Ex-vivo Xenoperfusion Of Wild Type And Galtko.hcd55 Pig Livers With Human Whole Blood
Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D87
Keywords: Antibodies, Liver, Machine preservation, Miniature pigs
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Xenotransplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Pig-to-human liver xenotransplantation is not currently feasible due to rapid and profound thrombocytopenia, coagulopathy and hyperacute rejection. Successful development of genetically modified swine to overcome these immunologic barriers will require a rapid and efficient model to evaluate efficacy of different genetic constructs. Here, we report our ex-vivo liver xenoperfusion model with wild type (WT) and genetically modified swine.
*Methods: Livers from WT (n=5) and GalTKO.hCD55 (n=4) swine were perfused under physiologic conditions with freshly collected type-matched human whole blood and plasma. Perfusion was continued until failure, defined by cessation of blood flow from high vascular resistance, severe metabolic derangements and/or grossly necrotic macroscopic appearance.
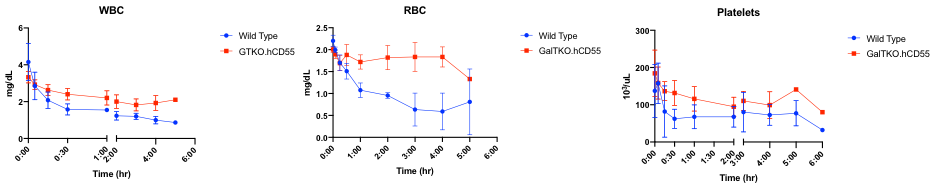
*Results: After commencement of perfusion, a progressive decrease in blood flow and corresponding rise in vascular resistance was observed in all livers. WT livers failed after 1.5-7 hours of perfusion, with two livers developing acute thrombosis after 1.5 and 3 hours resulting in immediate cessation of blood flow. Remaining WT livers failed due to progressively decreasing blood flows and gross necrosis. GalTKO.hCD55 livers failed after 4-6 hours of perfusion, all secondary to reduced blood flows and necrosis. The WBC count was significantly higher in GalTKO.hCD55 livers (p=0.0161). Likewise, the RBC count was better preserved in GalTKO.hCD55 perfusions compared to WT (p=0.003). Marked thrombocytopenia occurred within 30 minutes in both groups, without significant difference.
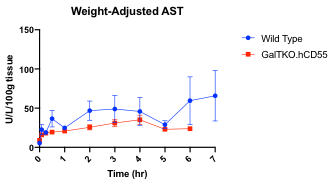
Serum AST was higher in the WT group without reaching significance.
Histology confirmed the presence of severe vascular congestion and ischemic necrosis in both groups.
*Conclusions: WT pig livers develop marked RBC and WBC sequestration and thrombocytopenia after exposure to human whole blood and are susceptible to failure due to graft thrombosis. GalTKO.hCD55 modified swine experience these perturbations to a lesser degree, however the modifications are not sufficiently protective to support prolonged ex-vivo function.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Detelich D, Rickert C, Eymard C, Carroll C, Kimura S, Yeh H, Markmann J. Ex-vivo Xenoperfusion Of Wild Type And Galtko.hcd55 Pig Livers With Human Whole Blood [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/ex-vivo-xenoperfusion-of-wild-type-and-galtko-hcd55-pig-livers-with-human-whole-blood/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress