Gingival Mesenchymal Stem Cells (GMSCs) Mitigate Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Regulating Macrophage Polarization Through miR-199a-3p
Organ Transplant Center, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 404
Keywords: Ischemia, Liver, Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kB), Stem cells
Session Information
Session Name: Basic: Ischemia Reperfusion & Organ Rehabilitation II
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 3:15pm-3:27pm
Presentation Time: 3:15pm-3:27pm
Location: Virtual
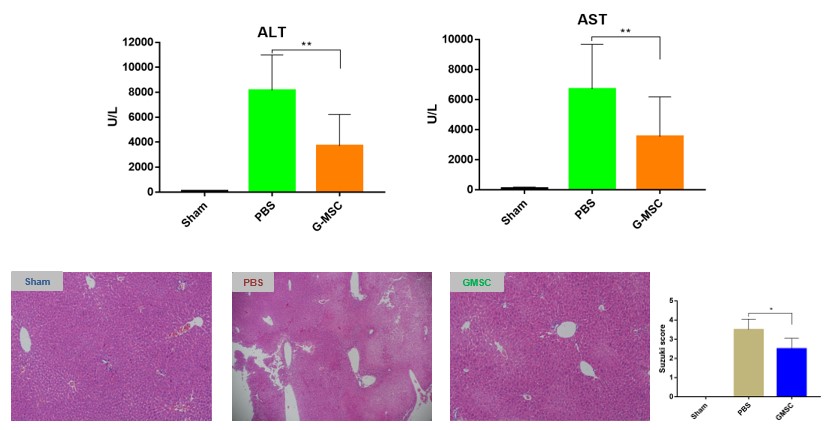
*Purpose: Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) have been increasingly studied in organ ischemia-reperfusion injury, but the mechanism is still unclear. This study explored the immunoregulatory effects of GMSCs on macrophages after liver ischemia / reperfusion (I / R) and its significance in the repair of ischemia-reperfusion injury.
*Methods: GMSCs were treated in a 70% ischemia-reperfusion injury model of mice. Degree of liver IRI relieved by GMSCs was judged by the levels of liver HE and serum liver enzymes and the expression of related inflammatory factors, such as IL-1β, IL-6. Macrophages were cleared with clodronate liposomes to observe the effect on GMSCs. Real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) technology was used to analyze the expression of inflammatory cytokines and the expression level of macrophage surface markers. Transcriptomics was used to explore the mechanism related to macrophages, and bioinformatics to explore the relationship between miRNAs and target genes, observe the effect on macrophage polarization by silencing the corresponding miRNA.
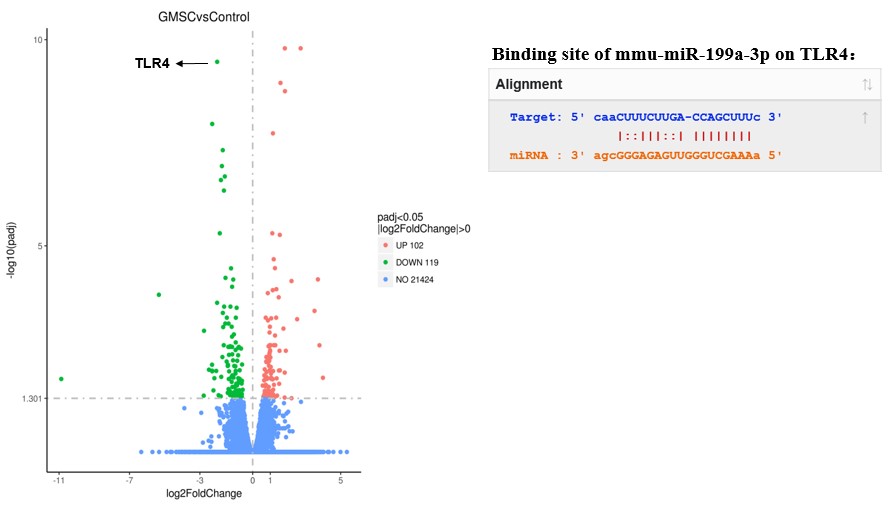
*Results: GMSCs to mice through intravenous injection after liver I/R reduced injury size and alleviated inflammation level in liver and serum. Systemic depletion of macrophages with clodronate liposomes abolished the curative effects of GMSCs. GMSCs modified the polarization of M1 macrophages to M2 macrophages both in vivo and in vitro. Transcriptomics of liver tissues and bioinformatics analysis implicated toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) as a potent candidate mediator of macrophage polarization and miR-199a-3p as a upstream target. Diminishing miR-199a-3p in GMSCs partially attenuated its modulation of macrophage polarization. Likewise, knock down of TLR4 also conferred liver-protective efficacy and reduced inflammation level in a mouse model of liver I/R.
*Conclusions: Our study shows that GMSCs regulate the polarization of macrophages from M1 to M2 through miR-199a-3p, thereby reducing liver IRI. This study provides new insights into GMSCs as a potential treatment for liver IRI.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang Y, Chen M, Ju W, Wang T, Chen Z, Huang C, Xie R, Zhao Q, Guo Z, He X. Gingival Mesenchymal Stem Cells (GMSCs) Mitigate Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Regulating Macrophage Polarization Through miR-199a-3p [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/gingival-mesenchymal-stem-cells-gmscs-mitigate-liver-ischemia-reperfusion-injury-by-regulating-macrophage-polarization-through-mir-199a-3p/. Accessed March 1, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress