β-Glucuronidase Gene Expression in Stool Samples Associated with Chronic Allograft Dysfunction in Kidney Transplants
1Medicine, HCMC, University of MN (UMN), Minneapolis
2Minneapolis Medical Research Foundation (MMRF), Mpls
3Computer Science, UMN, Mpls
4Biostatistics, UMN, Mpls
5College of Pharmacy, UMN, Mpls.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C116
Keywords: Gene expression, Graft function, Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Regimens and Drug Minimization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Background: Myocophenolate mofetil (MMF) is a prodrug that is extensively and rapidly converted to the active component, mycophenolic acid (MPA). MPA undergoes extensive enterohepatic recycling (EHR) through excretion of the phenolic glucuronide (MPAG) metabolite into the bile, followed by intestinal deglucuronidation of MPAG back to MPA by the bacterial microflora and then reabsorption. We hypothesize that the β-glucuronidases produced by gut microbes influence EHR, MPA immunosuppressive activity and thus outcomes post-transplant (tx).
Methods: β-glucuronidase gene expression from rectal swabs was compared in 5 cases and 4 controls enrolled in DeKAF Genomics. Cases were those with worsening kidney function posttx compared to 3 month baseline Cr and controls had stable Cr. Total microbial RNA was extracted from swabs stored in RNAlater. Random primed cDNA synthesis and amplification was performed using the Illumina ScriptSeq v2 RNA-Seq library preparation kit after depleting human and microbial rRNA. Completed RNAseq libraries were multiplexed and sequenced on HiSeq 4000 using 150 bp paired end mode generating between 27-100 million reads per sample. Finally, the transcriptomic reads were mapped against a custom database comprised of 6587 RefSeq bacterial β-glucuronidase genes using BURST DNA aligner.The Reads Per Kilobase of transcript per Million mapped reads (RPKM) values for the β-glucuronidase genes were calculated for each sample (Fig 1A).
Results: Tx recipients with worse kidney function than their 3 month baseline were more likely to have a lower β-glucuronidase expression (Wilcoxon rank sum, p=0.031) which would result in less EHR, lower MPA plasma concentrations and potential under-immunosuppression (Fig 1B).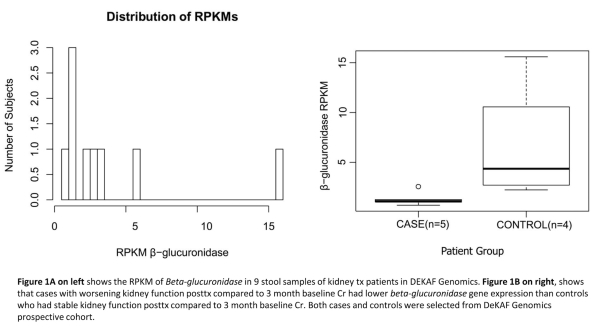
Conclusion: β–glucuronidases produced by gut microbes may be associated with outcomes post-transplant.
CITATION INFORMATION: Israni A., Knights D., Al-Ghalith G., Muthusamy A., Wu B., Oetting W., Schaldt D., Remmel R., Jacobson P., For DeKAF Genomics & GEN03 Investigators β-Glucuronidase Gene Expression in Stool Samples Associated with Chronic Allograft Dysfunction in Kidney Transplants Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Israni A, Knights D, Al-Ghalith G, Muthusamy A, Wu B, Oetting W, Schaldt D, Remmel R, Jacobson P. β-Glucuronidase Gene Expression in Stool Samples Associated with Chronic Allograft Dysfunction in Kidney Transplants [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/glucuronidase-gene-expression-in-stool-samples-associated-with-chronic-allograft-dysfunction-in-kidney-transplants/. Accessed July 15, 2025.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
