Identification of Molecular Markers for Liver Cirrhosis (NASH) by Single-Nucleus RNA Sequencing
1Dept of Surgery, Transplant Research Institute, James D. Eason Transplant Institute, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN, 2Bioinformatics, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN, 3Department of Surgery, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 219
Keywords: Fibrosis, Gene expression, Genomics, Liver cirrhosis
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarker Discovery and Immune Modulation
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 4:27pm-4:39pm
Presentation Time: 4:27pm-4:39pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a progressive disease and it constitutes a significant portion of the chronic liver diseases that affected more than 800 million people worldwide. Every one or two patients with NAFLD will have rising fat contents overtime in their liver cells which leads to inflammation of the organ that might end up in cirrhosis. Liver transplant is the only effective treatment method for those end-stage liver diseases. This study aimed to identify the molecular and cellular mechanisms of fibrosis/cirrhosis caused by NASH at the single nucleus level.
*Methods: Single-cell/nucleus RNA sequencing have tremendous opportunities to understand the disease conditions with their revolutionizing ability in basic and clinical studies. Due to technical limitations of obtaining live cells from frozen archival tissues, we isolated single nuclei from fresh-frozen (FF) samples including normal, 30% fat and fibrotic liver tissues (NASH, cirrhosis). We captured >30,000 nuclei in Gel-Bead V3 by using droplet-based 10X genomic chromium platform. We analyzed the data in Cell-Ranger 3.1.0 and visualized UMAP clusters in Loupe Cell Browser
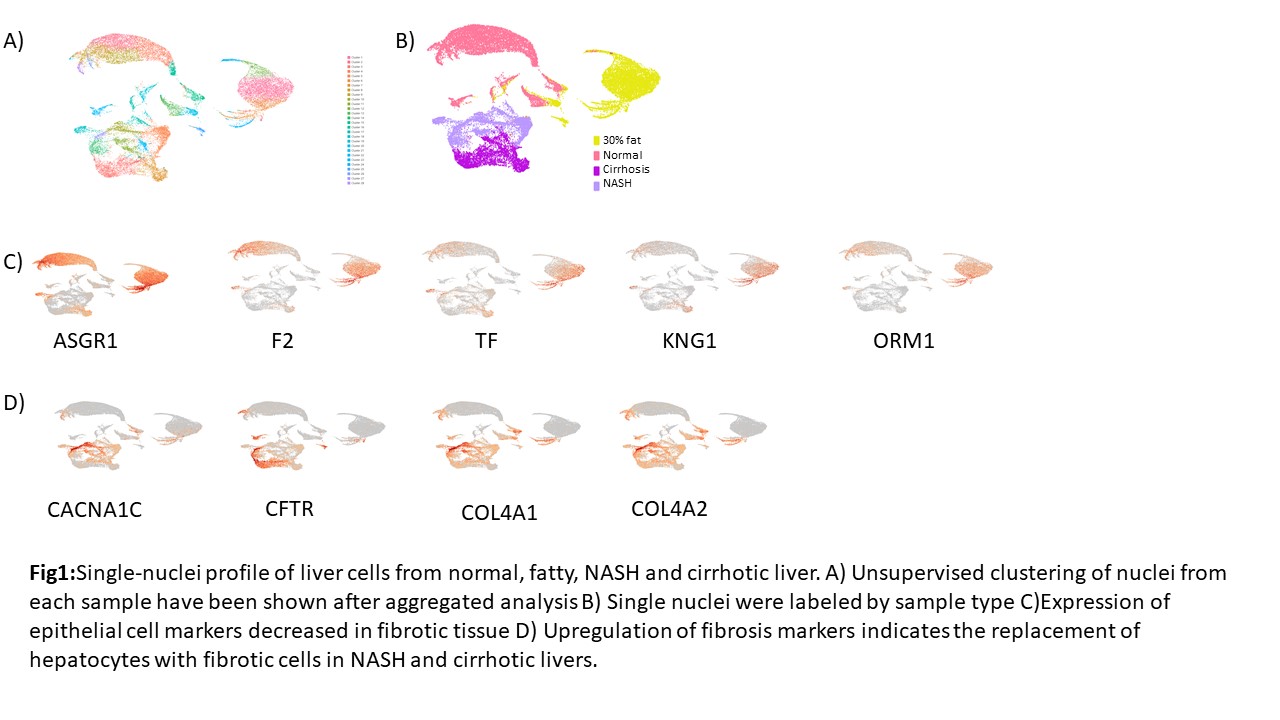
*Results: Due to the high content of parenchymal cells (hepatocyte and cholangiocytes) in the liver, we mainly identified the epithelial cells in our liver samples. Interestingly, hepatocytes showed diverse clustering among normal and 30% fat livers (Fig1A, B). Furthermore, we observed more heterogeneous cell profiles in fibrotic tissues. We identified comparable expression of ASGR1, F2, TF, KNG1, and ORM1 between normal and fatty liver, however, their expressions are significantly diminished in the cells of fibrotic niche (Fig 1C). Epithelial cells of normal or fatty liver were replaced by fibrotic cells during NASH and Cirrhosis as we expected, and the replacement of those cells has been correlated with the elevated level of CACNA1C,CFTR,COL4A1, and COL4A2 (Fig 1D).
*Conclusions: In this study, we performed single nuclei isolation from frozen liver samples for the first time and identified different cell/nucleus clustering depending on the sample type. Our results will increase the understanding of human liver fibrosis by NASH and help us to develop better treatment methods for NAFLD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kuscu C, Mouhammed A, Kuscu C, Wolen AR, Eason JD, Maluf D, Mas V. Identification of Molecular Markers for Liver Cirrhosis (NASH) by Single-Nucleus RNA Sequencing [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/identification-of-molecular-markers-for-liver-cirrhosis-nash-by-single-nucleus-rna-sequencing/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress