Exenatide Reduces Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Donation after Cardiac Death Rat Kidney Transplantation
1Department of Organ Transplantation, People's Hospital of Jiangxi Province, Nanchang, Jiangxi Province, China
2Department of Pathology, Central Hospital of Wuhan, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei Province, China
3Department of Urologic Surgery, People's Hospital of Jiangxi Province, Nanchang, Jiangxi Province, China
4Department of Vascular Surgery, People's Hospital of Jiangxi Province, Nanchang, Jiangxi Province, China
5Department of Urologic Surgery, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei Province, China.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D26
Keywords: Apoptosis, Donation, Ischemia, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Immunosuppression Preclinical Studies
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 5, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Background: Exenatide provide protection against warm Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury (IRI) in the rat heart and kidney. We hypothesized that Exenatide reduces IRI in a rat donation after cardiac death (DCD) kidney transplantation (KTx) model. Method: The LEW donor rats were pretreated with Exenatide 2 hrs before induction of cardiac cessation, grafts underwent 20 min warm ischemia and 24 hrs cold storage in the UW. Grafts were engrafted into LEW recipients who were nephrectomized bilaterally. Histology, apoptosis from blood and tissue. A second set of experiments were performed using the same experimental design to assess renal function and post-transplant survival. Result: At the end of CS, Exenatide had significantly reduced TUNEL+ cells(n=6, p<0.05), and decreased scores of acute tubular necrosis after 24 hrs(n=6, p<0.05). Exenatide treatment improved renal function and survival rates (p<0.05). Furthermore, Exenatide reduced protein levels of PARP and VDAC-1 in donor grafts and mRNA upregulation for proinflammatory mediators (IL-6, TNF-α, iNOS) in grafts. Conclusion: Our data show that Exenatide decreased the IRI of DCD kidneys in rat transplant models and improve function of renal grafts.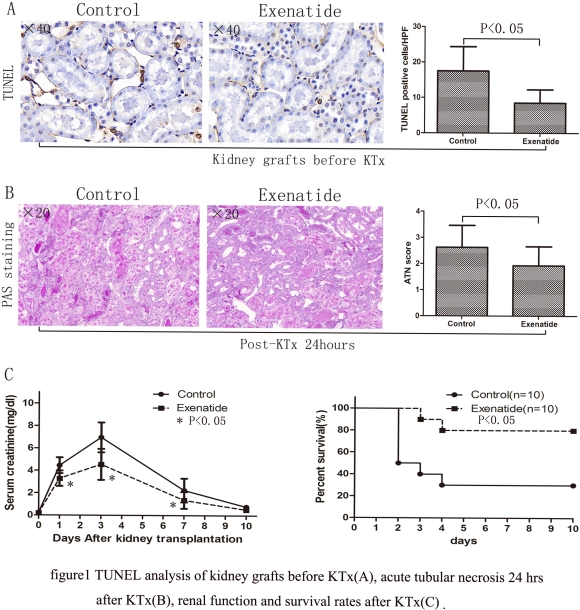
CITATION INFORMATION: Yang H., Shi Y., Li X., Long C., Xu Z., Luo L., Luo W., Zhang Y., Zeng T., Chen M., Li H., Wang Z. Exenatide Reduces Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Donation after Cardiac Death Rat Kidney Transplantation Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yang H, Shi Y, Li X, Long C, Xu Z, Luo L, Luo W, Zhang Y, Zeng T, Chen M, Li H, Wang Z. Exenatide Reduces Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Donation after Cardiac Death Rat Kidney Transplantation [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/exenatide-reduces-ischemia-reperfusion-injury-in-donation-after-cardiac-death-rat-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
