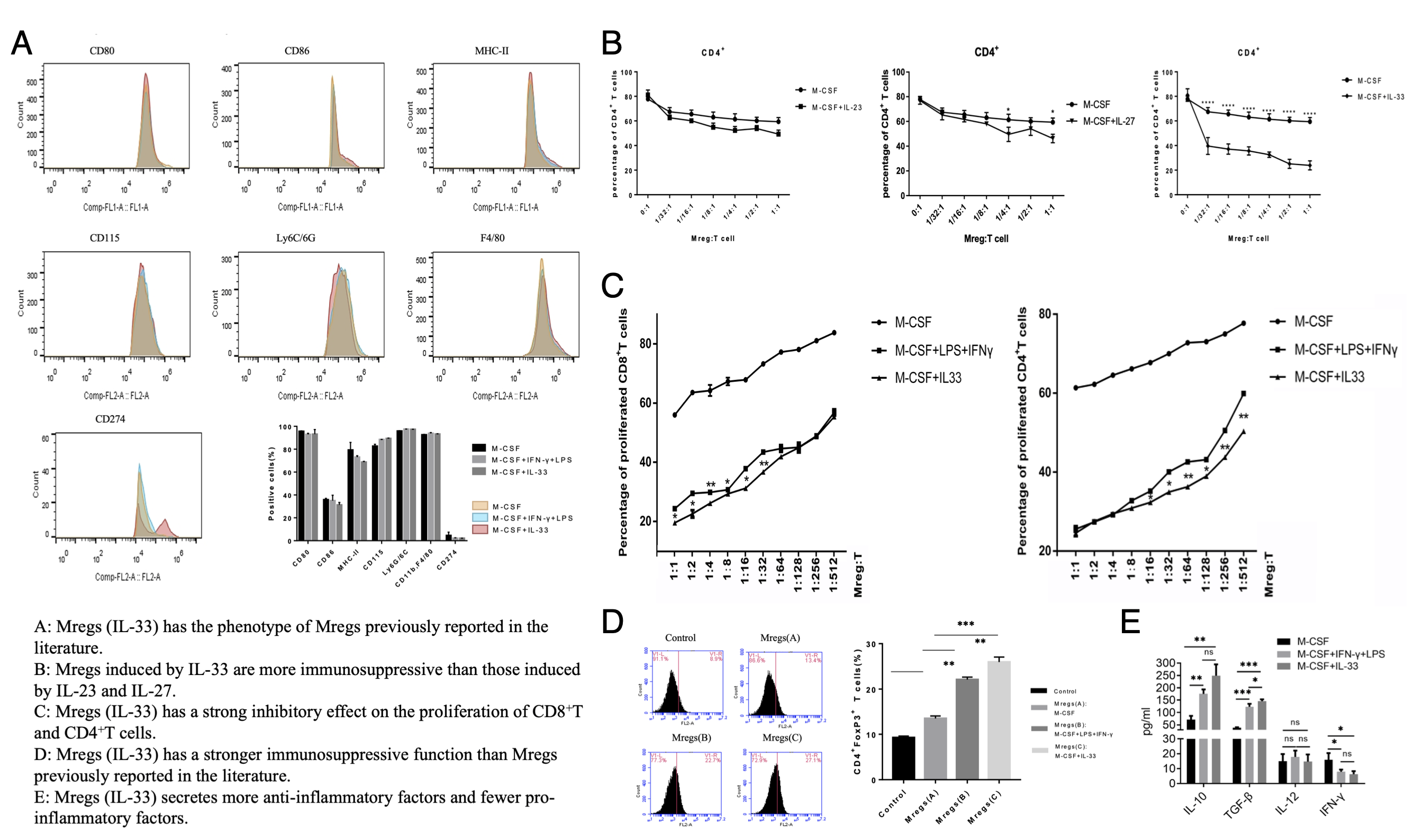
*Purpose: The occurrence of acute and chronic rejections after transplantation are key factors that affect the survival of the recipients. Induction of transplantation immune tolerance is the most ideal treatment option to prevent rejection. Adoptive infusion of immunoregulatory cells is an effective method for inducing transplantation immune tolerance that has attracted much attention. Studies have reported that regulatory macrophages (Mregs) play an important role in inducing immune tolerance, but their immunosuppressive function and induction efficiency reported in those literature were not satisfactory. It is of great significance to explore a new efficient induction system and obtain Mregs with stronger immunosuppressive function, and to clarify the mechanism of its immunosuppressive effect, which can provide a theoretical foundation for adoptive infusion of Mregs in clinical kidney transplantation in the future.
*Methods: M-CSF combined with IL-33 were used to induce bone marrow precursor cells to obtain macrophages. After the phenotype of the Mregs was identified, the immunosuppressive function and induction efficiency of Mregs obtained by the classical induction scheme and the IL-33 induction scheme were compared through the T cell suppression experiment. Subsequently, collecting the cells obtained in the T cell suppression experiment and the content of Tregs was detected by flow cytometry. Then, collecting the supernatant of the Mregs induction system and detecting the expression of secretory effector molecules in the supernatant by ELISA to analyze the potential mechanisms.
*Results: We found that the phenotype of macrophages induced by IL-33 conformed to the characteristics of Mregs. Compared with Mregs (M-CSF) and Mregs (IFN-γ+LPS) obtained by classical induction scheme, Mregs (IL-33) had a stronger ability to inhibit T cell proliferation even at a lower concentration. Further research found that Mregs (IL-33) co-cultured with CD4+ T cells can promote the high expression of Foxp3 in CD4+ T cells, and the efficiency of inducing and expanding Tregs was higher than that of Mregs (IFN-γ+LPS). Besides, compared with Mregs (M-CSF), Mregs (IL-33) secreted more IL-10, TGF-β, and lower IFN-γ. While compared with Mregs (IFN-γ+LPS), the TGF-β secreted by Mregs (IL-33) was significantly increased.
*Conclusions: M-CSF combined with IL-33 in vitro induction amplification system can induce Mregs with stronger immunosuppressive function, and the Mregs (IL-33) mainly exert immunosuppressive function by regulating the expression of immune effector molecules and inducing the amplification of Tregs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wu J, Zhang F, Wang W. Il-33 Induced Regulatory Macrophages Inhibit Transplantation Immune Rejection by Inducing Tregs [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/il-33-induced-regulatory-macrophages-inhibit-transplantation-immune-rejection-by-inducing-tregs/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress